rexresearch
rexresearch1
Fritz-Albert
POPP, et al.
Biophotons
Biophotons
Research Papers
G. Lednyiczky & O. Zhalko-Tytarenko : Biological Resonance -- Resonance in Biology [ PDF ]
Dr Switzer : Biophoton Nutrition & Cyclical Eating [ PDF ]
R. VanWijk : Biophotons & Biocommunication ( J. Sci. Exploration) [ PDF ]
C. Jiin-Ju : Physical Properties of Biophotons and Their Biological Functions ( Indian J. of Experimental Biology 46: 371-277, May 2008 ) [ PDF ]
Fritz-Albert Popp : Properties of Biophotons and Their Theoretical Implications ( Indian J. of Experimental Biology 41 : 391-402 ( May 2003 ) [ PDF ]
Peter Gariaev [ Gajarev ], et al : The DNA Wave Biocomputer [ PDF ]
V. Voiekov, et al. : Biophoton Research in Blood Reveals Its Holistic Properties [ PDF ]
Related: Optogenetics
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20221457
Biophotons
as neural communication signals demonstrated by in situ
biophoton autography
Y. Sun, et al.
Cell to cell
communication by biophotons has been demonstrated in plants,
bacteria, animal neutrophil granulocytes and kidney cells.
Whether such signal communication exists in neural cells is
unclear. By developing a new biophoton detection method,
called in situ biophoton autography (IBA), we have
investigated biophotonic activities in rat spinal nerve roots
in vitro. We found that different spectral light stimulation
(infrared, red, yellow, blue, green and white) at one end of
the spinal sensory or motor nerve roots resulted in a
significant increase in the biophotonic activity at the other
end. Such effects could be significantly inhibited by procaine
(a regional anaesthetic for neural conduction block) or
classic metabolic inhibitors, suggesting that light
stimulation can generate biophotons that conduct along the
neural fibers, probably as neural communication signals. The
mechanism of biophotonic conduction along neural fibers may be
mediated by protein-protein biophotonic interactions. This
study may provide a better understanding of the fundamental
mechanisms of neural communication, the functions of the
nervous system, such as vision, learning and memory, as well
as the mechanisms of human neurological diseases.Y. Sun, et al.
Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2010 Mar;9(3):315-22.
doi: 10.1039/b9pp00125e.
Biophotons as neural communication signals demonstrated by in situ biophoton autography
Sun
Y1, Wang C, Dai J.
Cell to cell
communication by biophotons has been demonstrated in plants,
bacteria, animal neutrophil granulocytes and kidney cells.
Whether such signal communication exists in neural cells is
unclear. By developing a new biophoton detection method,
called in situ biophoton autography (IBA), we have
investigated biophotonic activities in rat spinal nerve roots
in vitro. We found that different spectral light stimulation
(infrared, red, yellow, blue, green and white) at one end of
the spinal sensory or motor nerve roots resulted in a
significant increase in the biophotonic activity at the other
end. Such effects could be significantly inhibited by procaine
(a regional anaesthetic for neural conduction block) or
classic metabolic inhibitors, suggesting that light
stimulation can generate biophotons that conduct along the
neural fibers, probably as neural communication signals. The
mechanism of biophotonic conduction along neural fibers may be
mediated by protein-protein biophotonic interactions. This
study may provide a better understanding of the fundamental
mechanisms of neural communication, the functions of the
nervous system, such as vision, learning and memory, as well
as the mechanisms of human neurological diseases.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3294033
F.
Popp, et al. : Physical aspects of biophotons
By comparing the
theoretically expected results of photon emission from a
chaotic (thermal) field and those of an ordered (fully
coherent) field with the actual experimental data, one finds
ample indications for the hypothesis that 'biophotons'
originate from a coherent field occurring within living
tissues. A direct proof may be seen in the hyperbolic
relaxation dynamics of spectral delayed luminescence under
ergodic conditions. A possible mechanism has to be founded on
Einstein's balance equation and, under stationary conditions,
on energy conservation including a photochemical potential. It
is shown that the considered equations deliver, besides the
thermal equilibrium, a conditionally stable region far away
from equilibrium, which can help to describe both 'biophoton
emission' and biological regulation.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15244274
Indian J Exp Biol. 2003 May;41(5):514-27
Bajpai
R. : Quantum coherence of biophotons and living systems
Coherence is a
property of the description of the system in the classical
framework in which the subunits of a system act in a
cooperative manner. Coherence becomes classical if the agent
causing cooperation is discernible otherwise it is quantum
coherence. Both stimulated and spontaneous biophoton signals
show properties that can be attributed to the cooperative
actions of many photon-emitting units. But the agents
responsible for the cooperative actions of units have not been
discovered so far. The stimulated signal decays with
non-exponential character. It is system and situation specific
and sensitive to many physiological and environmental factors.
Its measurable holistic parameters are strength, shape,
relative strengths of spectral components, and excitation
curve. The spontaneous signal is non-decaying with the
probabilities of detecting various number of photons to be
neither normal nor Poisson. The detected probabilities in a
signal of Parmelia tinctorum match with probabilities expected
in a squeezed state of photons. It is speculated that an in
vivo nucleic acid molecule is an assembly of intermittent
quantum patches that emit biophoton in quantum transitions.
The distributions of quantum patches and their lifetimes
determine the holistic features of biophoton signals, so that
the coherence of biophotons is merely a manifestation of the
coherence of living systems.BioPhoton Patents
WO2017026567
-- LED
LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR BIOPHOTON
The present invention relates to an LED lighting system for a biophoton, comprising: an illuminator comprising an LED illumination part for irradiating LED light, a heating part formed to encompass the illumination part and being heated in the forward direction, and an ion generator formed inside the illumination part and simultaneously generating cations and anions so as to clean the surrounding air; and a control unit for controlling, by considering average temperature by location, via wireless communication, the heating temperature of the heating part, and light quality and luminosity with respect to the illumination of the illumination part. Therefore, the present invention promotes the healthy growth of a growth product by being constructed as a package, which has illumination, heating and air cleaning functions integrated as one, in the fields of growable plants and poultry shed farms, and can simultaneously reduce investments for equipment costs and reduce the energy for equipment operation
The present invention relates to an LED lighting system for a biophoton, comprising: an illuminator comprising an LED illumination part for irradiating LED light, a heating part formed to encompass the illumination part and being heated in the forward direction, and an ion generator formed inside the illumination part and simultaneously generating cations and anions so as to clean the surrounding air; and a control unit for controlling, by considering average temperature by location, via wireless communication, the heating temperature of the heating part, and light quality and luminosity with respect to the illumination of the illumination part. Therefore, the present invention promotes the healthy growth of a growth product by being constructed as a package, which has illumination, heating and air cleaning functions integrated as one, in the fields of growable plants and poultry shed farms, and can simultaneously reduce investments for equipment costs and reduce the energy for equipment operation
DE19541735
-- Use
of hydrothermal rock deposits e.g. calcite precursors
Use of
hydrothermal rock deposits is claimed, to improve the light
quantum resonance effect in the body by molecular disperse
division. The rock deposits are present in healing, thermal,
brine, mud, sulphur and mineral deposits, completely returned to
molecular dispersion, completely homogenised with noble
crystals, plant and animal materials as colloidal compounds, for
better control of biophoton radiation through nanocrystals,
between natural inorganic and natural organic materials. The
rock deposits provide precursors of calcite, aragonite,
dolomite, marble, zinc blende, smithsonite, wurzite, manganite,
hausmannite, neptunite, hornblende, calaverite, stephanite,
hessite, krennerite, chalcosine, bornite, linnaeite, magnetic
pyrites, carrolite, ilmenite, ullmannite, marcasite,
klinozoisite, pyrophylite, nacrite, aukerite, rhodochrosite,
kutnahorite, epistilbite, heulandite, fluorspar, basnaesite,
creedite, synchisite, tunisite, chalbasite, graphite, coal,
apophylite, sellaite, karpholite, brookite, potassium feldspar,
plagioclase, aoebite, vesuvian, elbaite, dravite, schorl,
buergerite, tsilaisite, uvite, liddicoatite, siderite, hot
springs deposit, hydrocarbonate, calcium carbonate, sulphate,
free carbonic acid, dissolved oxygen, metasilicic acid,
metaboric acid, titanic acid, succinic acid, benzoic acid,
sulphur, brine, traces of iron, chromium, titanium, aluminium,
gold, silver, platinum, selenium, molybdenum, ammonium, calcium,
lithium, sodium, chlorite, iodide, fluorine, bromine, thermal
salts, potassium, magnesium, cobalt, zinc, meerschaum
(sepiolite), tartar and similar or different inorganic
materials. Also claimed are compositions with volatile, liquid,
viscous, waxy, pulverised or solid, skin-tolerated, natural or
allergologically (sic) tolerable carriers.WO2016110969 -- BIOPHOTON MEASUREMENT
DEVICE
The present invention is a biophoton measurement device having the following: one or a plurality of light irradiation means disposed atop a test subject surface; one or a plurality of light detection means disposed atop the test subject surface; a retaining part for retaining the light irradiation means and the light detection means; a mounting tool for mounting the retaining part on the test subject; and a means for altering an SD distance defined by the distance between a light irradiation means and a light detection means. The retaining part is configured so as to be able to retain the light irradiation means and light detection means so that there are at least two kinds of SD distances.
The present invention is a biophoton measurement device having the following: one or a plurality of light irradiation means disposed atop a test subject surface; one or a plurality of light detection means disposed atop the test subject surface; a retaining part for retaining the light irradiation means and the light detection means; a mounting tool for mounting the retaining part on the test subject; and a means for altering an SD distance defined by the distance between a light irradiation means and a light detection means. The retaining part is configured so as to be able to retain the light irradiation means and light detection means so that there are at least two kinds of SD distances.
CN104383539
-- Cell
nucleus targeted biophoton diagnosis and treatment agent and
preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a cell nucleus targeted biophoton diagnosis and treatment agent and a preparation method thereof. The cell nucleus targeted biophoton diagnosis and treatment agent comprises gadolinium doped upconversion fluorescence nano particles, first photosensitizer doped first solid silicon oxide layers coating the gadolinium doped upconversion fluorescence nano particles, second photosensitizer doped second solid silicon oxide layers coating the first solid silicon oxide layers and cell nucleus targeting ligands covalently grafted on the outer surfaces of the second solid silicon oxide layers, wherein at least one of the first photosensitizer and the second photosensitizer is capable of absorbing visible light emitted by the gadolinium doed upconversion fluorescence nano particles under irradiation of near-infrared lights to produce singlet oxygen, and/or at least one of the first photosensitizer and the second photosensitizer is capable of catalyzing water decomposition under the condition of X ray radiation to produce active oxygen radicals
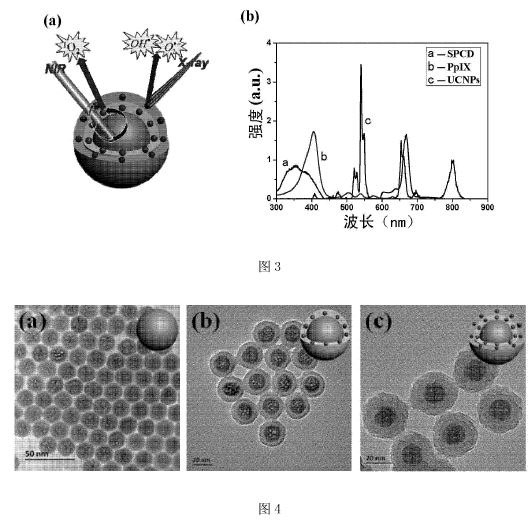
The invention relates to a cell nucleus targeted biophoton diagnosis and treatment agent and a preparation method thereof. The cell nucleus targeted biophoton diagnosis and treatment agent comprises gadolinium doped upconversion fluorescence nano particles, first photosensitizer doped first solid silicon oxide layers coating the gadolinium doped upconversion fluorescence nano particles, second photosensitizer doped second solid silicon oxide layers coating the first solid silicon oxide layers and cell nucleus targeting ligands covalently grafted on the outer surfaces of the second solid silicon oxide layers, wherein at least one of the first photosensitizer and the second photosensitizer is capable of absorbing visible light emitted by the gadolinium doed upconversion fluorescence nano particles under irradiation of near-infrared lights to produce singlet oxygen, and/or at least one of the first photosensitizer and the second photosensitizer is capable of catalyzing water decomposition under the condition of X ray radiation to produce active oxygen radicals
US2015053626 -- WATER FILTRATION AND
TREATMENT SYSTEMS AND METHODS
Implementations of the present invention relate to systems, methods, and apparatus for filtering and treating water, such as tap water, well water, spring water, etc., and producing drinking, bathing, and swimming water. More specifically, such systems, methods, and apparatus can produce purified water by removing substantially all suspended as well as dissolved solids, undesirable acids, gasses and all and any contaminates from the water. Additionally, the systems, methods, and apparatus can produce reprogrammed high biophoton mineralized drinking water by chilling vortexing over proprietary lodestones, ingenious, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks and creating bicarbonate ions in the water introducing minerals and/or salts into the water.
Implementations of the present invention relate to systems, methods, and apparatus for filtering and treating water, such as tap water, well water, spring water, etc., and producing drinking, bathing, and swimming water. More specifically, such systems, methods, and apparatus can produce purified water by removing substantially all suspended as well as dissolved solids, undesirable acids, gasses and all and any contaminates from the water. Additionally, the systems, methods, and apparatus can produce reprogrammed high biophoton mineralized drinking water by chilling vortexing over proprietary lodestones, ingenious, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks and creating bicarbonate ions in the water introducing minerals and/or salts into the water.
WO2014093049 -- WATER STABILIZATION,
REVITALIZATION, FILTRATION AND TREATMENT SYSTEMS AND METHODS
Implementations of the present invention relate to systems, methods, and apparatus for filtering and treating water, such as tap water, well water, spring water, etc., and producing drinking, bathing, and swimming water. More specifically, such systems, methods, and apparatus can produce purified water by removing substantially all suspended as well as dissolved solids, undesirable acids, gasses and all and any contaminates from the water. Additionally, the systems, methods, and apparatus can produce reprogrammed high biophoton mineralized drinking water by chilling vortexing over proprietary lodestones, ingenious, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks and creating bicarbonate ions in the water introducing minerals and/or salts into the water
Implementations of the present invention relate to systems, methods, and apparatus for filtering and treating water, such as tap water, well water, spring water, etc., and producing drinking, bathing, and swimming water. More specifically, such systems, methods, and apparatus can produce purified water by removing substantially all suspended as well as dissolved solids, undesirable acids, gasses and all and any contaminates from the water. Additionally, the systems, methods, and apparatus can produce reprogrammed high biophoton mineralized drinking water by chilling vortexing over proprietary lodestones, ingenious, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks and creating bicarbonate ions in the water introducing minerals and/or salts into the water
CN103034620 -- Frequency-domain
characteristic analyzing method of excited BPE (Biophoton
Emission) signal of wheat grain
The invention relates to a frequency-domain characteristic analyzing method of an excited BPE (Biophoton Emission) signal of wheat grains. The method comprises the steps of: first, carrying out one-dimensional stable wavelet denoising pretreatment for an excited BPE signal of wheat grains obtained; and then, analyzing the frequency-domain characteristics by a Fourier analytic method so as to extract the excited BPE information of the wheat grains accurately and completely. The effect of the method is verified by the embodiment. The result shows that the method reflects the frequency-domain characteristics of the excited BPE signal of the wheat grains well.
The invention relates to a frequency-domain characteristic analyzing method of an excited BPE (Biophoton Emission) signal of wheat grains. The method comprises the steps of: first, carrying out one-dimensional stable wavelet denoising pretreatment for an excited BPE signal of wheat grains obtained; and then, analyzing the frequency-domain characteristics by a Fourier analytic method so as to extract the excited BPE information of the wheat grains accurately and completely. The effect of the method is verified by the embodiment. The result shows that the method reflects the frequency-domain characteristics of the excited BPE signal of the wheat grains well.
CN102967368 -- Power spectrum
analysis method for spontaneous BPE (biophoton emission)
information of wheat grains
The invention discloses a characteristic analysis method for spontaneous BPE (biophoton emission) information of wheat grains. The characteristic analysis method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing spontaneous BPE time-domain data, the amplitude of which changes along with time, of the wheat grains to eliminate singular values of the data; then computing an autocorrelation function of the spontaneous BPE data of the wheat grains; and finally, acquiring a power spectrum distribution function of the spontaneous BPE information of the wheat grains by virtue of a correlation function method, and computing three characteristic parameters including spectrum edge frequency (SEF), spectrum gravity frequency (SGF) and power spectrum entropy (PSE) to describe the characteristics of a power spectrum of the wheat grains. The characteristic analysis method is simple in thinking, ensures clearness and definiteness of the characteristics, and can reveal frequency domain information implied in the existing time domain data and improve descriptive power to the spontaneous BPE information of the wheat grains.
The invention discloses a characteristic analysis method for spontaneous BPE (biophoton emission) information of wheat grains. The characteristic analysis method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing spontaneous BPE time-domain data, the amplitude of which changes along with time, of the wheat grains to eliminate singular values of the data; then computing an autocorrelation function of the spontaneous BPE data of the wheat grains; and finally, acquiring a power spectrum distribution function of the spontaneous BPE information of the wheat grains by virtue of a correlation function method, and computing three characteristic parameters including spectrum edge frequency (SEF), spectrum gravity frequency (SGF) and power spectrum entropy (PSE) to describe the characteristics of a power spectrum of the wheat grains. The characteristic analysis method is simple in thinking, ensures clearness and definiteness of the characteristics, and can reveal frequency domain information implied in the existing time domain data and improve descriptive power to the spontaneous BPE information of the wheat grains.
RU2436497 -- METHOD OF DETERMINING
INDICATIONS FOR CARRYING OUT RADIO- AND CHEMOTHERAPY
FIELD: medicine. ^ SUBSTANCE: Invention relates to medicine, radiobiology and can be applied in treatment of malignant tumours. Risk of development of radio- and chemotherapy complications is predicted by determination in patient's spectrum of antioxidants of -carotenoids concentration by means of biophoton scanner directing light ray at palm projection of Ho-Ku point. Index of skin carotinoids (ISC) is determined and if ISC value is less than 12000, conclusion about possible development of complications during radio- and chemotherapy is made. ^ EFFECT: method ensures acceleration and simplification of determination of indications for carrying out radio- and polychemotherapy, high accuracy of predicting risk of complications in case if such treatment is carried out.
FIELD: medicine. ^ SUBSTANCE: Invention relates to medicine, radiobiology and can be applied in treatment of malignant tumours. Risk of development of radio- and chemotherapy complications is predicted by determination in patient's spectrum of antioxidants of -carotenoids concentration by means of biophoton scanner directing light ray at palm projection of Ho-Ku point. Index of skin carotinoids (ISC) is determined and if ISC value is less than 12000, conclusion about possible development of complications during radio- and chemotherapy is made. ^ EFFECT: method ensures acceleration and simplification of determination of indications for carrying out radio- and polychemotherapy, high accuracy of predicting risk of complications in case if such treatment is carried out.
CN201861626 -- Device quantitatively
measuring traditional Chinese medicine science 'syndrome'
through biophoton radiation of human body
The utility model discloses a device quantitatively measuring traditional Chinese medicine science 'syndrome' through the biophoton radiation of human body, which comprises a darkroom, a detector, a preamplifier and a processor. The detector is arranged in the darkroom, the preamplifier is connected with the detector through a circuit, the processor is connected with the preamplifier through a circuit, the detector is used for measuring biophotons from acupuncture points, the preamplifier is used for converting and amplifying biophoton signals received by the detector, and the processor records the intensity value of the biophotons from the acupuncture points and processes the measured value. A method of quantitatively measuring the traditional Chinese medicine science 'syndrome' through the biophoton radiation of the human body: a person enters the darkroom, the detector is moved to be close to the acupuncture point to be detected, a shutter on the detector is opened, biophotons from the acupuncture points to be detected are measured, the strength value of the biophotons from the acupuncture points to be detected is recorded through the processor and the measured value is processed by the processor. The device is quick, sensitive and reliable and has no damage on the human body.
The utility model discloses a device quantitatively measuring traditional Chinese medicine science 'syndrome' through the biophoton radiation of human body, which comprises a darkroom, a detector, a preamplifier and a processor. The detector is arranged in the darkroom, the preamplifier is connected with the detector through a circuit, the processor is connected with the preamplifier through a circuit, the detector is used for measuring biophotons from acupuncture points, the preamplifier is used for converting and amplifying biophoton signals received by the detector, and the processor records the intensity value of the biophotons from the acupuncture points and processes the measured value. A method of quantitatively measuring the traditional Chinese medicine science 'syndrome' through the biophoton radiation of the human body: a person enters the darkroom, the detector is moved to be close to the acupuncture point to be detected, a shutter on the detector is opened, biophotons from the acupuncture points to be detected are measured, the strength value of the biophotons from the acupuncture points to be detected is recorded through the processor and the measured value is processed by the processor. The device is quick, sensitive and reliable and has no damage on the human body.
CN102004089 -- Device and method for
detecting property of traditional Chinese medicine
The invention discloses device and method for detecting the property of the traditional Chinese medicine. The device comprises an excitation light source, a sample chamber, a biophoton measuring system and a data processing system, wherein the excitation light source is used for generating excitation light; the light emitted by the exciting light source can be incident into the sample chamber; the biophoton measuring system is used for measuring the intensity of the biophoton emitted by the sample after being excited in the sample chamber; and the data processing system is used for analyzing and processing data measured by the biophoton measuring system which is connected with the data processing system by a circuit. The invention also discloses the method for detecting the property of the traditional Chinese medicine, comprising the following steps of: placing the powdery sample into the sample chamber; exciting the light source to emit the excitation light for irradiating the sample; detecting the intensity of the biophoton emitted by the sample after being excited by using the biophoton measuring system; and transmitting the information data into the data processing system for analyzing, thereby judging the properties of cold, heat and moderate and the degrees of the traditional Chinese medicine of the sample.
The invention discloses device and method for detecting the property of the traditional Chinese medicine. The device comprises an excitation light source, a sample chamber, a biophoton measuring system and a data processing system, wherein the excitation light source is used for generating excitation light; the light emitted by the exciting light source can be incident into the sample chamber; the biophoton measuring system is used for measuring the intensity of the biophoton emitted by the sample after being excited in the sample chamber; and the data processing system is used for analyzing and processing data measured by the biophoton measuring system which is connected with the data processing system by a circuit. The invention also discloses the method for detecting the property of the traditional Chinese medicine, comprising the following steps of: placing the powdery sample into the sample chamber; exciting the light source to emit the excitation light for irradiating the sample; detecting the intensity of the biophoton emitted by the sample after being excited by using the biophoton measuring system; and transmitting the information data into the data processing system for analyzing, thereby judging the properties of cold, heat and moderate and the degrees of the traditional Chinese medicine of the sample.
US2005154317 -- Apparatus and method
for detecting an acupoint or other site of interest
In an apparatus for
detecting an acupoint using an intensity of biophotons emitted
from a living system in response to magnetic field stimuli, and
a method for detecting an acupoint, the apparatus includes a
magnetic field application unit for applying a magnetic field to
a predetermined site of the living system, a biophoton
measurement unit for measuring the intensity of the biophotons
emitted from the predetermined site of the living system, and an
acupoint determination unit for determining whether the
predetermined site is an acupoint based on the intensity of the
biophotons measured by the biophoton measurement unit.US2002173831 -- Acupuncture needle
Acupuncture needle
having a grasping and a puncturing end comprising a hollow
needle body and a coaxially located light conducting element
therein, a reception and emission surface for biophoton
radiation at the distal puncturing end of the needle and a prism
with a 180 DEG reflection and in light conducting contact with
the light conducting element at the proximal grasping end of the
needle.
KR100637032 -- HEALTH ASSESSMENT
DEVICE USING BIOPHOTON
The present invention
relates to a health diagnostic apparatus, and more particularly,
to a health diagnostic apparatus using a living body photon that
diagnoses a health state of an object to be inspected by
detecting and analyzing a living body photon of a living body
emitted from an object to be inspected. The organism
spontaneously emits visible light in the visible light region
without external stimulation, and biophotons of the emitted
light are closely related to the metabolism of the organism.
This study of biophotons began in the early 1920s when Russian
scientist A. Gurwitsch discussed the question of how biological
tissues transmit and transform information about the size and
shape of different organs. It is also argued that the release is
due to biochemical reactions within the tissue associated with
the oxidative metabolic process of the organism, or is due to
the production of reactive oxygen species and the activity of
enzymes. Thus, the linkage between biomolecules and the
metabolism of an organism has not been elucidated yet, but
biomedical emission from an organism is closely related to the
physiological or pathological state of the organism, And health
professionals in the field of life sciences. Generally, a
photomultiplier, which is a photodetector, is used for the
measurement of a biophoton, which is a device used for detecting
light in the vicinity of a visible light. When a photoelectron,
which is a light, is collided with a metal surface, Is an
electron tube that amplifies minute photoelectrons by utilizing
the phenomenon that not only is reflected but also energy is
given to electrons in a solid and new electrons are ejected from
the metal surface, that is, secondary electron emission
phenomenon occurs. Hereinafter, a structure and a method for a
health diagnosis using a bio-photon according to a conventional
technique for diagnosing a health state of a hand, which is a
target site to be inspected, of a person to be inspected will be
described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. 1
is a block diagram schematically showing a conventional
bio-photon-based health diagnostic apparatus.KR100637031 -- HEALTH ASSESSMENT DEVICE USING BIOPHOTON
The present invention relates to a bio-photon-based health diagnostic apparatus, and more particularly, to a bio-photon-based health check-up apparatus for diagnosing the health state of an object to be inspected by detecting and analyzing the number of bio- The organism spontaneously emits visible light in the visible light region without external stimulation, and biophotons of the emitted light are closely related to the metabolism of the organism. This study of biophotons began in the early 1920s when Russian scientist A. Gurwitsch discussed the question of how biological tissues transmit and transform information about the size and shape of different organs. It is also argued that the release is due to biochemical reactions within the tissue associated with the oxidative metabolic process of the organism, or is due to the production of reactive oxygen species and the activity of enzymes. Thus, the linkage between biomolecules and the metabolism of an organism has not been elucidated yet, but biomedical emission from an organism is closely related to the physiological or pathological state of the organism, And health professionals in the field of life sciences. Generally, a photomultiplier, which is a photodetector, is used for measuring biomagnetism, which is a device used for detecting light in the vicinity of a visible light. When a photoelectron, which is a light, is collided with a solid surface, In addition, it is an electron tube that amplifies a minute optoelectronic current by taking advantage of the fact that energy is given to electrons in a solid and new electrons are ejected from the solid surface, that is, secondary electron emission phenomenon occurs.
PURPOSE: An apparatus and a method are provided to count biophotons emitted from hands of an object person for measurement and diagnose the health condition of the object person in accordance with an analysis on the biophotons. CONSTITUTION: An apparatus comprises a dark chamber(15), two optical detectors, two signal converting units, and a counting system. The dark chamber is divided into two sections, and has holes formed at a front surface of each of the sections. Each of the holes has a size allowing for passage of a hand of an object person for measurement. The optical detectors are arranged in each section of the dark chamber such that the optical detectors detect biophotons emitted from the object person for measurement. The signal converting units amplify the current signals output from the optical detectors, and convert the signals into countable square pulses.; The counting system counts square pulses which are converted by the signal converting units, in accordance with a tuned time interval. be utilized for medical diagnosis purpose
PURPOSE: A device and a method for detecting delayed luminescence are provided to efficiently measure the delayed luminescence by using a light detector. CONSTITUTION: A device for detecting delayed luminescence includes a light detector, light shielding box(11), a shutter(13), a light source(15), and a data processing unit(20). The light detector detects biophoton emitted from a test sample. The light shielding box(11) shields the light detector from external light. The shutter(13) is positioned between the test sample and the light detector and adjusts light such that the biophoton emitted from the test sample reaches the light detector or not. The shutter light source(15) is attached to the bottom surface of the shutter(13). The light source(13) turns on light when the shutter(13) is opened and turns off light when the shutter(13) is closed.
KR100836491 -- METHOD FOR PRODUCING OR TESTING SKIN CARE COSMETICS BY BIOPHOTON MEASUREMENT AND SKIN CARE COSMETICS PRODUCED OR TESTED THEREBY
US2009054885 -- BIOPHOTON MEASURING
INSTRUMENT
Biophoton measuring
instrument comprises a light illuminating section for
illuminating a sample with a light having a predetermined
wavelength and reactive with oxidized hemoglobins and reduced
hemoglobins through an illuminating optical fiber, a light
detecting section for detecting and amplifying the light passing
through a detecting optical fiber and the sample, a signal
processing section adapted for computing the hemoglobin temporal
variation information on the oxidized hemoglobins, the reduced
hemoglobins and the whole hemoglobins in the sample from the
signal detected by the light detecting section and having noise
detecting means for arithmetically processing the detected
signal and judging/detecting whether the temporal variation
information is the noise (low S/N noise); attributed to the
presence of an obstacle to the pass of the light between the
sample and the end face of the optical fiber or the noise
(mirror noise ) attributed to the damage to the light
illuminating section, and a display section for displaying the
noise signal judged/detected by the signal processing section to
enable identification of the type of the noise.WO02100484 -- SKIN ADHESIVE DRESSING
COMPRISING A LIGHT-EMITTING OR RADIATION-EMITTING DEVICE,
AND METHOD FOR THE USE THEREOF
The invention firstly
relates to a skin adhesive dressing (4) comprising at least one
adhesive surface that adheres to the skin and optionally
comprising a sterile nonwoven fabric that at least partially
covers a wound. The novel skin adhesive dressing (4) has a
through opening (10), which leaves the wound, in essence,
accessible and which is provided with a covering (9). This
covering is transparent to light or is transparent to radiation
and is placed on the side of the skin adhesive dressing (4)
facing away from the wound. The invention also relates to a
light-emitting or radiation-emitting device (11), particularly
for a skin adhesive dressing (4) of the aforementioned type.
This device comprises a light source or radiation source (1), a
power source (2), and an electric circuit that connects the
light source or radiation source (1) to the power source (2),
all of which being at least partially covered by or contained in
a housing (5). The light source or radiation source (1) is
preferably configured as a biophoton source, and the power
source (2) is preferably configured as a direct-current source.
The invention also relates to a method for enhancing human
well-being while using the inventive skin adhesive dressing (4)
as well as the inventive light-emitting or radiation-emitting
device (11).DE202006007899
-- Biophoton resonance
method for medical therapy of organ systems, involves
penetrating biological body in electromagnetic waves, so
that its physiological, biochemical and biophysical
functions are enhanced
The method involves
generating longitudinal electromagnetic waves through vibratory
resonators (2), which consist of current-carrying electrical
conductors (1) and can be shifted by sound waves comprising
infrasonic and ultrasonic waves into mechanical resonance
vibrations. The electromagnetic waves appear in resonance to
biophotons, bioelectrical frequencies and biological vibrations.
A biological body penetrates in the electromagnetic waves, so
that its physiological, biochemical and biophysical functions
are enhanced.ATA75796
/ AT403009 -- Combination crystal/coloured light therapy
apparatus with biophoton energy
The apparatus for
coloured light therapy consists of a stand to which a halogen
light source is fixed by means of a holder. In a further holder,
coloured glass discs can be inserted in front of the light
source. In front of the lamp, a ground crystal is inserted to
optimize the light diffraction. A pot additionally fixed to the
stand is used to contain precious stones, flower essences or
homeopathic solutions.Fritz-Albert
POPP Biophoton Patents
US7692788 -- Method for quickly
determining qualities/qualitative changes in any system
ZA9208094
-- Method and means of determining the health
conditions of a living creature.
The invention relates
to a method and device for determining the state of health of
a living being. The invention provides for a selected,
physiological parameter of the living being, e.g. the
conductivity of the skin, to be recorded on a statistically
significant multiplicity of measuring points distributed over
a defined part of the body of the living being, for the
frequency distribution of the recorded measurements to be
determined and compared with a reference frequency
distribution of the selected, physiological parameter. The
reference frequency distribution is a logarithmic distribution
which can be determined directly from the measurements
obtained from the particular test subject by statistical
methods. The invention permits reliable statements to be made
regarding the overall state of health of the test subject.US2006270055 -- Method for testing external
influences on biological tissues
The
invention relates to a method for testing external
influences on biological systems by measuring "ultraweak
photon emissions (biophotons) and "delayed luminescence",
based on non-local and different changes of photon emissions
on different points of the tissue through exposure to the
external influence. The changes can vary to such an extent
that the slightest differences in the influences can be can
be registered with the highest sensitivity.US4458531
-- Method of and apparatus for examining biological
effects in cell-lots
EP0430150
-- Method for testing quality and quality
changes of biological systems and organochemical
compositions interacting with these systems using
measurements of ultraweak photon emission.
Known
status parameters for the quality of biological systems,
foodstuffs and organic chemical compounds interacting with
the latter are with the methods of comparative statistical
analysis with measured parameters of ultraweak photon
emission. This makes it possible to reflect reproducibly the
quality content and the vitality of a biological system in
the sense of Erwin Schrödinger's quality term by means of
measured parameters, to measure the quality of foodstuffs
and to determine in advance expected changes in quality on
storage, and to predict the biocompatibility of organic
chemical compounds. Foodstuffs irradiated for preservation
purposes can still be distinguished significantly from
non-irradiated even one year after the irradiation by the
intensity of the photon emission. Environmental effects on
live systems can be characterised almost directly as
environmental stress or damage by observing the ultraweak
photon emission over a short time.EP1776042
-- DEVICE FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FUNCTIONAL
VALUES
The
invention relates to a device for the determination of
functional values of biological systems, whereby in
particular, the conductivity of the skin is recorded as a
functional value. The measured values for the conductivity
are determined using an electrode matrix (1) in a measuring
device (11), whereby a current circuit to a reference
electrode (13) is formed and the measured values are
subsequently stored and analysed.EP1340066
-- METHOD FOR DETECTING BACTERIAL INFECTION
The
invention relates to a method for detecting bacterial
infection or contamination of or in products in order to be
able to rapidly determine the product's quality or
sterility. To this end, the intensity of photon emission of
a nutrient medium is determined and measured with a sample
of the object to be examined.EP1188041
-- METHOD, SYSTEM AND USE OF MEASURING DEVICES
FOR DETERMINING THE GERMINABILITY OF SEEDS
A process
(I) and apparatus for determining the germination
characteristics of seed corn by bio-photon and water
moisture detection, are new. In a process (I) to determine
the germination capacity of seed grain especially cereals,
the seed grain is first exposed to light pulses for a
defined period and the exposure then terminated. A
measurement is made of at least one characteristic of the
light then emitted by the seed without further light
stimulation especially the residual luminescence or
spontaneous light emission. The light emitted gives an
indication of the germination capacity of the seed. In
addition a further measurement is made especially of the
seed grain water content, and is used as a correction factor
to the germination characteristic based on the light value.
An Independent claim is also included for apparatus for use
in (I).EP1126271
-- Method and device for determining the
malignancy of tumor tissue and for choosing substances
beneficial to the tissue
Method
involves measurement of the bio-photon emission from tumor
tissue using a very sensitive light detector. The tissue can
first be excited using illumination with suitable wavelength
light, using ultrasound, etc and then the value of emitted
light measured. From the measurements a suitable medicine
can be selected to treat the tumor. An Independent claim is
made for a system for treating malignant cancers by
determining the degree of malignancy from light measurements
and then determining the optimum medicine.DE102005058332 -- Method for optimal
interpretation of data evaluating regulatory capacity of
biological system, in particular human being, comprises
use of factor analysis and comparison with reference data
One of
the physiological parameters of a biological system in
particular of a human being, which can be the galvanic skin
response, is measured at a large number of subjects. The
data are evaluated by using various appropriate statistical
methods. The log-normal distribution and the Gaussian
distribution are calculated. The resulting matrix is used as
a base for a factor analysis already containing the data of
a reference group. The position of the factors can be used
as a criterion for the evaluation of the condition of an
individual regarding the regulatory capacity of his/her
system.DE102004055200 -- Functional value e.g. regulating
capability, determining method for e.g. human being,
involves evaluating light signal after deviation from pure
random distribution and correlation to ideally regulating
distribution
The
method involves evaluating a light signal after a deviation
from a pure random distribution and a correlation to an
ideally regulating distribution. A strewing portion of a
photon is measured, where the photon is used for stimulation
of a biological system. The light signal is utilized as a
trigger pulse for treatment of a relevant skin area of the
biological system.DE10147701
-- Testing for the smallest possible quality
differences between biological tissue by measurement of
bio-photon emission and application of photon count
statistics
Method
for testing for the smallest possible quality differences
between biological tissue by measurement of bio-photon
emission and delayed luminescence. Measurement of photon
emission is with or without the effect of interacting
agents. Differences in measurements are determined using
photon count statistics.DE10132549
-- Determining heat regulating capacity of
biological systems involves irradiating with infrared
light, detecting relaxation of photon intensity and
compensating using hyperbolic function
The
process involves determining the quality and/or quality
changes of biological systems by measuring the ultra-weak
photon emission of a system subjected to the light after
ending the radiation. The biological system is irradiated
with infrared light and the relaxation of the photon
intensity is detected against time and then the relaxation
function of the investigated system is compensated using a
hyperbolic function.DE4439451
-- Examining changes in the condition of
biological tissue
In a
method for examining changes in the condition of human,
animal or plant tissue by measurement of ultra-weak photo
emission, the new feature is that the measuring parameters
of the emission are employed.DE4401169 -- Faster procedure
for detecting differences in fluid characteristics
A method for discriminating between the characteristics of similar fluids employs differences in the respective photon emissions of fluid samples after their identical excitation at a controlled temperature. Each sample (1) is successively enclosed in a transparent quartz vessel having a pair of titanium electrodes (2,3) supplied with a DC potential of typically 18 volts. An excitation system (4) activates the sample either by energising a tungsten light source of controlled spectrum or by EM/sound waves of constant intensity and wavelength. After a definite period of excitation the luminescence of the sample is measured by the detector(s).
A method for discriminating between the characteristics of similar fluids employs differences in the respective photon emissions of fluid samples after their identical excitation at a controlled temperature. Each sample (1) is successively enclosed in a transparent quartz vessel having a pair of titanium electrodes (2,3) supplied with a DC potential of typically 18 volts. An excitation system (4) activates the sample either by energising a tungsten light source of controlled spectrum or by EM/sound waves of constant intensity and wavelength. After a definite period of excitation the luminescence of the sample is measured by the detector(s).
DE4308520
-- Method for differentiating between
homozygotes, heterozygotes and normal cells of an organism
A method
is specified for differentiating between homozygotes,
heterozygotes and normal cells of an organism. It is
characterised in that the cells to be investigated are
irradiated with UV light and/or treated with a substance
which partly damages the cells and the intensity of the
photon emission of these cells is subsequently measured. The
method is preferably used before X-ray diagnosis in which
the risk of inducing a disease triggered by the radiation is
to be no greater than the probability of early diagnosis of
a disease.DE3040855 -- Examining
biological effects on foodstuffs of seeds - by measuring
intensity of ultra-weak photon radiation in vitro
DE3038255
-- Examining biological effects on foodstuffs
of seeds - by measuring intensity of ultra-weak photon
radiation in vitro
A
measurement of the spontaneous or stimulated emission of
ultra-weak photon radiation is used as an in vitro parameter
of a cell lot. The parameter is used to detect possible
cell-damaging or regenerating effects or to act as a quality
control. The measured quantity is either the photon
intensity or a photon statistic e.g. the distribution of
numbers of photons emitted in a measuring interval. The
ultra-weak radiation is typically in the infra red band and
has an energy very much less than that of thermal radiation.
Typically the radiation is 10 power (-10) less than thermal
radiation. The radiation is detected by a photo multiplier
with a gain of over 10 power 6. The method may be used to
determine whether a cell lot is in a healthy state.
Alternatively it can be used to determine the effect of an
agent on the cells. The method is partic. suitable for
quality control in foodstuffs.DE2844217 -- Diagnosis of
tumours and direction of treatment - by measuring
ultra-weak photon emission characteristics of sample
tissue
US2006270055 -- Method for testing
external influences on biological tissues
The invention relates
to a method for testing external influences on biological
systems by measuring "ultraweak photon emissions (biophotons)
and "delayed luminescence", based on non-local and different
changes of photon emissions on different points of the tissue
through exposure to the external influence. The changes can vary
to such an extent that the slightest differences in the
influences can be can be registered with the highest
sensitivity.US4458531 -- Method of and
apparatus for examining biological effects in cell-lots
In a method of testing
the biological effects of cell-lots, which release a
characteristic or stimulatable ultra-weak photon radiation, the
intensity and/or the photon statistic of the ultra-weak photon
radiation is measured, as the test factor, for the purpose of
the in vitro examination of substances for possible
cell-damaging or regenerating effects, or for the purpose of
carrying out quality control on biological substances, such as
foodstuffs, edible plants or seed materials.EP0430150 -- Method for testing
quality and quality changes of biological systems and
organochemical compositions interacting with these systems
using measurements of ultraweak photon emission.
Known status parameters
for the quality of biological systems, foodstuffs and organic
chemical compounds interacting with the latter are with the
methods of comparative statistical analysis with measured
parameters of ultraweak photon emission. This makes it possible
to reflect reproducibly the quality content and the vitality of
a biological system in the sense of Erwin Schrödinger's quality
term by means of measured parameters, to measure the quality of
foodstuffs and to determine in advance expected changes in
quality on storage, and to predict the biocompatibility of
organic chemical compounds. Foodstuffs irradiated for
preservation purposes can still be distinguished significantly
from non-irradiated even one year after the irradiation by the
intensity of the photon emission. Environmental effects on live
systems can be characterised almost directly as environmental
stress or damage by observing the ultraweak photon emission over
a short time.EP1776042 -- DEVICE FOR THE
DETERMINATION OF FUNCTIONAL VALUES
The invention relates
to a device for the determination of functional values of
biological systems, whereby in particular, the conductivity of
the skin is recorded as a functional value. The measured values
for the conductivity are determined using an electrode matrix
(1) in a measuring device (11), whereby a current circuit to a
reference electrode (13) is formed and the measured values are
subsequently stored and analysed.EP1340066 -- METHOD FOR DETECTING
BACTERIAL INFECTION
The invention relates
to a method for detecting bacterial infection or contamination
of or in products in order to be able to rapidly determine the
product's quality or sterility. To this end, the intensity of
photon emission of a nutrient medium is determined and measured
with a sample of the object to be examined.EP1188041 -- METHOD, SYSTEM AND USE
OF MEASURING DEVICES FOR DETERMINING THE GERMINABILITY OF
SEEDS
A process (I) and
apparatus for determining the germination characteristics of
seed corn by bio-photon and water moisture detection, are new.
In a process (I) to determine the germination capacity of seed
grain especially cereals, the seed grain is first exposed to
light pulses for a defined period and the exposure then
terminated. A measurement is made of at least one characteristic
of the light then emitted by the seed without further light
stimulation especially the residual luminescence or spontaneous
light emission. The light emitted gives an indication of the
germination capacity of the seed. In addition a further
measurement is made especially of the seed grain water content,
and is used as a correction factor to the germination
characteristic based on the light value. An Independent claim is
also included for apparatus for use in (I).EP1126271 -- Method and device for
determining the malignancy of tumor tissue and for choosing
substances beneficial to the tissue
Method involves
measurement of the bio-photon emission from tumor tissue using a
very sensitive light detector. The tissue can first be excited
using illumination with suitable wavelength light, using
ultrasound, etc and then the value of emitted light measured.
From the measurements a suitable medicine can be selected to
treat the tumor. An Independent claim is made for a system for
treating malignant cancers by determining the degree of
malignancy from light measurements and then determining the
optimum medicine.DE102005058332 -- Method for optimal
interpretation of data evaluating regulatory capacity of
biological system, in particular human being, comprises use
of factor analysis and comparison with reference data
One of the
physiological parameters of a biological system in particular of
a human being, which can be the galvanic skin response, is
measured at a large number of subjects. The data are evaluated
by using various appropriate statistical methods. The log-normal
distribution and the Gaussian distribution are calculated. The
resulting matrix is used as a base for a factor analysis already
containing the data of a reference group. The position of the
factors can be used as a criterion for the evaluation of the
condition of an individual regarding the regulatory capacity of
his/her system.DE102004055200 -- Functional value e.g.
regulating capability, determining method for e.g. human
being, involves evaluating light signal after deviation from
pure random distribution and correlation to ideally
regulating distribution
The
method involves evaluating a light signal after a deviation
from a pure random distribution and a correlation to an
ideally regulating distribution. A strewing portion of a
photon is measured, where the photon is used for stimulation
of a biological system. The light signal is utilized as a
trigger pulse for treatment of a relevant skin area of the
biological system.
DE10147701 -- Testing for the
smallest possible quality differences between biological
tissue by measurement of bio-photon emission and application
of photon count statistics
Method for testing for
the smallest possible quality differences between biological
tissue by measurement of bio-photon emission and delayed
luminescence. Measurement of photon emission is with or without
the effect of interacting agents. Differences in measurements
are determined using photon count statistics.DE10132549 -- Determining heat
regulating capacity of biological systems involves
irradiating with infrared light, detecting relaxation of
photon intensity and compensating using hyperbolic function
The process involves
determining the quality and/or quality changes of biological
systems by measuring the ultra-weak photon emission of a system
subjected to the light after ending the radiation. The
biological system is irradiated with infrared light and the
relaxation of the photon intensity is detected against time and
then the relaxation function of the investigated system is
compensated using a hyperbolic function.DE4439451 -- Examining changes in
the condition of biological tissue
In a method for
examining changes in the condition of human, animal or plant
tissue by measurement of ultra-weak photo emission, the new
feature is that the measuring parameters of the emission are
employed.DE4401169 -- Faster procedure for
detecting differences in fluid characteristics
A
method for discriminating between the characteristics of
similar fluids employs differences in the respective photon
emissions of fluid samples after their identical excitation at
a controlled temperature. Each sample (1) is successively
enclosed in a transparent quartz vessel having a pair of
titanium electrodes (2,3) supplied with a DC potential of
typically 18 volts. An excitation system (4) activates the
sample either by energising a tungsten light source of
controlled spectrum or by EM/sound waves of constant intensity
and wavelength. After a definite period of excitation the
luminescence of the sample is measured by the detector(s).
DE4308520 -- Method for
differentiating between homozygotes, heterozygotes and
normal cells of an organism
A method is specified
for differentiating between homozygotes, heterozygotes and
normal cells of an organism. It is characterised in that the
cells to be investigated are irradiated with UV light and/or
treated with a substance which partly damages the cells and the
intensity of the photon emission of these cells is subsequently
measured. The method is preferably used before X-ray diagnosis
in which the risk of inducing a disease triggered by the
radiation is to be no greater than the probability of early
diagnosis of a disease.DE3040855 -- Examining biological
effects on foodstuffs of seeds - by measuring intensity of
ultra-weak photon radiation in vitro
A
measurement of the spontaneous or stimulated emission of
ultra-weak photon radiation is used as an in vitro parameter
of a cell lot. The parameter is used to detect possible
cell-damaging or regenerating effects or to act as a quality
control. The measured quantity is either the photon intensity
or a photon statistic e.g. the distribution of numbers of
photons emitted in a measuring interval. The ultra-weak
radiation is typically in the infra red band and has an energy
very much less than that of thermal radiation. Typically the
radiation is 10 power (-10) less than thermal radiation. The
radiation is detected by a photo multiplier with a gain of
over 10 power 6. The method may be used to determine whether a
cell lot is in a healthy state. Alternatively it can be used
to determine the effect of an agent on the cells. The method
is partic. suitable for quality control in foodstuffs.
DE3038255 -- Examining biological
effects on foodstuffs of seeds - by measuring intensity of
ultra-weak photon radiation in vitro
A measurement of the
spontaneous or stimulated emission of ultra-weak photon
radiation is used as an in vitro parameter of a cell lot. The
parameter is used to detect possible cell-damaging or
regenerating effects or to act as a quality control. The
measured quantity is either the photon intensity or a photon
statistic e.g. the distribution of numbers of photons emitted in
a measuring interval. The ultra-weak radiation is typically in
the infra red band and has an energy very much less than that of
thermal radiation. Typically the radiation is 10 power (-10)
less than thermal radiation. The radiation is detected by a
photo multiplier with a gain of over 10 power 6. The method may
be used to determine whether a cell lot is in a healthy state.
Alternatively it can be used to determine the effect of an agent
on the cells. The method is partic. suitable for quality control
in foodstuffs.DE19538768 -- Detection of
microbial contamination, e.g. in food, drink and water
Detection of microbial contamination comprises measurement of
the intensity of photons emitted by a sample in a polar
solvent. A voltage is applied to electrodes placed in the
sample and the measured photon emission intensity is compared
with a control to determine the presence or absence of
contamination.
Example
Into a 10 ml quartz cuvette, two needle-shaped circuit boards are inserted in parallel at a distance of 5 mm and connected to a DC voltage source. To the cuvette are added successively 8 ml of pure saline solution (3 mM / l of saline), the same solution with an additional concentration of 10 Rhizobium japonicum 1132-2 bacteria / ml and the same solution with a concentration of 100 Rhizobium japonicum 1132- 2 bacteria / ml.
In any case, a DC voltage of 80 volts is applied for a period of 5 seconds. At the same time, the intensities of photon emission (in number of photons / 100 ms) are measured over the period of 5 s. The measurement is repeated three times. The mean values and scatterings of the three measurements are formed. Table I contains the results. Table I
The result shows that this method can significantly detect 10 bacteria / ml.
Example
Into a 10 ml quartz cuvette, two needle-shaped circuit boards are inserted in parallel at a distance of 5 mm and connected to a DC voltage source. To the cuvette are added successively 8 ml of pure saline solution (3 mM / l of saline), the same solution with an additional concentration of 10 Rhizobium japonicum 1132-2 bacteria / ml and the same solution with a concentration of 100 Rhizobium japonicum 1132- 2 bacteria / ml.
In any case, a DC voltage of 80 volts is applied for a period of 5 seconds. At the same time, the intensities of photon emission (in number of photons / 100 ms) are measured over the period of 5 s. The measurement is repeated three times. The mean values and scatterings of the three measurements are formed. Table I contains the results. Table I
The result shows that this method can significantly detect 10 bacteria / ml.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VgdyXh4m9Mc
Future Science – The Wave Genome – Quantum Holography of DNA with Ulrike Granögger
GAJAREV, Pjotr, & POPONIN, Vladimir: DNA Biocomputer Reprogramming ~ DNA can be reprogrammed by light and frequency; articles, videos, complete patents & book.
KANCHZHEN, Tszyan: Microwave Transfer of Biological Information ~ Exchange genetic characteristics between species, & healing, rejuvenation.
Books
Das Problem der
Zellteilung physiologisch betrachtet
A. Gurwitsch
Handbook of Biophotonics
J. Popp, et al.
Interview Die Botschaft der Nahrung
F. Popp
Biophotonics : Optical Science & Engineering for the 21st Century
X. Shen, et al.
Biomedical Photonics Handbook, Vol. 3 -- Therapeutics and Advanced Biophotonics
T. Vo-Dinh, et al.
Biophotonics and Coherent Systems in Biology
L. Belousov, et al.
Biophotonics and Healing
S. Preston
Biophotons
J. Chang, etal.
Integrative Biophysics -- Biophotonics
F-A. Popp, et al
Introduction to Biophotonics
P. Prasad
Light In Shaping Life -- Biophotons in Biology and Medicine
R. Van Wijk
Die Mitogensiche Strahlung
S. Gurwitsch
A. Gurwitsch
Handbook of Biophotonics
J. Popp, et al.
Interview Die Botschaft der Nahrung
F. Popp
Biophotonics : Optical Science & Engineering for the 21st Century
X. Shen, et al.
Biomedical Photonics Handbook, Vol. 3 -- Therapeutics and Advanced Biophotonics
T. Vo-Dinh, et al.
Biophotonics and Coherent Systems in Biology
L. Belousov, et al.
Biophotonics and Healing
S. Preston
Biophotons
J. Chang, etal.
Integrative Biophysics -- Biophotonics
F-A. Popp, et al
Introduction to Biophotonics
P. Prasad
Light In Shaping Life -- Biophotons in Biology and Medicine
R. Van Wijk
Die Mitogensiche Strahlung
S. Gurwitsch
Mistletoe, Viscum album
http://www.examiner.com/holistic-health-in-miami/holiday-herb-mistletoe-brings-cancer-cure-as-biophoton-research-shows-herb-s-healing-power
December 31, 2009
A UK woman has disclosed how she cured her cancer with the holiday herb mistletoe after declining chemotherapy treatment. Joan van Holsteijn obtained injections of a medicine made from mistletoe berries, the plant associated in popular culture with Christmas-time kisses. This treatment has apparently brought Joan a cure to her cancer, as the tumors have disappeared. Joan had been diagnosed with non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma after doctors discovered a tumor the size of an egg in her leg. Within 18 months of initiating the mistletoe treatment the tumor was gone and scans showed no further trace of the cancer. Joan is pleased that she made the decision to refuse chemotherapy due to the debilitating effects of chemotherapy drugs and their role in depleting the immune system, the very system the body needs functioning well to use its own resources for healing cancer.
Joan now keeps springs of mistletoe in her home, not to invite holiday kisses but to invite others to hear about her wonderful experience of recovery from lymphoma using this herbal treatment. This treatment is well-known in Europe, while Americans are unlikely to have heard of it. Even those who are aware of this herbal therapy may not know about some surprising research that explains how mistletoe seems to help the body clear away cancers. This research comes from the work of Dr. Fritz-Albert Popp, who is a pioneer in research on biophotons and their role in cellular communication. Dr. Popp discovered that changes in the body's biophoton emissions are associated with cancer and other illnesses. Biophotons are photons of light emitted in living systems. Popp found that carcinogenic chemicals can be recognized by their property of disrupting biophoton emissions and the coherence of light waves. Based on this, he surmised that there may be compounds which have the opposite effect of helping restore healthy biophoton emissions and resuming coherent light patterns. Of all the alleged cancer-busting substances Popp tested, only mistletoe was able to return the biophoton emissions of cancer cells back to normal. When this happened the cancers went into remission.
In Popp's view, health is a state of perfect subatomic communication, and ill health is a state of communication breakdown. We are ill when our waves are out of synch. Popp believes that our cells and DNA use electromagnetic spectrum waves to communicate and transfer information. Substances that disturb or enhance the transmission of these waves in varying frequency ranges (wavelengths) can influence our health. In cancer patients, Popp found that natural cycles of light emission were disrupted, light waves were losing coherence, and thus the cancer cells were out of attunement to the rest of the body. Scientists have long known that photorepair allows damaged cells to regenerate. This process of light being used to restore life to cells functions best within a certain frequency range. This frequency range falls within the ultraviolet light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Not surprisingly, Popp had discovered that known carcinogens (cancer causing chemicals) act to disrupt the transmission of light in that range.
Mistletoe appears to assist cancer patients due to the subtle energetic properties it contains. Vibrational medicine is a key frontier in the healing arts, and this herb is one example of how research in natural therapies and vibrational energy can help us find ways to restore health and bring balance and harmony to our lives. The next time you see a sprig of mistletoe, you may want to ponder this miracle healing herb and its life-giving properties...
http://www.viewzone.com
I get lots of suggestions for stories, and I really appreciate them. But some of them are too good to be true. An example of this was a story of a giant human skeleton -- maybe 40 feet tall -- that was discovered by a Russian archaeological team. The story had photos and links accompanying it and looked promising. But when the links were researched they went in a circle. Each link used the other link as the source. Finally the elements of the photos turned up and we recognized a good Photoshop job had fooled everyone.
I had this same experience this week when I was sent an article where a Russian (again) scientist, Pjotr Garjajev, had managed to intercept communication from a DNA molecule in the form of ultraviolet photons -- light! What's more, he claimed to have captured this communication from one organism (a frog embryo) with a laser beam and then transmitted it to another organisms DNA (a salamander embryo), causing the latter embryo to develop into a frog!
But this was just the beginning.
Dr. Garjajev claims that this communication is not something that happens only inside the individual cells or between one cell and another. He claims organisms use this "light" to "talk" to other organisms and suggested that this could explain telepathy and ESP. It was like human beings already had their own wireless internet based on our DNA. Wow!
I tried to find a scientific journal that had this experiment. All I could find were blogs and other websites that carried the same story, word for word, without any references. That is until I stumbled on the work of Fritz-Albert Popp [right]. Then everything I had just read seemed very plausible.
Fritz-Albert Popp thought he had discovered a cure for cancer. I'm not convinced that he didn't.
It was 1970, and Popp, a theoretical biophysicist at the University of Marburg in Germany, had been teaching radiology -- the interaction of electromagnetic (EM) radiation on biological systems. Popp was too early to worry about things like cellphones and microwave towers which are now commonly linked with cancers and leukemia. His world was much smaller.
He'd been examining two almost identical molecules: benzo[a]pyrene, a polycyclic hydrocarbon known to be one of the most lethal carcinogens to humans, and its twin (save for a tiny alteration in its molecular makeup), benzo[e]pyrene. He had illuminated both molecules with ultraviolet (UV) light in an attempt to find exactly what made these two almost identical molecules so different.
Why Ultra-violet light?
Popp chose to work specifically with UV light because of the experiments of a Russian biologist named Alexander Gurwitsch who, while working with onions in 1923, discovered that roots could stimulate a neighboring plant's roots if the two adjacent plants were in quartz glass pots but not if they were in silicon glass pots. The only difference being that the silicon filtered UV wavelengths of light while the quartz did not. Gurwitsch theorized that onion roots could communicate with each other by ultraviolet light.
All vibrations of energy are part of the electro-magnetic spectrum. These include electrical energy, heat, sound, light, radio waves and radioactive waves. UV light is merely a small portion of the spectrum of EM energy with a very short wavelength.
What Popp discovered was that benzo[a]pyrene (the cancer producing molecule) absorbed the UV light, then re-emitted it at a completely different frequency -- it was a light "scrambler". The benzo[e]pyrene (harmless to humans), allowed the UV light to pass through it unaltered.
Popp was puzzled by this difference, and continued to experiment with UV light and other compounds. He performed his test on 37 different chemicals, some cancer-causing, some not. After a while, he was able to predict which substances could cause cancer. In every instance, the compounds that were carcinogenic took the UV light, absorbed it and changed or scrambled the frequency.
There was another odd property of these compounds: each of the carcinogens reacted only to light at a specific frequency -- 380 nm (nanometres) in the ultra-violet range. Popp kept wondering why a cancer-causing substance would be a light scrambler. He began reading the scientific literature specifically about human biological reactions, and came across information about a phenomenon called 'photorepair'.
It is well known from biological laboratory experiments that if you blast a cell with UV light so that 99 per cent of the cell, including its DNA, is destroyed, you can almost entirely repair the damage in a single day just by illuminating the cell with the same wavelength at a much weaker intensity. To this day, scientists don't understand this phenomenon, called photorepair, but no one has disputed it.
Popp also knew that patients with xeroderma pigmentosum [right] eventually die of skin cancer because their photorepair system can't repair solar damage. He was also struck by the fact that photorepair works most efficiently at 380 nm -- the same frequency that the cancer-causing compounds react to and scramble.
This was where Popp made his logical leap. If the carcinogens only react to this frequency, it must somehow be linked to photorepair. If so, this would mean that there must be some kind of light in the body responsible for photorepair. A compound must cause cancer because it permanently blocks this light and scrambles it, so photorepair can't work anymore. It seemed logical, but was it true?
Popp was freaked out by this. He wrote about it in a paper and a prestigious medical journal agreed to publish it.
Not long after that, Popp was approached by a student named Bernhard Ruth, who asked Popp to supervise his work for his doctoral dissertation. Popp told Ruth he was prepared to do so if the student could show that light was emanating from the human body.
This meeting was fortuitous for Popp because Ruth happened to be an excellent experimental physicist. Ruth thought the idea was ridiculous, and immediately set to work building equipment to prove Popp's hypothesis wrong.
Within two years, Ruth had constructed a machine resembling a big X-ray detector which used a photomultiplier to count light, photon by photon. Even today, it is still one of the best pieces of equipment in the field. The machine had to be highly sensitive because it had to measure what Popp assumed would be extremely weak emissions.
In an old documentary film taken in the laboratory at the International Institute of Biophysics, Dr. Popp opens a chamber about the size of a bread box. He places a fresh cutting from a plant and a wooden match in a plastic container inside the dark chamber and closed the light proof door. Immediately he switches on the photomultiplyer and the image shows up on a computer screen. The match stick is black while the green, glowing silhouette of the leaves is clearly visible.
Dr. Popp exclaims, "We now know, today, that man is essentially a being of light."
In 1976, they were ready for their first test with cucumber seedlings. The photomultiplier showed that photons, or light waves, of a surprisingly high intensity were being emitted from the seedlings. In case the light had to do with an effect of photosynthesis, they decided that their next test -- with potatoes -- would be to grow the seedling plants in the dark. This time, when the seedlings were placed in the photomultiplier, they registered an even higher intensity of light. What's more, the photons in the living systems they'd examined were more coherent than anything they'd ever seen.
Popp began thinking about light in nature. Light was present in plants and was used during photosynthesis. When we eat plant foods, he thought, it must be that we take up the photons and store them.
When we consume broccoli, for example, and digest it, it is metabolised into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water, plus the light stored from the sun and photosynthesis. We extract the CO2 and eliminate the water, but the light, an EM wave, must be stored. When taken in by the body, the energy of these photons dissipates and becomes distributed over the entire spectrum of EM frequencies, from the lowest to the highest.
This energy is the driving force for all the molecules in our body. Before any chemical reaction can occur, at least one electron must be activated by a photon with a certain wavelength and enough energy.
The biochemist and Nobel Prize winner Lehninger mentions in his textbook that some reactions in the living cell happen quite a lot faster than what corresponds to 37C temperature. The explanation seems to be that the body purposely directs chemical reactions by means of electromagnetic vibrations (biophotons).
Photons (Light) control everything in the cell
Photons switch on the body's processes like an orchestra conductor bringing each individual instrument into the collective sound. At different frequencies, they perform different functions. Popp found that molecules in the cells responded to certain frequencies, and that a range of vibrations from the photons caused a variety of frequencies in other molecules of the body.
This theory has been supported by Dr. Veljko Veljkovic who now heads the Center for Multidisciplinary Research and Engineering, Institute of Nuclear Sciences Vinca. She dared to ask the question that has forever puzzled cellular biologists: What is it that enabled the tens of thousands of different kinds of molecules in the organism to recognize their specific targets? Living processes depend on selective interactions between particular molecules, and that is true for basic metabolism to the subtlest nuances of emotion. It's like trying to find a friend in a very big very crowded ballroom in the dark.
The conventional picture of a cell even now is that of a bag of molecules dissolved in water. And through bumping into one another by chance -- random collisions -- those molecules that have complementary shapes lock onto to each other so the appropriate biochemical reactions can take place. This 'lock and key' model has been refined to a more flexible (and realistic) 'induced fit' hypothesis that allows each molecule to change shape slightly to fit the other better after they get in touch, but the main idea remains the same.
It is supposed to explain how enzymes can recognize their respective substrates, how antibodies in the immune system can grab onto specific foreign invaders and disarm them. By extension, that's how proteins can 'dock' with different partner proteins, or latch onto specific nucleic acids to control gene expression, or assemble into ribosomes for translating proteins, or other multi-molecular complexes that modify the genetic messages in various ways. But with thousands -- or even hundreds of thousands of reactions happening each second in just one cell this seems pushing the "mechanical" concept a bit too far.
What has been proposed is that somehow each molecule sends out a unique electromagnetic field that can "sense" the field of the complimentary molecule. It's as if there is a "dance" in the cellular medium and the molecules move to the rythm. The music is supplied by the biophoton.
"Veljkovic and Cosic proposed that molecular interactions are electrical in nature, and they take place over distances that are large compared with the size of molecules. Cosic later introduced the idea of dynamic electromagnetic field interactions, that molecules recognize their particular targets and vice versa by electromagnetic resonance. In other words, the molecules send out specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves which not only enable them to 'see' and 'hear' each other, as both photon and phonon modes exist for electromagnetic waves, but also to influence each other at a distance and become ineluctably drawn to each other if vibrating out of phase (in a complementary way)." -- The Real Bioinformatics Revolution: Proteins and Nucleic Acids Singing to One Another? (Paper available at report@i-sis.org.uk)
"There are about 100,000 chemical reactions happening in every cell each second. The chemical reaction can only happen if the molecule which is reacting is excited by a photon... Once the photon has excited a reaction it returns to the field and is available for more reactions... We are swimming in an ocean of light."
These 'biophoton emission', as Popp called them, provided an ideal communication system for the transfer of information to many cells across the organism. But the single most important question remained: where was the light coming from?
A particularly gifted student talked him into another experiment. It is known that when ethidium bromide is applied to samples of DNA, it insinuates itself in between the base pairs of the double helix, causing DNA to unwind. The student suggested that, after applying the chemical, they measure the light coming from the sample. Popp found that the greater the concentration of ethidium, the more the DNA unravelled, but also the stronger the intensity of light. Conversely, the less he used, the less light was emitted.
He also found that DNA could send out a wide range of frequencies, some of which seemed to be linked to certain functions. If DNA stored this light, it would naturally emit more light on being unzipped.
These and other studies proved to Popp that one of the most essential sources of light and biophoton emissions was DNA. DNA was like the master tuning fork of the body. It would strike a particular frequency and certain molecules would follow. It was also possible, he realised, that he had stumbled upon the missing link in current DNA theory that could account for perhaps the greatest miracle of all in human biology -- how a single cell can turn into a fully formed human being.
How cells "talk" to each other
When you get a cut or scratch on your skin, the cells that are injured somehow signal the surrounding healthy cells to begin reproducing copies of themselves to fill in and mend the opening. When the skin is back to normal, a signal is sent to the cells to tell them to stop reproducing. Scientists have wondered exactly how this works.
With biophoton emissions, Popp believed he had an answer to this question. This phenomenon of coordination and communication could only occur in a holistic system with one central orchestrator. Popp showed in his experiments that these weak light emissions were sufficient to orchestrate the body's repairs. The emissions had to be low intensity because these communications took place on a very small, intracellular, quantum level. Higher intensities would have an effect only in the world of the large and would create too much "noise" to be effective.
The number of photons emitted seemed to be linked to the organism's position on the evolutionary scale -- the more complex the organism, the fewer photons were emitted. Rudimentary animals and plants tended to emit 100 photons/cm2/sec at a wavelength of 200-800 nm, corresponding to a very-high-frequency EM wave well within the visible range, whereas humans emit only 10 photons/cm2/sec at the same frequency.
In one series of studies, Popp had one of his assistants -- a 27-year-old healthy young woman -- sit in the room every day for nine months while he took photon readings of a small area of her hand and forehead. Popp then analysed the data and discovered, to his surprise, that the light emissions followed certain set patterns -- biological rhythms at 7, 14, 32, 80 and 270 days -- and similarities were also noted by day or night, by week and by month, as though the body were following the world's biorhythms as well as its own.
Cancer is a loss of coherent light
So far, Popp had studied only healthy individuals and found an exquisite coherence at the quantum level. But what kind of light is present in those who are ill?
Popp tried out his machine on a series of cancer patients. In every instance, these patients had lost those natural periodic rhythms as well as their coherence. The lines of internal communication were scrambled. They had lost their connection with the world. In effect, their light was going out.
Just the opposite is seen with multiple sclerosis: MS is a state of too much order. Patients with this disease are taking in too much light, thereby inhibiting their cells' ability to do their job. Too much cooperative harmony prevented flexibility and individuality -- like too many soldiers marching in step as they cross a bridge, causing it to collapse. Perfect coherence is an optimal state between chaos and order. With too much cooperation, it is as though individual members of the orchestra are no longer able to improvise. In effect, MS patients are drowning in light.
Popp also examined the effects of stress. In a stressed state, the rate of biophoton emissions goes up -- a defence mechanism designed to restore the patient's equilibrium.
Popp now recognized that what he'd been experimenting with was even more than a cure for cancer or Gestaltbildung. Here was a model which provided a better explanation than the current neo-Darwinist theory for how all living things evolve on the planet. Rather than a system of fortunate but ultimately random error, if DNA uses frequencies of every variety as an information tool, this suggests instead a feedback system of perfect communication through waves that encode and transfer information.
"Good vibes" means coherent light
Popp came to realize that light in the body might even hold the key to health and illness. In one experiment, he compared the light from free-range hens' eggs with that from penned-in, caged hens. The photons in the former were far more coherent than those in the latter.
Popp went on to use biophoton emissions as a tool for measuring the quality of food. The healthiest food had the lowest and most coherent intensity of light. Any disturbance in the system increased the production of photons. Health was a state of perfect subatomic communication, and ill health was a state of communication breakdown. We are ill when our waves are out of synch.
Bio Photon emission detection is currently used commercially in the food industry. Agricultural science is looking at Bio-photon emissions to determine plant health for the purposes of food quality control. Biophotonen is a company working for development and practical applications of biophotonics. The work is based on a variety of patents. "Biophotonen" solves practical problems of food industry, environmental industry, cosmetics, etc.
Off-shoots of Dr. Popp's discovery
In the 1970s Dr. Veljko Veljkovic, who now heads the Center for Multidisciplinary Research and Engineering, Institute of Nuclear Sciences Vinca, also discovered a method for predicting which of the hundreds of new chemicals made by the rapidly expanding chemical industry were carcinogenic, by calculating certain electronic, biophotonic properties of the molecules. This method was soon found equally applicable to predicting organic chemicals that were mutagenic, or toxic, and even those that were antibiotic, or cytostatic (anticancer). Veljkovic's institute in Belgrade has since teamed up with other European laboratories to apply the same method to drug discovery, especially against AIDS disease.
Biophoton Therapy
Biophoton therapy is the application of light to particular areas of the skin for healing purposes. The light, or photons, that are emitted by these units are absorbed by the skin's photoreceptors and then travel through the body's nervous system to the brain, where they help regulate what is referred to as our human bio-energy. By stimulating certain areas of the body with specific quantities of light, biophoton therapy can help reduce pain as well as aid in various healing processes throughout the body.
The theory behind biophoton therapy is based on the work of Dr. Franz Morell and has been expanded by the work of Doctors L.C. Vincent and F.A. Popp, who theorized that light can affect the electromagnetic oscillation, or waves of the body and regulate enzyme activity.
It took some 25 years for Popp to gather converts from among the scientific community. Slowly, a few select scientists around the globe began to consider that the body's communication system might be a complex network of resonance and frequency. Eventually, they would form the International Institute of Biophysics, composed of 15 groups of scientists from international centres around the world.
Popp and his new colleagues went on to study the light emissions from several organisms of the same species, first in an experiment with a type of water flea of the genus Daphnia. What they found was nothing short of astonishing. Tests with a photomultiplier showed that the water fleas were sucking up the light emitted from each other. Popp tried the same experiment on small fish and got the same result. According to his photomultiplier, sunflowers were like biological vacuum cleaners, moving in the direction of the most solar photons to hoover them up. Even bacteria swallowed photons from the media they were put in.
Communication between organisms
Thus, it dawned on Popp that these emissions had a purpose outside of the body. Wave resonance wasn't only being used to communicate inside the body, but between living things as well. Two healthy beings engaged in 'photon sucking', as he called it, by exchanging photons. Popp realised that this exchange might unlock the secret of some of the animal kingdom's most persistent conundrums: how schools of fish or flocks of birds create perfect and instantaneous coordination. Many experiments on the homing ability of animals demonstrate that it has nothing to do with following habitual trails, scents or even the EM fields of the earth, but rather some form of silent communication that acts like an invisible rubber band, even when the animals are separated by miles of distance.
For humans, there was another possibility. If we could take in the photons of other living things, we might also be able to use the information from them to correct our own light if it went awry.
Death Transmission via the Paranormal "Light" Channel
Some extremely interesting experiments were performed by V.P. Kaznacheyev et al regarding the paranormal transmission of death by light inter-organism communication.
Briefly, two groups of cells were selected from the same cell culture and one sample placed on each side of a window joining two environmentally shielded rooms. The cell cultures were in quartz containers. One cell culture was used as the initiation sample and was subjected to a deadly mechanism - virus, germ, chemical poison, irradiation, ultraviolet rays, etc. The second cell culture was observed, to ascertain any transmitted effects from the culture sample being killed.
When the window was made of ordinary glass, the second sample remained alive and healthy. When the window was made of quartz, the second sample sickened and died with the same symptoms as the primary sample.
The experiments were done in darkness, and over 5,000 were reported by Kaznacheyev and his colleagues. The onset of induced complementary sickness and death in the second culture followed a reasonable time -- say two to four hours -- behind sickness and death in the primary culture.
The major transmission difference between window glass and quartz is that quartz transmits both ultraviolet and infrared well, while glass is relatively opaque to ultraviolet and infrared. Both quartz and glass transmit visible light. Thus glass is a suppressor of the paranormal channel, while quartz is not.
In 1950, Western researchers found that cells could be killed in darkness with ultraviolet radiation, kept shielded from visible light for twenty-four hours or longer, and then if radiated with visible light the cells would start reviving by hundreds of thousands even though they had been clinically dead.
Specifically, every cell emits mitogenetic radiation in the ultraviolet range twice: when it is born and when it dies. The UV photon emitted at death contains the exact virtual state pattern of the condition of the cell at death. The healthy cells are bombarded with death messages from those that are dying, and this diffuses the death pattern throughout the healthy culture, eventually kindling into the same death pattern there.
[V.P. Kaznacheyev et al, "Distant Intercellular Interactions in a System of Two Tissue Cultures," Psychoenergetic Systems, Vol. 1, No. 3, March 1976, pp 141-142.]
Popp had begun experimenting with such an idea. If cancer-causing chemicals could alter the body's biophoton emissions, then it might be that other substances could reintroduce better communication. Popp wondered whether certain plant extracts could change the character of the biophoton emissions from cancer cells to make them communicate again with the rest of the body. He began experimenting with a number of non-toxic substances purported to be successful in treating cancer. In all but one instance, these substances only increased the photons from tumour cells, making them even more deadly to the body.
The single success story was mistletoe, which appeared to help the body to 'resocialise' the photon emissions of tumour cells back to normal. In one of numerous cases, Popp came across a woman in her thirties who had breast and vaginal cancer. Popp found a mistletoe remedy that created coherence in her cancer tissue samples. With the agreement of her doctor, the woman stopped any treatment other than the mistletoe extract and, after a year, all her laboratory tests were virtually back to normal.
To Popp, homoeopathy was another example of photon sucking. He had begun to think of it as a 'resonance absorber'. Homoeopathy rests upon the notion that like is treated with like. A plant extract that at full strength can cause hives in the body is used in an extremely diluted form to get rid of it. If a rogue frequency in the body can produce certain symptoms, it follows that a high dilution of a substance which can produce the same symptoms would also carry that frequency. Like a resonating tuning fork, a suitable homoeopathic solution might attract and then absorb the abnormal oscillations, allowing the body to return to normal health.
Popp thought that electro-magnetic molecular signalling might even explain acupuncture. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, the human body has a system of meridians, running deep in the tissues, through which flows an invisible energy the Chinese call ch'i, or the life force. The ch'i supposedly enters the body through these acupuncture points and flows to deeper organ structures (which do not correspond to those in Western biology), providing energy (or the life force). Illness occurs when this energy is blocked at any point along the pathways. According to Popp, the meridian system transmits specific energy waves to specific zones of the body.
Research has shown that many of the acupuncture points have a dramatically reduced electrical resistance compared with the surrounding skin (10 kilo-ohms and 3 mega-ohms, respectively). Orthopaedic surgeon Dr Robert Becker, who has done a great deal of research on EM fields in the body, designed a special electrode recording device that rolls along the body like a pizza cutter. His many studies have shown electrical charges on every one of the people tested corresponding to the Chinese meridian points.
[Extracted from The Field: The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe, by Lynne McTaggart]
Light in human consciousness
I mention this latest work for those who may wish to explore the boundaries of photon research and theory. In a ground-breaking paper with the lengthy title of "Orchestrated Objective Reduction of Quantum Coherence in Brain Microtubules: The 'Orch OR' Model for Consciousness" by Stuart Hameroff and Roger Penrose, the brain is described as a quantum computer whose main architecture are the cytoskeletal microtubules and other structures within each of the brain's neurons.
If you examine a neuron, you will see that there are many hollow tubes surrounding the axon. These microtubules have been thought of as a kind of scaffold to support the nerve fiber. But they are now getting a second look as the possible architecture of our consciousness.
The particular characteristics of microtubules that make them suitable for quantum effects include their crystal-like lattice structure, hollow inner core, organization of cell function and capacity for information processing. According to the researchers, their size appears perfectly designed to transmit photons in the UV range.
[Above:] Schematic of central region of neuron (distal axon and dendrites not shown), showing parallel arrayed microtubules interconnected by MAPs. Microtubules in axons are lengthy and continuous, whereas in dendrites they are interrupted and of mixed polarity. Linking proteins connect microtubules to membrane proteins including receptors on dendritic spines.
"Traditionally viewed as the cell's 'bone-like' scaffolding, microtubules and other cytoskeletal structures now appear to fill communicative and information processing roles. Theoretical models suggest how conformational states of tubulins within microtubule lattices can interact with neighboring tubulins to represent, propagate and process information as in molecular-level 'cellular automata' computing systems." -- Hameroff and Watt, 1982; Rasmussen et al, 1990; Hameroff et al, 1992
In their paper, Hameroff and Penrose present a model linking microtubules to consciousness using quantum theory. In their model, quantum coherence emerges, and is isolated in brain microtubules until a threshold related to quantum gravity is reached. The resultant self-collapse creates an instantaneous "now" event. Sequences of such events create a flow of time, and consciousness.
Don't worry if you can't understand this. It's heavy reading but it does show that the existence of internal photons -- inner light -- is very real and is the basis of virtually all human cellular and systemic function.
Could the Russian scientists really have changed a salamander embryo into a frog with lasers? I prefer to wait until the actual details of the experiment are published and reviewed -- but I am much less apt to dismiss this as fiction now that I know about our inner lights.
http://books.google.com/books?id=VtNaz_vSnIIC&pg=PA54&lpg=PA54&dq=Popp+mistletoe&source=bl&ots=yeswwqdMFm&sig=shfjLuUwPf9A5m3rMLhcQaAHnEI&hl=en&ei=8cXXTq-iCsmKsQKnvYH0DQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=3&sqi=2&ved=0CDYQ6AEwAg#v=onepage&q=Popp%20mistletoe&f=false
http://naturalnews.com
http://www.naturalpedia.com/mistletoe.html
This particular mistletoe may or may not be poisonous, but too little is known about it for any wise person to use it for anything but holding up at Christmas time and kissing beneath. MISTLETOE, VISCUM, EUROPEAN mistletoe (VISCUM ALBUM) This branch of mistletoe definitely contains toxic amines and is considered poisonous. MORNING GLORY (IPOMOEA PURPUREA) The seeds of this particular morning glory do contain amides of lysergic acid, but with a potency much less than that of LSD." - Earl Mindell, Earl Mindell's Vitamin Bible for the 21st Century
"The single success story was mistletoe, which seemed to help the body to 'resocialize' the photon emission of tumor cells back to normal. In one of numerous cases, Popp came across a woman in her thirties with breast and vaginal cancer. Popp tried mistletoe and other plant extracts on samples of her cancerous tissue and found that one particular mistletoe remedy created coherence in the tissue similar to that of the body. With the agreement of her doctor, the woman began forgoing any treatment other than this mistletoe extract." - Lynne Mctaggart, The Field - The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe
"Popp tried mistletoe and other plant extracts on samples of her cancerous tissue and found that one particular mistletoe remedy created coherence in the tissue similar to that of the body. With the agreement of her doctor, the woman began forgoing any treatment other than this mistletoe extract. After a year, all her laboratory tests were virtually back to normal. A woman who was given up as a terminal cancer case had her proper light restored, just by taking a herb.2? To Fritz-Albert Popp, homeopathy was another example of photon sucking. He had begun to think of it as a 'resonance absorber'." --- Lynne Mctaggart, The Field - The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe
"Iscador P contains mistletoe extract from V. pini (mistletoe from pine trees). • Iscador Qu contains mistletoe extract from V. quercus (mistletoe from oak trees). The three types are also available formulated with low concentrations (10~8 g per 100 mg fresh plant extract) of certain metal salts, such as those of copper and mercury. A lectin-standardized extract, also prepared according to the anthroposophic approach, is available, although this formulation does not include metal salts." --- Dr. Michael Heinrich, Joanne Barnes, Simon Gibbons and Elizabeth M. Williamson, Fundamentals of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy
"A recent study shows that mistletoe can induce a condition known as eosinophilic (an increase in the number of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell) in healthy adults. [Journal Society Integrative Oncology 4: 3-7, 2006] mistletoe extract has been shown to reduce adverse effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy on the microcirculation and the immune system of cancer patients. [Anticancer Research 25:601-10, 2005] Iscador is popular in Germany where it was recently shown to improve survival (slightly) among malignant melanoma patients. --- Bill Sardi, You Don't Have to be Afraid of Cancer Anymore
"Disch Med Wochenschr 125: 1222-26, 2000] A study of patients who had undergone bladder cancer surgery did not find that mistletoe extract significantly delayed recurrence of cancer. [Journal Urology 168: 72-75, 2002] In 2002, a German medical journal reported that mistletoe therapy has not gained an established placed in the treatment of cancer and no overall improvement in survival had been reported."
"Alternative Therapy Health Medicine 7: 57-66, 68-72, 2001 ] For comparison, some widely promoted anticancer drugs like Erbitux only extend life by an average of four months and cost $48,000. A survey of German physicians found that the probability to achieve complete or partial remissions with mistletoe extract was estimated to be 6% and 15% respectively. [Disch Med Wochenschr 125: 1222-26, 2000] A study of patients who had undergone bladder cancer surgery did not find that mistletoe extract significantly delayed recurrence of cancer." --- Bill Sardi, You Don't Have to be Afraid of Cancer Anymore
"With the agreement of her doctor, the woman began forgoing any treatment other than this mistletoe extract. After a year, all her laboratory tests were virtually back to normal. A woman who was given up as a terminal cancer case had her proper light restored, just by taking a herb.2? To Fritz-Albert Popp, homeopathy was another example of photon sucking. He had begun to think of it as a 'resonance absorber'. Homeopathy rests upon the notion that like is treated with like. A plant extract that at full strength can cause hives in the body is used in an extremely dilute form to cure them." --- Lynne Mctaggart, The Field - The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe
"The host trees are usually at least twenty years old before mistletoe encroaches, and they are not usually killed by the mistletoe. The plant forms pendant bushes where it grows. Its leaves are thick, oval to round, and 1 to 2 inches long. Its small, inconspicuous, sticky, white flowers are about V4 inch long. It is dioecious, meaning that male and female flowers are borne on different plants." --- Brigitte Mars, A.H.G., The Desktop Guide to Herbal Medicine: The Ultimate Multidisciplinary Reference to the Amazing Realm of Healing Plants, in a Quick-study, One-stop Guide
"Indeed, Frazer concludes that the Golden Bough itself was probably a sprig of berries still used ceremonially today: mistletoe..." - Adam Leith Gollne, The Fruit Hunters: A Story of Nature, Adventure, Commerce and Obsession
"Lectin-standardized mistletoe extracts, which are distinct from anthroposophical mistletoe preparations, are also available, particularly in Germany. mistletoe products prepared from different host trees are prescribed for patients with different types of cancer. Treatment is usually given by subcutaneous injection, although the intravenous injection route is sometimes used, and oral formulations are also available. In the preparation of anthroposophical medicines, particular attention is paid to the source and methods of farming used in growing plant raw materials." --- Dr. Michael Heinrich, Joanne Barnes, Simon Gibbons and Elizabeth M. Williamson, Fundamentals of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy
"In folk medicine, mistletoe is also used for attacks of dizziness, amenorrhea, and joint diseases. Side effects: Refer to the German Commission E monograph excerpt; with long-term administration, allergic reactions may occur. Making the tea: Pour cold water over 2.5 g finely cut dried herb. Allow to stand at room temperature for 10— 12 hours and then strain. Drink 1— 2 cups daily (see also: Indications). 1 teaspoon = about 2.5 g. Tea preparations: mistletoe herb is offered as a single herb tea in loose pack and in filter tea bags and is a component of cardiac/circulation herbal tea formulas." --- Josef A. Brinckmann and Michael P. Lindenmaier, Herbal Drugs and Phytopharmaceuticals: A Handbook for Practice on a Scientific Basis
"MISTLETOE • Viscum album (European mistletoe); Phoradendron flavescens (American mistletoe). A parasitical plant with a root firmly attached to the wood of the tree on which it grows, it was sacred to the Druids and reputedly used by them to cure sterility and epilepsy; and as an antidote for poisons. Hippocrates and Galen used it as an external remedy and internally to treat sleep disorders. It is also used in "organic" cosmetics. See also Juniper Berry. MITRACARPUS SCABER • A South American vine. MIXED CRESOLS • A preservative. See Cresols. MIXED IONONES • Fragrance ingredients." --- Ruth Winter, M.S., A Consumer's Dictionary of Cosmetic Ingredients
"Medicinal species containing lectins include Phytolacca decandra, Viscum album, Urtica dioica and Juglans nigra (Lewis and Elvin-Lewis 1977). mistletoe (Viscum album) contains lectins, viscotoxins (low-molecular-weight polypeptides), amines, polysaccharides, alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpenes, sterols, fatty acids and phenyl-propanoids. mistletoe lectins have been found to bind to erythrocytes, lymphocytes, leucocytes, macrophages, glycoproteins and plasma proteins." --- Andrew Pengelly, The Constituents of Medicinal Plants: An Introduction to the Chemistry and Therapeutics of Herbal Medicine
"Rudolph Steiner, PhD popularized the use of mistletoe in the early 20th century. A certain lectin in mistletoe has been found to inhibit the growth of proliferating cells. By the 1980s, about 40,000 patients worldwide were receiving Iscador, a fermented form of mistletoe that is injected. Iscador and its variations are licensed in Germany as drugs. -Stanislaw R. Burzynski, MD, PhD theorized that certain anti-neoplastons, or naturally occurring peptides, could inhibit the growth of tumor cells without interrupting normal cell growth." --- Patrick Quillin, PhD,RD,CNS, Beating Cancer with Nutrition
"Mistletoe In a Phase I/II study, the effect of mistletoe (Eurixor) treatment was evaluated in 16 patients with pancreatic cancer. mistletoe was administered twice a week by subcutaneous injection. Apart from one anaphylactic reaction, which necessitated suspension of treatment for a few days, no severe side effects were observed. Eight patients (50%) showed a CT-verified status of "no change" (according to the World Health Organization criteria) for at least 8 weeks. Median survival time in all patients was 5.6 months (range = 1.5-26.5 months). --- The Life Extension Editorial Staff, Disease Prevention and Treatment
"All except two patients claimed that mistletoe had a positive effect on their quality of life, with an obvious decline only during the last weeks of life. These results indicate that mistletoe can stabilize quality of life and therefore may help patients to maintain adequate life quality in their few remaining months (Friess et al. 1996). Another, more recent paper described a patient with inoperable cancer of the pancreas who developed marked eosinophilia during treatment (on day 22) with injections of Viscum album (mistletoe)." --- The Life Extension Editorial Staff, Disease Prevention and Treatment
"Mistletoe In a Phase I/II study, the effect of mistletoe (Eurixor) treatment was evaluated in 16 patients with pancreatic cancer. mistletoe was administered twice a week by subcutaneous injection. Apart from one anaphylactic reaction, which necessitated suspension of treatment for a few days, no severe side effects were observed. Eight patients (50%) showed a CT-verified status of "no change" (according to the World Health Organization criteria) for at least 8 weeks. Median survival time in all patients was 5.6 months (range = 1.5-26.5 months)." --- The Life Extension Editorial Staff, Disease Prevention and Treatment
"Scientists found that cultures of human cells produced more antitumor hormones when they were treated with a mistletoe protein. Since then, some clinics have adopted Iscador for treatment of cancer. A few warnings are in order for the herbal enthusiast eager to experiment. Steiner's extract is made from European mistletoe plants. mistletoe berries are poisonous, so never eat them. The stems and leaves must be processed before they are used as medicine, and the finished product raises one's blood pressure and pulse. Those with heart problems should not use it." --- William L. Fischer, How to Fight Cancer & Win
"The mistletoe most widely sold in America is Phoradendron flavescens, but it is the true mistletoe of Europe that holds the best medicinal properties and should be used. Dead Men DO Tell Tales "What I'm about to share with you is worthy of an investigation by the great Sherlock Holmes himself. mistletoe has been used since the time of Christ for alleviating the symptoms of hypertension. But the evidence doesn't come from ancient Celtic inscriptions painted on a broken pottery shard or stiff piece of leather; instead it comes from the stomach of a very waterlogged and mummified ancient Briton." --- John Heinerman, Heinerman's Encyclopedia of Healing Herbs and Spices
"History & Folklore In Norse mythology, a mistletoe bough was used to slay Balder, the god of peace. The plant was subsequently entrusted to the goddess of love, and kissing under it became obligatory. Medicinal Actions & Uses European mistletoe is chiefly used to lower blood pressure and heart rate, ease anxiety, and promote sleep. In low doses it also relieves panic attacks, headaches, and improves concentration. European mistletoe is also prescribed for tinnitus and epilepsy. In anthroposophical medicine, extracts of the berries are injected to treat cancer." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"Mistletoe [Viscum album) Popular throughout Europe, mistletoe is one of the most widely used plants for hypertension and in the treatment of cancer. It is the main therapy used to treat cancer by anthroposophical physicians. Iscador, a fermented extract of Viscum album, reduces the leukocytopenia produced by radiation and chemotherapy. mistletoe is tumor-inhibiting and cytotoxic to a number of different tumor types. It also increases natural killer-cells. Viscum's cytotoxic components include viscumin and viscotoxins. Viscumin is a lectin component that causes agglutination of tumor cells." --- Donald R. Yance, j r.,C.N., M.H., A.H.G., with Arlene Valentine, Herbal Medicine, Healing and Cancer: A Comprehensive Program for Prevention and Treatment
"European herbalists have a couple of different ways of using mistletoe as a heart sedative and antihypertensive. One way is to take equal parts (about two tablespoons each) of mistletoe and hawthorn berries and lemon balm leaves and steep them in two pints of boiling water for 25 minutes. One-half cup of the warm tea is taken morning and evening. The other way is to soak 4 teaspoons of chopped mistletoe in 1-1/4 pints of cold water overnight, and take one cup of the cool beverage first thing the next morning." --- John Heinerman, Heinerman's Encyclopedia of Healing Herbs and Spices
"Recent studies on the anticancer activities of mistletoe (Viscum album) and its alkaloids. Oncology; 43(suppl l):42-50. 1986 Konopa J, Woynarowski JM, Lewandowska-Gumieniak M. Isolation of viscotoxins. Cytotoxic basic polypeptides from Viscum album L. Hoppe-Seylers Z Physiol Chem; 361(10): 1525-1533. 1980 Kovacs E, Hajto T & Hostanska K. Improvement of DNA repair in lymphocytes of breast cancer patients treated with Viscum album extract (Iscador): Eur J Cancer; 27(1):1672-1676. 1991 Metzner G, Franz H, Kindt A, et al." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"Effects of a standardized mistletoe preparation on metastatic B16 melanoma colonization in murine lungs. Drug Res; 48:497-502. 1998 Woynarowski J & Konopa J. Interaction between DNA and viscotoxins. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem; 361(10): 1535-1545. 1980 Zarkovic N, Kalisnik T, Loncaric I et al: Comparison of the effects of Viscum album lectin ML-1 and fresh plant extract (Isorel) on cell growth in vitro and tumorigenicity of melanoma B16F10. Cancer Biother Radiopharmacol; 13:121 -131." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"Action of viscumin, a toxic lectin from mistletoe, on cells in culture. J Biol Chem. Nov 25;257(22): 13271-7. 1982 Timoshenko AV et al. Influence of the galactoside-specific lectin from Viscum album and its subunits on cell aggregation and selected intracellular parameters of rat thymocytes. In: PM; 61(2):130-133. 1995 Timoshenko AV & Gabius HJ. Efficient induction of superoxide release from human neutrophils by the galactoside-specific lectin from Viscum album. Biol Chem; 374:237-243. 1993 Wagner H. Die Mistel in der Tumortherapie. In: DAZ; 132(20):1087/1088." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"It served as a urinary aid and was used in the treatment of epilepsy, in combination with mistletoe and peony. At the end of the 19th century, the drug was applied as an ointment for rheumatism. The infusion is used as a remedy for worm infestation, to treat stomach disorders and cramps and to promote menstruation. In Greece, it is used as a tonic and stimulant. precautions and adverse reactions BURNING BUSH ROOT AND HERB Health risks or side effects following the proper administration of designated therapeutic dosages are not recorded." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"MISTLETOE • Viscum album (European mistletoe); Phoradendron flavescens (American mistletoe). A parasitical plant with a root firmly attached to the wood of the tree on which it grows, it was sacred to the Druids and reputedly used by them to cure sterility and epilepsy; and as an antidote for poisons. Hippocrates and Galen used it as an external remedy and internally to treat sleep disorders. It is also used in "organic" cosmetics. See also Juniper Berry.
"Tieghem (Loranthaceae)—mistletoe This Australian plant, which is similar to the true mistletoe (Viscum album L.; Loranthaceae), is a parasite on several plants, including Duboisia myoporoides (see Duboisia spp.). The leaves contain scopolamine and are smoked in Australia as an inebriant (Bock 1994, 85*). It is possible that the scopolamine is extracted from the host tree Duboisia myoporoides as a result of the mistletoe's parasitic activity and is then incorporated into the plant's own tissue. Bernoullia flammea Oliver in Hook." --- Christian Ratsch, The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications
"In vitro effects of mistletoe extracts and mistletoe lectins. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1993; 43:1221-27. 95. Bussing A Suzart K et al. Induction of apoptosis in human lymphocytes treated with Viscum album L. is mediated by the mistletoe lectins. Cancer Letters 1996; 99:59-72. 96. Mochizuki, et al. Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside-Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3, of red ginseng. Biological if Pharmaceutical Bulletin 1995 Sept; 18(9)4197-202. 97. Block G, Patterson B, Subar A." --- David Hoffman, FNIMH, AHG, Medical Herbalism: The Science Principles and Practices Of Herbal Medicine
"Mistletoe (Viscum album) contains lectins, viscotoxins (low-molecular-weight polypeptides), amines, polysaccharides, alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpenes, sterols, fatty acids and phenyl-propanoids. mistletoe lectins have been found to bind to erythrocytes, lymphocytes, leucocytes, macrophages, glycoproteins and plasma proteins. Cytotoxic activity has been demonstrated for the glycoprotein fraction, alkaloid fraction and Iscador™ (plant juice preparation)—positive in vitro and in vivo. Human studies with Iscador™ have shown slight improvement over controls, with best results for colon cancer." --- Andrew Pengelly, The Constituents of Medicinal Plants: An Introduction to the Chemistry and Therapeutics of Herbal Medicine
"Injectable mistletoe should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Turmeric (page 753) may be another useful herb with immune effects in people infected with HIV. One preliminary trial found that curcumin, the main active compound in turmeric, helped improve CD4+ cell counts.92 The amount used in this study was 1 gram three times per day by mouth. These results differed from those found in a second preliminary trial using 4.8 or 2.7 grams of curcumin daily. In that study, there was no apparent effect of curcumin on HIV replication rates." --- Alan R. Gaby, M.D., Jonathan V. Wright, M.D., Forrest Batz, Pharm.D. Rick Chester, RPh., N.D., DipLAc. George Constantine, R.Ph., Ph.D. Linnea D. Thompson, Pharm.D., N.D., The Natural Pharmacy: Complete A-Z Reference to Natural Treatments for Common Health Conditions
"European mistletoe was the "golden" bough that saved the legendary Aeneas from the underworld. Habitat & Cultivation Native to Europe and northern Asia, European mistletoe grows on host trees, especially apple trees. It is harvested in autumn. parts Used Leaves, branches, berries. Constituents European mistletoe contains glycoproteins, polypeptides (viscotoxins), flavonoids, caffeic and other acids, lignans, acetylcholine, and, in the berries, polysaccharides. Viscotoxins inhibit tumors and stimulate immune resistance." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"European mistletoe was the "golden" bough that saved the legendary Aeneas from the underworld. Habitat & Cultivation Native to Europe and northern Asia, European mistletoe grows on host trees, especially apple trees. It is harvested in autumn. parts Used Leaves, branches, berries. Constituents European mistletoe contains glycoproteins, polypeptides (viscotoxins), flavonoids, caffeic and other acids, lignans, acetylcholine, and, in the berries, polysaccharides. Viscotoxins inhibit tumors and stimulate immune resistance." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"Kleijnen J, Knopschild P, (1994) mistletoe treatment for cancer. Review of controlled trials in humans. Phytomedicine 1:255-260. Kwaja TA et al, (1980) Experientia 36:599. Loew, B, In: Loew D, Rietbrock N: Phytopharmaka II: Forschung und klinische Anwendung, Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt, 1996. Luther P et al., (1980) Int J Biochem 11:429. Miiller J, (1962) Ger Offen DE 1:130:112. Olsnes S et al„ (1982) J Biol Chem 257:1371. Rentea R et al., (1981) Lab Invest. 44(1):43." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"The stem of mistletoe is used for its calming effect; in the treatment of mental and physical exhaustion; as a tranquilizer against nervous conditions such as agitation, anxiety and increased excitability. visci albi herba ¦ Rheumatism ¦ Tumor therapy adjuvant For treating degenerative inflammation of the joints by stimulating cuti-visceral reflexes following local inflammation brought about by intradermal injections. Also used as a palliative therapy for malignant tumors through non-specific stimulation." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"Schwarz T et al, Stimulation by a stable, standardised mistletoe preparation of cytokine production in an in vitro human skin bioassay. In: PM 62, Abstracts of the 44th Ann Congress of GA, 1996. Stirpe F et al, (1982) J Biol Chem 257(22): 13271. Timoshenko AV et al, Influence of the galactoside-specific lectin from Viscum album and its subunits on cell aggregation and selected intracellular parameters of rat thymocytes. In: PM 61(2):130-133. 1995. Uhlenbrock S, Weihnachten, Miraculix und die Anthroposophie. In: PZ 140(51/52):4602-4603. 1995. Wagner H et al, (1986) Planta Med (2): 102." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"I was impressed to leam that the Maoris were aware of the mistletoe's medical properties. mistletoe ?Viscum album ?was widely used by the Maoris for the prevention of illness and disease and nowadays it once again holds an important place in herbal medicine. Since the rediscovery of this plant it has been used as an excellent remedy for balancing blood pressure, to treat migraines and epilepsy, and is also used by cancer patients." --- Jan De Vries, Life Without Arthritis: The Maori Way
"Three subspecies of parasitic mistletoe ?one parasitic on broad-leaved trees and two on coniferous trees ?are native to Europe. Common mistletoe is the one that interests us most. The leafy tips of young twigs without the thick basal stems and without the berries are the parts used medicinally. These are collected only in the wild and therefore include, albeit in small quantities, also mistletoe subspecies parasitic on coniferous trees ?subsp. abietis and subsp. austriacum." --- Frantisek Stary, The Natural Guide to Medicinal Plants and Herbs
"Local reactions can occur with parenteral administration of mistletoe extracts (wheal formation, possibly also necroses), chills, fever, headache, anginal complaints, orthostatic circulatory disorders and allergic reactions. The wheal formation and the elevation of body temperature are considered signs of immune system stimulation and therefore as positive therapeutic effects. DOSAGE visci albi herba Mode of Administration: Fresh plant, cut and powdered herb for the preparation of solutions for injections. Preparation: A medicinal tea is prepared using 2." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"Mistletoe. mistletoe is a cardiac tonic that stimulates circulation. Fifteen drops taken three times a day, or three cups of tea daily, help lower blood pressure and alleviate heart strain. mistletoe should not be overused, nor should the berries be eaten. Motherwort. Helps stabilize the electrical rhythm of the heart. The amount taken should be monitored by a doctor. Wild yam. Stimulates production of DHEA. Low levels of this hormone have been related to higher incidences of heart disease. Wild yam can provide added protection and is completely safe." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"Reinsubstanz Gegen Standardisierten Extrakt" [Comparative Studies on the Immunoactive Action of Galactoside-Specific mistletoe Lectin: Pure Substance Compared to the Standardized Extract], Arzneimittelforschung 43, no. 2 (February 1993): 166-69. Iscador, a mistletoe (Viscum album) extract, was shown to have an anti-breast-cancer effect. T. Hajto, "Immunomodulatory Effects of Iscador: A Viscum Album Preparation," Oncology, 43, suppl. (1986): 51-65. Breast cancer patients in a study were administered a single infusion of iscador, an extract of mistletoe (Viscum album) intravenously." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"Loranthaceae) A relative of mistletoe (Viscum album L.), Phrygilanthus eugenioides is used in the voodoo cult as a magical plant. It is said to have psychoactive or hallucinogenic powers (Schultes and Farnsworth 1982, 187*; Schultes and Hofmann 1980, 367*). Curiously, the ancient texts suggest that mistletoe may also produce psychoactive effects (cf. Benthamia alyxifolia). Podophyllum peltatum L." --- Christian Ratsch, The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications
"MISTLETOE Of two notable studies of mistletoe, the plant hung up at Christmas, one indicated that iscador, an extract from European mistletoe, when combined with lactobacillus, doubles the ability of natural killer cells to destroy malignant cells; while a second examination, reported at a 1992 AIDS conference, indicated one extract from the herb "had anti-HIV, immunomodulating and anti-cancer activities in 12 symptomatic HIV disease patients followed for 6 years." --- Gary Null, James Feast, AIDS: A Second Opinion
"Rudolph Steiner, PhD popularized the use of mistletoe in the early 20th century. A certain lectin in mistletoe has been found to inhibit the growth of proliferating cells. By the 1980s, about 40,000 patients worldwide were receiving Iscador, a fermented form of mistietoe that is injected. Iscador and its variations are licensed in Germany as dmgs. -Stanislaw R. Burzynski, MD, PhD theorized that certain anti-neoplastons, or naturally occurring peptides, could inhibit the growth of tumor cells without intermpting normal cell growth." --- Patrick Quillin, Beating Cancer with Nutrition
"PHARMACOLOGY: Despite the popular knowledge that the two types of mistletoe have opposite pharmacologic effects (ie, American mistletoe: Stimulates smooth muscle, raises blood pressure, increases uterine and intestinal motility; European mistletoe: Reduces blood pressure, antispasmodic, calming agent), investigations have shown that the stems and leaves of these plants contain the proteinaceous phoratoxins and viscotoxins and thus exert similar pharmacologic effects." --- Ara Dermarderosian, Guide to Popular Natural Products
"BOTANY: American mistletoe comprises the Phoradendron species and European misdetoes V. album, V. abi-etis and V. austriacum. Mistletoes are semiparasitic woody perennials commonly found on oaks and other deciduous trees. These evergreen plants produce small white berries and are used as Christmas ornaments. These plants should not be confused with the New Zealand mistletoe (Ileostylus micran-thus), which contains cytotoxic compounds that may be derived from the host tree {Podocarpus totara)." --- Ara Dermarderosian, Guide to Popular Natural Products
"PHARMACOLOGY: Despite the popular knowledge that the two types of mistletoe have opposite pharmacologic effects (ie, American mistletoe: Stimulates smooth muscle, raises blood pressure, increases uterine and intestinal motility; European mistletoe: Reduces blood pressure, antispasmodic, calming agent), investigations have shown that the stems and leaves of these plants contain the proteinaceous phoratoxins and viscotoxins and thus exert similar pharmacologic effects." --- Ara Dermarderosian, Guide to Popular Natural Products
"Mistletoe. mistletoe is a cardiac tonic that stimulates circulation. Fifteen drops taken three times a day, or three cups of tea daily, help lower blood pressure and alleviate heart strain. mistletoe should not be overused, nor should the berries be eaten. Motherwort. Helps stabilize the electrical rhythm of the heart. The amount taken should be monitored by a doctor. Wild yam. Stimulates production of DHEA. Low levels of this hormone have been related to higher incidences of heart disease. Wild yam can provide added protection and is completely safe." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"A study examining the effects of a mistletoe extract on breast cancer patients found an immune-enhancing effect. J. Beuth et al., "Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Immu-naktiven Wirkung von Galaktosid-Spezifischem Mistellektin. Reinsubstanz Gegen Standardisierten Extrakt" [Comparative Studies on the Immunoactive Action of Galactoside-Specific mistletoe Lectin: Pure Substance Compared to the Standardized Extract], Arzneimittelforschung 43, no. 2 (February 1993): 166-69. Iscador, a mistletoe (Viscum album) extract, was shown to have an anti-breast-cancer effect. T." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"Journal Society Integrative Oncology 4: 3-7, 2006] mistletoe extract has been shown to reduce adverse effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy on the microcirculation and the immune system of cancer patients. [Anticancer Research 25:601-10, 2005] Iscador is popular in Germany where it was recently shown to improve survival (slightly) among malignant melanoma patients. [Arzneimiftelforschung 55:38-49, 2005] Iscador has also been shown to prolong survival among breast cancer patients." --- Bill Sardi, You Don't Have to be Afraid of Cancer Anymore
"Iscador (Mistletoe) Iscador is the trade name for a mistletoe preparation that has been used by European physicians since 1920. Iscador consists of fermented extracts of European mistletoe (Viscum album), some forms of which are combined with small amounts of metals to produce anticancer effects.227 Originally conceived by Rudolf Steiner (1864-1925), Austrian scientist and founder of anthroposophic medicine, the therapeutic success of Iscador has been reported in nearly 5,000 case studies." --- Larry Trivieri, Jr., Alternative Medicine the Definitive Guide, Second Edition
"History & Folklore In Norse mythology, a mistletoe bough was used to slay Balder, the god of peace. The plant was subsequently entrusted to the goddess of love, and kissing under it became obligatory. Medicinal Actions & Uses European mistletoe is chiefly used to lower blood pressure and heart rate, ease anxiety, and promote sleep. In low doses it also relieves panic attacks, headaches, and improves concentration. European mistletoe is also prescribed for tinnitus and epilepsy. In anthroposophical medicine, extracts of the berries are injected to treat cancer." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"In this review article, the author notes that studies from their lab have demonstrated that mistletoe extact exhibits significant anticancer activity against a variety of experimental tumor systems, in vitro and in vivo, particularly those modeling for lung, breast and colon carcinomas. —T.A. Khwaga, "Biopharmacological Studies of Different Components of Viscum Album (Mistletoe)," Anticancer Research, 10(5B), 1990, p. 1374-1375. This study examined the antiproliferative effects of Viscum album C, Viscum album Qu and Viscum album M on melanoma cell lines." --- Gary Null, Ph.D., The Clinician's Handbook of Natural Healing
"This study examined the cellular aspects of the immunomodulating activity of propriety mistletoe extract (Eurixor) standardized for mistletoe lectin-1 (ML-1) in 20 mammary cancer patients. Results showed that subcutaneous injections of the different dosages (0.5 and 1.0 ng ML-1/kg body weight, twice a week, for 5 weeks) led to statistically significant increases of defined peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets (helper T cells, natural killer cells) which are gerneally beleived to be involved in antitumor activity." --- Gary Null, Ph.D., The Clinician's Handbook of Natural Healing
"This study isolated a tumor reducing component from mistletoe extract (Iscador) and identified to be a peptide of approximate molecular weight 5000. The isolated peptide reduced the solid tumour induced by Dalton's lymphoma ascites tumour cells in mice and was highly cytotoxic to the DLA cells but was not cytotoxic to normal lymphocytes, indicating a cell dependent specificity. —G. Kuttan, et al., "Isolation and Identification of a Tumour Reducing Component from mistletoe Extract (Iscador)," Cancer Letters, 41(3), August 30, 1988, p. 307-314." --- Gary Null, Ph.D., The Clinician's Handbook of Natural Healing
"Petricic J and Kalogjera Z: Isolation of glucosides from mistletoe leaves (Viscum album L.). Acta Pharm Jugosl 30,163,1980. 10. Wagner H, et al.: Phenylpropanes and lignanes of Viscum album. Planta Medica 2,102, 1986. 11. Petkov V: Plants with hypotensive, antiatheromatous and coronary dilatating action. Am J Chin Med 7,197-236,1979. 12. Hajto T: Immunomodulating effects of Iscador: A Viscum album preparation. Oncology 43(Suppl. 1), 51-65,1986. 13. Jordan E and Wagner H: Detection and quantitative determination of lectins and viscotoxins in mistletoe preparations." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"Since pharmacologically active compounds appear to be concentrated within the mistletoe, different host trees providing different chemical constituents could be used for different therapeutic action. In addition, the proteins/lectins are present only in aqueous (water) extracts, indicating therapeutic activity may differ from aqueous and alcoholic/aqueous (tincture) extracts. The alcoholic/aqueous extracts would also demonstrate considerably less toxicity. History and folk use Mistletoe was held in great reverence by the druids. Dressed in white robes, they would search for the sacred plant." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"The historic use of mistletoe for cancer is now being tested by research. It is interesting to note that mistletoe grows on trees similar to a cancerous growth in the body. Contraindications: It is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the emmenagogue and abortifacient effects in animals which are associated with tyramine. It is also contraindicated in protein hypersensitivity and chronic, progressive infections like tuberculosis and AIDS. This is a potentially dangerous herb and should only be used by skilled practitioners." --- Sharol Tilgner, N.D., Herbal Medicine From the Heart of the Earth
"The blood pressure-lowering activity may depend on the form in which the mistletoe is administered and the host tree from which it was collected. Studies indicate aqueous extracts are more effective and the highest hypotensive activity was demonstrated by a macerate of leaves of mistletoe growing on willow, gathered in January.11 If nonprotein viscum components (e.g., flavonoids, phenol carboxylic acids, phenylpropanes, and lignans) were shown to possess blood pressure-lowering action, then alcoholic solutions (tinctures and fluid extracts) may be useful solutions." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"Even the mistletoe growing on the mulberry tree has positive therapeutic properties not unlike European mistletoe (Viscum album). Both are used for hypertension and are classified as being antispasmodic and antirheumatic. Both have analgesic and anticarcinogenic properties. They are used for hypertension and to relieve rheumatic pains and spasms especially of the upper part of the body. Dose, 9-15 grams." --- Michael Tierra, The Way of Herbs
"In one study of women with breast cancer who were undergoing chemotherapy, half the patients were given a preparation of mistletoe, while half were given a placebo. After the fourth round of chemo, those getting mistletoe had three times as many white blood cells as the control group (3,000 count vs. 1,000 count). The Journal of the National Cancer Institute reported that polyphenals from green tea induced cell death in carcinoma cells in vitro. An extract of green algae showed a "pronounced antitumor effect" in mice." --- The Disinformation Company, Everything You Know Is Wrong: The Disinformation Guide to Secrets and Lies
"Skeptics make fun of the manner in which mistletoe is gathered. A quack-baiting Website sneers at claims that "the time of picking the plants [is] important because they react to the influences of the sun, moon, and planets." However, there is a core of rationality to many traditional practices. Certain chemicals in mistletoe can combine with metals to form organometaflic compounds, which have different biological or medicinal properties than the ones naturally found in the plant." --- Ralph W. Moss PhD, Herbs Against Cancer: History and Controversy
"Those with late-stage cancers say mistletoe makes a dramatic improvement in general health. See Materia Medica for dose. (Mistletoe resources, page 167.) • Vaccine-like preparations of killed bacteria stimulate dramatic activity in the immune system, including an increase in tumor necrosis factor which causes tumors to hemorrhage and liquefy. These preparations are currendy being tested on women with breast (and ovarian) cancers. • Chemotherapy is being urged on more and more women in earlier and earlier stages of breast cancer." --- Susun S. Weed, Breast Cancer? Breast Health! The Wise Woman Way
"Results & Notes: mistletoe has been used clinically in Europe for the treatment of breast (and other) cancers since 1926. It is most effective when injected under the skin near the tumor, but the tincture is also used orally as a systemic treatment. mistletoe is said to work by causing an inflammatory reaction which walls off the tumor, checking its growth and spread. References: 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, 18, 21, 23. Illustrated on page 158." --- Susun S. Weed, Breast Cancer? Breast Health! The Wise Woman Way
"Other Names: European mistletoe (Do not use American mistletoe) Type: Stimulating/Sedating Found in: Semiparasitic on deciduous trees in Europe, northern Asia. Part Used: Leaves and young twigs collected just before berries form; best after fermentation in water. Actions & Uses: Inhibits tumors; cytotoxic; cytostatic; enhances immune system (increases macrophages, natural killer cells, and T-cells); increases weight of thymus; tonifies heart and nerves. Important Constituents: Flavonoids, lectins, polypeptides, polysaccharides, saponins, tannins, tri-terpenes, viscotoxin." --- Susun S. Weed, Breast Cancer? Breast Health! The Wise Woman Way
"Heiny BM: Adjuvant treatment with standardized mistletoe extract reduces leukopenia and improves the quality of life of patients with advanced carcinoma of the breast getting palliative chemotherapy (VEC regimen). Krebsmedizin 12, 3-14,1991. 29. British Herbal Medicine Association, Scientific Committee: British Herbal Pharmacopoeia. British Herbal Medicine Association, Cowling, England, 1983, pp. 235-236. 30. Khwaja TA, et al.: Isolation of biologically active alkaloids from Korean mistletoe Viscum album, coloratum. Experientia 36, 599-600,1980. 31." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"Pharmacological activity of phenyl-propanoids of the mistletoe, Viscum album L. Host Pyrus caucasica Fed.', Phytomedicine 5: 11-17. Panossian, A., Wikman, G. and Wagner, H. 1999, 'Plant adaptogens III. Earlier and more recent aspects and concepts on their mode of action', Phytomedicine 6: 287-300. Pieretti, S., Di Giannuario, A., Capasso, A. and Nicoletti, M. 1992, 'Pharmacological effects of phenylpropanoid glycosides from Orobanche bederae', Phytotherapy Research 6: 83-93. Pintao, A., Pais, M., Coley, H. and Judson, I." --- Andrew Pengelly, The Constituents of Medicinal Plants: An Introduction to the Chemistry and Therapeutics of Herbal Medicine
"A Swiss study of fourteen breast cancer patients showed that a standardized extract of mistletoe, iscador, increased the rate at which breast cells were able to repair their DNA. Repairing DNA prevents mutations that can result in the formation of cancerous cells. At the beginning of the study, the rate at which cancer patients' cells repaired DNA damage was only 16 percent of that in healthy individuals. After just nine days of treatment, the rate increased to nearly 50 percent. In animal studies, mistletoe extracts prevent the spread of melanoma to lung tissue by approximately 80 percent." --- Phyllis A. Balch, CNC, Prescription for Herbal Healing: An Easy-to-Use A-Z Reference to Hundreds of Common Disorders and Their Herbal Remedies
"Tumors that are ordinarily immune to natural killer (NK) cells are conditioned by treatment with mistletoe to allow NK cells to "lock onto" and destroy cancer cells. mistletoe extracts increase the activity of NK cells by as much as five- to tenfold. The extracts also stimulate movement of immune cells called T cells that "patrol" the body seeking cancer and infection. In addition, these extracts also increase the production of beneficial free radicals that fight a wide range of cancers." --- Phyllis A. Balch, CNC, Prescription for Herbal Healing: An Easy-to-Use A-Z Reference to Hundreds of Common Disorders and Their Herbal Remedies
DE19538768 -- Detection of microbial
contamination, e.g. in food, drink and water
Into a 10 ml quartz
cuvette, two needle-shaped circuit boards are inserted in
parallel at a distance of 5 mm and connected to a DC voltage
source. To the cuvette are added successively 8 ml of pure
saline solution (3 mM / l of saline), the same solution with
an additional concentration of 10 Rhizobium japonicum 1132-2
bacteria / ml and the same solution with a concentration of
100 Rhizobium japonicum 1132- 2 bacteria / ml.
In any case, a DC voltage of 80 volts is applied for a period of 5 seconds. At the same time, the intensities of photon emission (in number of photons / 100 ms) are measured over the period of 5 s. The measurement is repeated three times. The mean values and scatterings of the three measurements are formed. Table I contains the results. Table I
The result shows that this method can significantly detect 10 bacteria / ml.
ZA9208094 -- Method and means of determining the health conditions of a living creature.
The invention relates to a method and device for determining the state of health of a living being. The invention provides for a selected, physiological parameter of the living being, e.g. the conductivity of the skin, to be recorded on a statistically significant multiplicity of measuring points distributed over a defined part of the body of the living being, for the frequency distribution of the recorded measurements to be determined and compared with a reference frequency distribution of the selected, physiological parameter. The reference frequency distribution is a logarithmic distribution which can be determined directly from the measurements obtained from the particular test subject by statistical methods. The invention permits reliable statements to be made regarding the overall state of health of the test subject.
US7692788 -- Method for quickly determining qualities/qualitative changes in any system
The invention relates to a method for testing the slightest quality differences or quality features of any objects and agents interacting therewith based on measuring the percentage scatter of "ultraweak" photon emissions ("biophotons" in biological systems) and the delayed luminescence in a scatter chamber (darkroom). These scatter percentages can vary to such an extent as to enable the sufficiently sensitive registration of slightest quality differences (quality features).
US4458531 -- Method of and apparatus for examining biological effects in cell-lots
In a method of testing the biological effects of cell-lots, which release a characteristic or stimulatable ultra-weak photon radiation, the intensity and/or the photon statistic of the ultra-weak photon radiation is measured, as the test factor, for the purpose of the in vitro examination of substances for possible cell-damaging or regenerating effects, or for the purpose of carrying out quality control on biological substances, such as foodstuffs, edible plants or seed materials.
EP0430150 -- Method for testing quality and quality changes of biological systems and organochemical compositions interacting with these systems using measurements of ultraweak photon emission.
Known status parameters for the quality of biological systems, foodstuffs and organic chemical compounds interacting with the latter are with the methods of comparative statistical analysis with measured parameters of ultraweak photon emission. This makes it possible to reflect reproducibly the quality content and the vitality of a biological system in the sense of Erwin Schrödinger's quality term by means of measured parameters, to measure the quality of foodstuffs and to determine in advance expected changes in quality on storage, and to predict the biocompatibility of organic chemical compounds. Foodstuffs irradiated for preservation purposes can still be distinguished significantly from non-irradiated even one year after the irradiation by the intensity of the photon emission. Environmental effects on live systems can be characterised almost directly as environmental stress or damage by observing the ultraweak photon emission over a short time.
EP1776042 -- DEVICE FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FUNCTIONAL VALUES
The invention relates to a device for the determination of functional values of biological systems, whereby in particular, the conductivity of the skin is recorded as a functional value. The measured values for the conductivity are determined using an electrode matrix (1) in a measuring device (11), whereby a current circuit to a reference electrode (13) is formed and the measured values are subsequently stored and analysed.
EP1340066 -- METHOD FOR DETECTING BACTERIAL INFECTION
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacterial infection or contamination of or in products in order to be able to rapidly determine the product's quality or sterility. To this end, the intensity of photon emission of a nutrient medium is determined and measured with a sample of the object to be examined.
EP1188041 -- METHOD, SYSTEM AND USE OF MEASURING DEVICES FOR DETERMINING THE GERMINABILITY OF SEEDS
A process (I) and apparatus for determining the germination characteristics of seed corn by bio-photon and water moisture detection, are new. In a process (I) to determine the germination capacity of seed grain especially cereals, the seed grain is first exposed to light pulses for a defined period and the exposure then terminated. A measurement is made of at least one characteristic of the light then emitted by the seed without further light stimulation especially the residual luminescence or spontaneous light emission. The light emitted gives an indication of the germination capacity of the seed. In addition a further measurement is made especially of the seed grain water content, and is used as a correction factor to the germination characteristic based on the light value. An Independent claim is also included for apparatus for use in (I).
EP1126271 -- Method and device for determining the malignancy of tumor tissue and for choosing substances beneficial to the tissue
Method involves measurement of the bio-photon emission from tumor tissue using a very sensitive light detector. The tissue can first be excited using illumination with suitable wavelength light, using ultrasound, etc and then the value of emitted light measured. From the measurements a suitable medicine can be selected to treat the tumor. An Independent claim is made for a system for treating malignant cancers by determining the degree of malignancy from light measurements and then determining the optimum medicine.
DE102005058332 -- Method for optimal interpretation of data evaluating regulatory capacity of biological system...
One of the physiological parameters of a biological system in particular of a human being, which can be the galvanic skin response, is measured at a large number of subjects. The data are evaluated by using various appropriate statistical methods. The log-normal distribution and the Gaussian distribution are calculated. The resulting matrix is used as a base for a factor analysis already containing the data of a reference group. The position of the factors can be used as a criterion for the evaluation of the condition of an individual regarding the regulatory capacity of his/her system.
DE102004055200 -- Functional value e.g. regulating capability, determining method for e.g. human being...
The method involves evaluating a light signal after a deviation from a pure random distribution and a correlation to an ideally regulating distribution. A strewing portion of a photon is measured, where the photon is used for stimulation of a biological system. The light signal is utilized as a trigger pulse for treatment of a relevant skin area of the biological system.
DE10355348 -- Function data determination method e.g. for regulation capabilities of biological system...
The method involves collecting a multiplicity of measured values of the conductivity of the skin and determining the frequency distribution of the measured values. The frequency distribution of the measured values is compared with a normal distribution (1) and a logarithmic normal distribution (2). The conductivity of the skin is determined on a hand. Approximately 500 measured values in approximately 10 minutes are determined. An independent claim is included for a device for the determination of function values.
DE10147701 -- Testing for the smallest possible quality differences between biological tissue by measurement of bio-photon emission and application of photon count statistics
Method for testng for the smallest possible quality differences between biological tissue by measurement of bio-photon emission and delayed luminescence. Measurement of photon emission is with or without the effect of interacting agents. Differences in measurements are determined using photon count statistics.
DE10132549 -- Determining heat regulating capacity of biological systems involves irradiating with infrared light, detecting relaxation of photon intensity and compensating using hyperbolic function
The process involves determining the quality and/or quality changes of biological systems by measuring the ultra-weak photon emission of a system subjected to the light after ending the radiation. The biological system is irradiated with infrared light and the relaxation of the photon intensity is detected against time and then the relaxation function of the investigated system is compensated using a hyperbolic function.
DE4439451 -- Examining changes in the condition of biological tissue
In a method for examining changes in the condition of human, animal or plant tissue by measurement of ultra-weak photo emission, the new feature is that the measuring parameters of the emission are employed.
DE4401169 -- Faster procedure for detecting differences in fluid characteristics
A method for discriminating between the characteristics of similar fluids employs differences in the respective photon emissions of fluid samples after their identical excitation at a controlled temperature. Each sample (1) is successively enclosed in a transparent quartz vessel having a pair of titanium electrodes (2,3) supplied with a DC potential of typically 18 volts. An excitation system (4) activates the sample either by energising a tungsten light source of controlled spectrum or by EM/sound waves of constant intensity and wavelength. After a definite period of excitation the luminescence of the sample is measured by the detector(s).
DE4308520 -- Method for differentiating between homozygotes, heterozygotes and normal cells of an organism
A method is specified for differentiating between homozygotes, heterozygotes and normal cells of an organism. It is characterised in that the cells to be investigated are irradiated with UV light and/or treated with a substance which partly damages the cells and the intensity of the photon emission of these cells is subsequently measured. The method is preferably used before X-ray diagnosis in which the risk of inducing a disease triggered by the radiation is to be no greater than the probability of early diagnosis of a disease.
DE3040855 // DE3038255 -- Examining biological effects on foodstuffs of seeds - by measuring intensity of ultra-weak photon radiation in vitro
A measurement of the spontaneous or stimulated emission of ultra-weak photon radiation is used as an in vitro parameter of a cell lot. The parameter is used to detect possible cell-damaging or regenerating effects or to act as a quality control. The measured quantity is either the photon intensity or a photon statistic e.g. the distribution of numbers of photons emitted in a measuring interval. The ultra-weak radiation is typically in the infra red band and has an energy very much less than that of thermal radiation. Typically the radiation is 10 power (-10) less than thermal radiation. The radiation is detected by a photo multiplier with a gain of over 10 power 6. The method may be used to determine whether a cell lot is in a healthy state. Alternatively it can be used to determine the effect of an agent on the cells. The method is partic. suitable for quality control in foodstuffs.
http://biophotonservices.com/dr-fritz-albert-popp/biophotons-and-relationship-to-the-ultraviolet-spectrum/
Biophoton Services // 1151 Harbor Bay Parkway, Suite 100, Alameda, CA 94502
Dr. Fritz Albert Popp showed with this experiment using onions that UV light causes onions to communicate with each other. He showed that cancer tumors reacted to high intensity levels of UV light in the range of 380 nanometers. By using a method called photo repair he illuminated cells with a weaker intensity of UV light, causing the DNA to undergo rapid healing.
It is only when UV light is at a lower intensity level that the healing of DNA occurs. With the help of a lab assistant, Dr. Popp built a machine called the “photomultiplier” which measures weak photon emissions that stimulate healing. While measuring these photons in humans, he discovered that the cells of the body have a biological rhythms of 7, 14, 32, 80 and 270 days respectively. These numbers all readily divided into 7. It also showed that people who had these disturbed biological rhythms were cancer patients. His research also showed that stress triggered an increase in biophotons, which short term can be beneficial to good health.
It is no surprise that foods highest in biophotons are also used as natural cancer cures, especially when you eat them within 3 hours after being picked from the ground. Dr. Gabriel Cousens states that people who have a junk food diet register 1,000 or less biophotons in their systems, whereas people eating a fresh raw food diet have 83,000 or more biophotons in their bodies.
Scientist Dr. Pjotr Garajajev used UV photons to transfer a frogs embryo into a salamanaders embryo, which in turn caused the salamander to give birth to a frog. Below is a video showing a machine where German researchers add biophotons to a dead leaf of a plant and how it “brings it back to life” again.
It is my theory that because mistletoe is highest in biophontons, which are connected to sunlight, and vitamin D promotes bone growth and stimulates the immune system, and many leukemia patients show a vitamin D deficiency, than foods highest in these “biophotons” would increase the flow of biophotons in the body.
Foods highest in biophotons: wild dandelion greens, nettles, grasses, mushrooms, nuts and berries
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18314258
Cancer Lett. 2008 Jun 18;264(2):218-28.
Molecular mechanisms of mistletoe plant extract-induced apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia in vivo and in vitro.
Seifert G1, Jesse P, Laengler A, Reindl T, Lüth M, Lobitz S, Henze G, Prokop A, Lode HN.
Abstract
Viscum album (Mistletoe) is one of the most widely used alternative cancer therapies. Aqueous mistletoe extracts (MT) contain the three mistletoe lectins I, II and III as one predominant group of biologically active agents. Although MT is widely used, there is a lack of scientifically sound preclinical and clinical data. In this paper, we describe for the first time the in vivo efficacy and mechanism of action of MT in lymphoblastic leukemia. For this purpose, we first investigated both the cytotoxic effect and the mechanism of action of two standardized aqueous MTs (MT obtained from fir trees (MT-A); MT obtained from pine trees (MT-P)) in a human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell line (NALM-6). MT-A, MT-P and ML-I inhibited cell proliferation as determined by Casy Count analysis at very low concentrations with MT-P being the most cytotoxic extract. DNA-fragmentation assays indicated that dose-dependent induction of apoptosis was the main mechanism of cell death. Finally, we evaluated the efficacy of MT-A and MT-P in an in vivo SCID-model of pre-B ALL (NALM-6). Both MTs significantly improved survival (up to 55.4 days) at all tested concentrations in contrast to controls (34.6 days) without side effects.
Popp, E.A. : "Photon Storage in Biological Systems";Electromagnetic Bioinformation, Proceedings of the Symposium, Marburg, September 5, 1977 (Munchen-wien-Baltimore (1979)
Popp, F. A., Ruth, B., Bahr, W., Bohm, J.,Grass, P., Grolig, G, Rattemeyer, M. Schmidt,H.G., and Wullle, P.;“Emission of Visible and Ultraviolet Radiation by Active Biological Systems”, Collective Phenomena, Vol. 3, pp. 187-214 (1981)
Popp, E.A., ed., Electromagnetic Bioinformation, Urban & Schwartzenberg, Munchen-Wien- Baltimore (1989)
Popp, F.A., et al., Recent Advances in Biophoton Research and Its Applications, eds. F.A.Popp et al, World Scientific, Singapore (1992)
Popp, F.A., and Li, K.H., “Hyperbolic Relaxation as a Sufficient Condition of a Fully Coherent Ergodic Field,” Int. J. Theor. Phys., Vol. 32, pp. 1573-1583 (1993)
Popp, F.A., Chang, J.J., Gu, Q., and Ho, M.W., “Nonsubstantial biocommunication in terms of Dicke’s theory,” in Bioelectrodynamics and Biocommunication, ed. by Ho, M.W., Popp, F.A., and Warnke, U., World Scientific, Singapore (1994)
Popp, F.A.; Gu, Q.; and Li, K.H.; “Biophoton Emission: Experimental Background and Theoretical Approaches,” Mod. Phys. Lett. B, Vol. 8, Nos. 21 & 22, pp. 1269-1296 (1994a)
Popp, F.A., Chang, J.J., Herzog, A., Yan, Z., and Yan, Y., “Evidence of Non-Classical (Squeezed) Light in Biological Systems,” Physics Letters A, Vol. 293, Nos. 1-2, pp. 98-
102 (2002)
Popp, F.A., “Properties of Biophotons and Their Theoretical Implications,” Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, Vol. 41, May, pp.391-402 (2003)
Popp, F.A., “Biophysical Aspects of the Psychic Situation,” International Institute of Biophysics, http://www.lifescientists.de/ib0203e_1.htm
ill be explained in more detail:
Example 1
Isolation of a chitin mistletoe lectin
1 kg leaves and twigs of mistletoe (Viscum album L.) are homogenized in 10 l of 20 mM acetic acid with a Waring blender.
The homogenate was filtered and centrifuged (8,000 g for 10 minutes), the supernatant is decanted and filtered through glass wool (to remove the floating particles).
After addition of 1.5 g / l CaCl 2 with 1N NaOH, the extract is adjusted to a pH 9.0 and held for 3 hours at 2 ° C.
The precipitate is separated by centrifugation (3,000 g for 10 min) removed and the clear extract is adjusted with 1 N acetic acid to pH 3.0.
After standing overnight in a cold room, the extract was centrifuged again (3,000 g for 10 minutes) and the supernatant is filtered through filter paper (Whatman 3MM).
The filtrate is dissolved in an equivalent amount of distilled water and applied to a cation exchange column (10 cm x 5 cm, 200 ml volume) of S Fast Flow (Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden) equilibrated with 20 mM acetic acid.
After loading the proteins, the column with 2 liters of 20 mM sodium formate (pH 3.8) is washed and the bound proteins were eluted with 500 ml of 0.5 M NaCl in the same buffer.
To eliminate the type 2 RIP lectins ML I, ML II and ML III, the desorbed protein mixture is subjected to the S Fast Flow column following affinity chromatography on a galactose-Sepharose 4B and fetuin-Sepharose 4B.
Thus, the partially purified protein fraction with 1 N NaOH to pH 7.4 and is set to a column (10 cm x 2.6 cm, about 50 ml) with galactose-Sepharose 4B applied, which is eliminated in ML-I.
After passing through the protein fraction of the column with 200 ml of PBS (phosphate buffered saline).
The ML-I-free fraction and the washed solution to a fetuin-Sepharose 4B column (10 cm x 2.6 cm, about 50 ml) was added for removal of ML II and ML III.
The unbound proteins (which are free of ML II, ML II and ML III) are the first 200 ml of PBS wash solution and combined on a chitin column (20 cm x 2.6 cm, approximately 100 ml - Type C-7170, Sigma brought).
Unbound proteins are removed by washing the column with PBS until the A280 fell below 0.01.
At the end of the lectin was desorbed with 20 mM acetic acid and then either dialyzed against PBS and stored at -20 ° C until his use or dialyzed against water and lyophilized.
Example 7
Influence the immune system
VisalbCBA causes the release of cytokines TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-j from peripheral mononuclear cells from healthy blood donors at concentrations> 90 ng / ml
A UK woman has disclosed how she cured her cancer with the holiday herb mistletoe after declining chemotherapy treatment. Joan van Holsteijn obtained injections of a medicine made from mistletoe berries, the plant associated in popular culture with Christmas-time kisses. This treatment has apparently brought Joan a cure to her cancer, as the tumors have disappeared. Joan had been diagnosed with non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma after doctors discovered a tumor the size of an egg in her leg. Within 18 months of initiating the mistletoe treatment the tumor was gone and scans showed no further trace of the cancer. Joan is pleased that she made the decision to refuse chemotherapy due to the debilitating effects of chemotherapy drugs and their role in depleting the immune system, the very system the body needs functioning well to use its own resources for healing cancer.
Joan now keeps springs of mistletoe in her home, not to invite holiday kisses but to invite others to hear about her wonderful experience of recovery from lymphoma using this herbal treatment. This treatment is well-known in Europe, while Americans are unlikely to have heard of it. Even those who are aware of this herbal therapy may not know about some surprising research that explains how mistletoe seems to help the body clear away cancers. This research comes from the work of Dr. Fritz-Albert Popp, who is a pioneer in research on biophotons and their role in cellular communication. Dr. Popp discovered that changes in the body's biophoton emissions are associated with cancer and other illnesses. Biophotons are photons of light emitted in living systems. Popp found that carcinogenic chemicals can be recognized by their property of disrupting biophoton emissions and the coherence of light waves. Based on this, he surmised that there may be compounds which have the opposite effect of helping restore healthy biophoton emissions and resuming coherent light patterns. Of all the alleged cancer-busting substances Popp tested, only mistletoe was able to return the biophoton emissions of cancer cells back to normal. When this happened the cancers went into remission.
In Popp's view, health is a state of perfect subatomic communication, and ill health is a state of communication breakdown. We are ill when our waves are out of synch. Popp believes that our cells and DNA use electromagnetic spectrum waves to communicate and transfer information. Substances that disturb or enhance the transmission of these waves in varying frequency ranges (wavelengths) can influence our health. In cancer patients, Popp found that natural cycles of light emission were disrupted, light waves were losing coherence, and thus the cancer cells were out of attunement to the rest of the body. Scientists have long known that photorepair allows damaged cells to regenerate. This process of light being used to restore life to cells functions best within a certain frequency range. This frequency range falls within the ultraviolet light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Not surprisingly, Popp had discovered that known carcinogens (cancer causing chemicals) act to disrupt the transmission of light in that range.
Mistletoe appears to assist cancer patients due to the subtle energetic properties it contains. Vibrational medicine is a key frontier in the healing arts, and this herb is one example of how research in natural therapies and vibrational energy can help us find ways to restore health and bring balance and harmony to our lives. The next time you see a sprig of mistletoe, you may want to ponder this miracle healing herb and its life-giving properties...
http://www.viewzone.com
Are humans really beings of
light?
by Dan Eden for viewzone.com
by Dan Eden for viewzone.com
I get lots of suggestions for stories, and I really appreciate them. But some of them are too good to be true. An example of this was a story of a giant human skeleton -- maybe 40 feet tall -- that was discovered by a Russian archaeological team. The story had photos and links accompanying it and looked promising. But when the links were researched they went in a circle. Each link used the other link as the source. Finally the elements of the photos turned up and we recognized a good Photoshop job had fooled everyone.
I had this same experience this week when I was sent an article where a Russian (again) scientist, Pjotr Garjajev, had managed to intercept communication from a DNA molecule in the form of ultraviolet photons -- light! What's more, he claimed to have captured this communication from one organism (a frog embryo) with a laser beam and then transmitted it to another organisms DNA (a salamander embryo), causing the latter embryo to develop into a frog!
But this was just the beginning.
Dr. Garjajev claims that this communication is not something that happens only inside the individual cells or between one cell and another. He claims organisms use this "light" to "talk" to other organisms and suggested that this could explain telepathy and ESP. It was like human beings already had their own wireless internet based on our DNA. Wow!
I tried to find a scientific journal that had this experiment. All I could find were blogs and other websites that carried the same story, word for word, without any references. That is until I stumbled on the work of Fritz-Albert Popp [right]. Then everything I had just read seemed very plausible.
Fritz-Albert Popp thought he had discovered a cure for cancer. I'm not convinced that he didn't.
It was 1970, and Popp, a theoretical biophysicist at the University of Marburg in Germany, had been teaching radiology -- the interaction of electromagnetic (EM) radiation on biological systems. Popp was too early to worry about things like cellphones and microwave towers which are now commonly linked with cancers and leukemia. His world was much smaller.
He'd been examining two almost identical molecules: benzo[a]pyrene, a polycyclic hydrocarbon known to be one of the most lethal carcinogens to humans, and its twin (save for a tiny alteration in its molecular makeup), benzo[e]pyrene. He had illuminated both molecules with ultraviolet (UV) light in an attempt to find exactly what made these two almost identical molecules so different.
Why Ultra-violet light?
Popp chose to work specifically with UV light because of the experiments of a Russian biologist named Alexander Gurwitsch who, while working with onions in 1923, discovered that roots could stimulate a neighboring plant's roots if the two adjacent plants were in quartz glass pots but not if they were in silicon glass pots. The only difference being that the silicon filtered UV wavelengths of light while the quartz did not. Gurwitsch theorized that onion roots could communicate with each other by ultraviolet light.
All vibrations of energy are part of the electro-magnetic spectrum. These include electrical energy, heat, sound, light, radio waves and radioactive waves. UV light is merely a small portion of the spectrum of EM energy with a very short wavelength.
What Popp discovered was that benzo[a]pyrene (the cancer producing molecule) absorbed the UV light, then re-emitted it at a completely different frequency -- it was a light "scrambler". The benzo[e]pyrene (harmless to humans), allowed the UV light to pass through it unaltered.
Popp was puzzled by this difference, and continued to experiment with UV light and other compounds. He performed his test on 37 different chemicals, some cancer-causing, some not. After a while, he was able to predict which substances could cause cancer. In every instance, the compounds that were carcinogenic took the UV light, absorbed it and changed or scrambled the frequency.
There was another odd property of these compounds: each of the carcinogens reacted only to light at a specific frequency -- 380 nm (nanometres) in the ultra-violet range. Popp kept wondering why a cancer-causing substance would be a light scrambler. He began reading the scientific literature specifically about human biological reactions, and came across information about a phenomenon called 'photorepair'.
It is well known from biological laboratory experiments that if you blast a cell with UV light so that 99 per cent of the cell, including its DNA, is destroyed, you can almost entirely repair the damage in a single day just by illuminating the cell with the same wavelength at a much weaker intensity. To this day, scientists don't understand this phenomenon, called photorepair, but no one has disputed it.
Popp also knew that patients with xeroderma pigmentosum [right] eventually die of skin cancer because their photorepair system can't repair solar damage. He was also struck by the fact that photorepair works most efficiently at 380 nm -- the same frequency that the cancer-causing compounds react to and scramble.
This was where Popp made his logical leap. If the carcinogens only react to this frequency, it must somehow be linked to photorepair. If so, this would mean that there must be some kind of light in the body responsible for photorepair. A compound must cause cancer because it permanently blocks this light and scrambles it, so photorepair can't work anymore. It seemed logical, but was it true?
Popp was freaked out by this. He wrote about it in a paper and a prestigious medical journal agreed to publish it.
Not long after that, Popp was approached by a student named Bernhard Ruth, who asked Popp to supervise his work for his doctoral dissertation. Popp told Ruth he was prepared to do so if the student could show that light was emanating from the human body.
This meeting was fortuitous for Popp because Ruth happened to be an excellent experimental physicist. Ruth thought the idea was ridiculous, and immediately set to work building equipment to prove Popp's hypothesis wrong.
Within two years, Ruth had constructed a machine resembling a big X-ray detector which used a photomultiplier to count light, photon by photon. Even today, it is still one of the best pieces of equipment in the field. The machine had to be highly sensitive because it had to measure what Popp assumed would be extremely weak emissions.
In an old documentary film taken in the laboratory at the International Institute of Biophysics, Dr. Popp opens a chamber about the size of a bread box. He places a fresh cutting from a plant and a wooden match in a plastic container inside the dark chamber and closed the light proof door. Immediately he switches on the photomultiplyer and the image shows up on a computer screen. The match stick is black while the green, glowing silhouette of the leaves is clearly visible.
Dr. Popp exclaims, "We now know, today, that man is essentially a being of light."
In 1976, they were ready for their first test with cucumber seedlings. The photomultiplier showed that photons, or light waves, of a surprisingly high intensity were being emitted from the seedlings. In case the light had to do with an effect of photosynthesis, they decided that their next test -- with potatoes -- would be to grow the seedling plants in the dark. This time, when the seedlings were placed in the photomultiplier, they registered an even higher intensity of light. What's more, the photons in the living systems they'd examined were more coherent than anything they'd ever seen.
Popp began thinking about light in nature. Light was present in plants and was used during photosynthesis. When we eat plant foods, he thought, it must be that we take up the photons and store them.
When we consume broccoli, for example, and digest it, it is metabolised into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water, plus the light stored from the sun and photosynthesis. We extract the CO2 and eliminate the water, but the light, an EM wave, must be stored. When taken in by the body, the energy of these photons dissipates and becomes distributed over the entire spectrum of EM frequencies, from the lowest to the highest.
This energy is the driving force for all the molecules in our body. Before any chemical reaction can occur, at least one electron must be activated by a photon with a certain wavelength and enough energy.
The biochemist and Nobel Prize winner Lehninger mentions in his textbook that some reactions in the living cell happen quite a lot faster than what corresponds to 37C temperature. The explanation seems to be that the body purposely directs chemical reactions by means of electromagnetic vibrations (biophotons).
Photons (Light) control everything in the cell
Photons switch on the body's processes like an orchestra conductor bringing each individual instrument into the collective sound. At different frequencies, they perform different functions. Popp found that molecules in the cells responded to certain frequencies, and that a range of vibrations from the photons caused a variety of frequencies in other molecules of the body.
This theory has been supported by Dr. Veljko Veljkovic who now heads the Center for Multidisciplinary Research and Engineering, Institute of Nuclear Sciences Vinca. She dared to ask the question that has forever puzzled cellular biologists: What is it that enabled the tens of thousands of different kinds of molecules in the organism to recognize their specific targets? Living processes depend on selective interactions between particular molecules, and that is true for basic metabolism to the subtlest nuances of emotion. It's like trying to find a friend in a very big very crowded ballroom in the dark.
The conventional picture of a cell even now is that of a bag of molecules dissolved in water. And through bumping into one another by chance -- random collisions -- those molecules that have complementary shapes lock onto to each other so the appropriate biochemical reactions can take place. This 'lock and key' model has been refined to a more flexible (and realistic) 'induced fit' hypothesis that allows each molecule to change shape slightly to fit the other better after they get in touch, but the main idea remains the same.
It is supposed to explain how enzymes can recognize their respective substrates, how antibodies in the immune system can grab onto specific foreign invaders and disarm them. By extension, that's how proteins can 'dock' with different partner proteins, or latch onto specific nucleic acids to control gene expression, or assemble into ribosomes for translating proteins, or other multi-molecular complexes that modify the genetic messages in various ways. But with thousands -- or even hundreds of thousands of reactions happening each second in just one cell this seems pushing the "mechanical" concept a bit too far.
What has been proposed is that somehow each molecule sends out a unique electromagnetic field that can "sense" the field of the complimentary molecule. It's as if there is a "dance" in the cellular medium and the molecules move to the rythm. The music is supplied by the biophoton.
"Veljkovic and Cosic proposed that molecular interactions are electrical in nature, and they take place over distances that are large compared with the size of molecules. Cosic later introduced the idea of dynamic electromagnetic field interactions, that molecules recognize their particular targets and vice versa by electromagnetic resonance. In other words, the molecules send out specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves which not only enable them to 'see' and 'hear' each other, as both photon and phonon modes exist for electromagnetic waves, but also to influence each other at a distance and become ineluctably drawn to each other if vibrating out of phase (in a complementary way)." -- The Real Bioinformatics Revolution: Proteins and Nucleic Acids Singing to One Another? (Paper available at report@i-sis.org.uk)
"There are about 100,000 chemical reactions happening in every cell each second. The chemical reaction can only happen if the molecule which is reacting is excited by a photon... Once the photon has excited a reaction it returns to the field and is available for more reactions... We are swimming in an ocean of light."
These 'biophoton emission', as Popp called them, provided an ideal communication system for the transfer of information to many cells across the organism. But the single most important question remained: where was the light coming from?
A particularly gifted student talked him into another experiment. It is known that when ethidium bromide is applied to samples of DNA, it insinuates itself in between the base pairs of the double helix, causing DNA to unwind. The student suggested that, after applying the chemical, they measure the light coming from the sample. Popp found that the greater the concentration of ethidium, the more the DNA unravelled, but also the stronger the intensity of light. Conversely, the less he used, the less light was emitted.
He also found that DNA could send out a wide range of frequencies, some of which seemed to be linked to certain functions. If DNA stored this light, it would naturally emit more light on being unzipped.
These and other studies proved to Popp that one of the most essential sources of light and biophoton emissions was DNA. DNA was like the master tuning fork of the body. It would strike a particular frequency and certain molecules would follow. It was also possible, he realised, that he had stumbled upon the missing link in current DNA theory that could account for perhaps the greatest miracle of all in human biology -- how a single cell can turn into a fully formed human being.
How cells "talk" to each other
When you get a cut or scratch on your skin, the cells that are injured somehow signal the surrounding healthy cells to begin reproducing copies of themselves to fill in and mend the opening. When the skin is back to normal, a signal is sent to the cells to tell them to stop reproducing. Scientists have wondered exactly how this works.
With biophoton emissions, Popp believed he had an answer to this question. This phenomenon of coordination and communication could only occur in a holistic system with one central orchestrator. Popp showed in his experiments that these weak light emissions were sufficient to orchestrate the body's repairs. The emissions had to be low intensity because these communications took place on a very small, intracellular, quantum level. Higher intensities would have an effect only in the world of the large and would create too much "noise" to be effective.
The number of photons emitted seemed to be linked to the organism's position on the evolutionary scale -- the more complex the organism, the fewer photons were emitted. Rudimentary animals and plants tended to emit 100 photons/cm2/sec at a wavelength of 200-800 nm, corresponding to a very-high-frequency EM wave well within the visible range, whereas humans emit only 10 photons/cm2/sec at the same frequency.
In one series of studies, Popp had one of his assistants -- a 27-year-old healthy young woman -- sit in the room every day for nine months while he took photon readings of a small area of her hand and forehead. Popp then analysed the data and discovered, to his surprise, that the light emissions followed certain set patterns -- biological rhythms at 7, 14, 32, 80 and 270 days -- and similarities were also noted by day or night, by week and by month, as though the body were following the world's biorhythms as well as its own.
Cancer is a loss of coherent light
So far, Popp had studied only healthy individuals and found an exquisite coherence at the quantum level. But what kind of light is present in those who are ill?
Popp tried out his machine on a series of cancer patients. In every instance, these patients had lost those natural periodic rhythms as well as their coherence. The lines of internal communication were scrambled. They had lost their connection with the world. In effect, their light was going out.
Just the opposite is seen with multiple sclerosis: MS is a state of too much order. Patients with this disease are taking in too much light, thereby inhibiting their cells' ability to do their job. Too much cooperative harmony prevented flexibility and individuality -- like too many soldiers marching in step as they cross a bridge, causing it to collapse. Perfect coherence is an optimal state between chaos and order. With too much cooperation, it is as though individual members of the orchestra are no longer able to improvise. In effect, MS patients are drowning in light.
Popp also examined the effects of stress. In a stressed state, the rate of biophoton emissions goes up -- a defence mechanism designed to restore the patient's equilibrium.
Popp now recognized that what he'd been experimenting with was even more than a cure for cancer or Gestaltbildung. Here was a model which provided a better explanation than the current neo-Darwinist theory for how all living things evolve on the planet. Rather than a system of fortunate but ultimately random error, if DNA uses frequencies of every variety as an information tool, this suggests instead a feedback system of perfect communication through waves that encode and transfer information.
"Good vibes" means coherent light
Popp came to realize that light in the body might even hold the key to health and illness. In one experiment, he compared the light from free-range hens' eggs with that from penned-in, caged hens. The photons in the former were far more coherent than those in the latter.
Popp went on to use biophoton emissions as a tool for measuring the quality of food. The healthiest food had the lowest and most coherent intensity of light. Any disturbance in the system increased the production of photons. Health was a state of perfect subatomic communication, and ill health was a state of communication breakdown. We are ill when our waves are out of synch.
Bio Photon emission detection is currently used commercially in the food industry. Agricultural science is looking at Bio-photon emissions to determine plant health for the purposes of food quality control. Biophotonen is a company working for development and practical applications of biophotonics. The work is based on a variety of patents. "Biophotonen" solves practical problems of food industry, environmental industry, cosmetics, etc.
Off-shoots of Dr. Popp's discovery
In the 1970s Dr. Veljko Veljkovic, who now heads the Center for Multidisciplinary Research and Engineering, Institute of Nuclear Sciences Vinca, also discovered a method for predicting which of the hundreds of new chemicals made by the rapidly expanding chemical industry were carcinogenic, by calculating certain electronic, biophotonic properties of the molecules. This method was soon found equally applicable to predicting organic chemicals that were mutagenic, or toxic, and even those that were antibiotic, or cytostatic (anticancer). Veljkovic's institute in Belgrade has since teamed up with other European laboratories to apply the same method to drug discovery, especially against AIDS disease.
Biophoton Therapy
Biophoton therapy is the application of light to particular areas of the skin for healing purposes. The light, or photons, that are emitted by these units are absorbed by the skin's photoreceptors and then travel through the body's nervous system to the brain, where they help regulate what is referred to as our human bio-energy. By stimulating certain areas of the body with specific quantities of light, biophoton therapy can help reduce pain as well as aid in various healing processes throughout the body.
The theory behind biophoton therapy is based on the work of Dr. Franz Morell and has been expanded by the work of Doctors L.C. Vincent and F.A. Popp, who theorized that light can affect the electromagnetic oscillation, or waves of the body and regulate enzyme activity.
It took some 25 years for Popp to gather converts from among the scientific community. Slowly, a few select scientists around the globe began to consider that the body's communication system might be a complex network of resonance and frequency. Eventually, they would form the International Institute of Biophysics, composed of 15 groups of scientists from international centres around the world.
Popp and his new colleagues went on to study the light emissions from several organisms of the same species, first in an experiment with a type of water flea of the genus Daphnia. What they found was nothing short of astonishing. Tests with a photomultiplier showed that the water fleas were sucking up the light emitted from each other. Popp tried the same experiment on small fish and got the same result. According to his photomultiplier, sunflowers were like biological vacuum cleaners, moving in the direction of the most solar photons to hoover them up. Even bacteria swallowed photons from the media they were put in.
Communication between organisms
Thus, it dawned on Popp that these emissions had a purpose outside of the body. Wave resonance wasn't only being used to communicate inside the body, but between living things as well. Two healthy beings engaged in 'photon sucking', as he called it, by exchanging photons. Popp realised that this exchange might unlock the secret of some of the animal kingdom's most persistent conundrums: how schools of fish or flocks of birds create perfect and instantaneous coordination. Many experiments on the homing ability of animals demonstrate that it has nothing to do with following habitual trails, scents or even the EM fields of the earth, but rather some form of silent communication that acts like an invisible rubber band, even when the animals are separated by miles of distance.
For humans, there was another possibility. If we could take in the photons of other living things, we might also be able to use the information from them to correct our own light if it went awry.
Death Transmission via the Paranormal "Light" Channel
Some extremely interesting experiments were performed by V.P. Kaznacheyev et al regarding the paranormal transmission of death by light inter-organism communication.
Briefly, two groups of cells were selected from the same cell culture and one sample placed on each side of a window joining two environmentally shielded rooms. The cell cultures were in quartz containers. One cell culture was used as the initiation sample and was subjected to a deadly mechanism - virus, germ, chemical poison, irradiation, ultraviolet rays, etc. The second cell culture was observed, to ascertain any transmitted effects from the culture sample being killed.
When the window was made of ordinary glass, the second sample remained alive and healthy. When the window was made of quartz, the second sample sickened and died with the same symptoms as the primary sample.
The experiments were done in darkness, and over 5,000 were reported by Kaznacheyev and his colleagues. The onset of induced complementary sickness and death in the second culture followed a reasonable time -- say two to four hours -- behind sickness and death in the primary culture.
The major transmission difference between window glass and quartz is that quartz transmits both ultraviolet and infrared well, while glass is relatively opaque to ultraviolet and infrared. Both quartz and glass transmit visible light. Thus glass is a suppressor of the paranormal channel, while quartz is not.
In 1950, Western researchers found that cells could be killed in darkness with ultraviolet radiation, kept shielded from visible light for twenty-four hours or longer, and then if radiated with visible light the cells would start reviving by hundreds of thousands even though they had been clinically dead.
Specifically, every cell emits mitogenetic radiation in the ultraviolet range twice: when it is born and when it dies. The UV photon emitted at death contains the exact virtual state pattern of the condition of the cell at death. The healthy cells are bombarded with death messages from those that are dying, and this diffuses the death pattern throughout the healthy culture, eventually kindling into the same death pattern there.
[V.P. Kaznacheyev et al, "Distant Intercellular Interactions in a System of Two Tissue Cultures," Psychoenergetic Systems, Vol. 1, No. 3, March 1976, pp 141-142.]
Popp had begun experimenting with such an idea. If cancer-causing chemicals could alter the body's biophoton emissions, then it might be that other substances could reintroduce better communication. Popp wondered whether certain plant extracts could change the character of the biophoton emissions from cancer cells to make them communicate again with the rest of the body. He began experimenting with a number of non-toxic substances purported to be successful in treating cancer. In all but one instance, these substances only increased the photons from tumour cells, making them even more deadly to the body.
The single success story was mistletoe, which appeared to help the body to 'resocialise' the photon emissions of tumour cells back to normal. In one of numerous cases, Popp came across a woman in her thirties who had breast and vaginal cancer. Popp found a mistletoe remedy that created coherence in her cancer tissue samples. With the agreement of her doctor, the woman stopped any treatment other than the mistletoe extract and, after a year, all her laboratory tests were virtually back to normal.
To Popp, homoeopathy was another example of photon sucking. He had begun to think of it as a 'resonance absorber'. Homoeopathy rests upon the notion that like is treated with like. A plant extract that at full strength can cause hives in the body is used in an extremely diluted form to get rid of it. If a rogue frequency in the body can produce certain symptoms, it follows that a high dilution of a substance which can produce the same symptoms would also carry that frequency. Like a resonating tuning fork, a suitable homoeopathic solution might attract and then absorb the abnormal oscillations, allowing the body to return to normal health.
Popp thought that electro-magnetic molecular signalling might even explain acupuncture. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, the human body has a system of meridians, running deep in the tissues, through which flows an invisible energy the Chinese call ch'i, or the life force. The ch'i supposedly enters the body through these acupuncture points and flows to deeper organ structures (which do not correspond to those in Western biology), providing energy (or the life force). Illness occurs when this energy is blocked at any point along the pathways. According to Popp, the meridian system transmits specific energy waves to specific zones of the body.
Research has shown that many of the acupuncture points have a dramatically reduced electrical resistance compared with the surrounding skin (10 kilo-ohms and 3 mega-ohms, respectively). Orthopaedic surgeon Dr Robert Becker, who has done a great deal of research on EM fields in the body, designed a special electrode recording device that rolls along the body like a pizza cutter. His many studies have shown electrical charges on every one of the people tested corresponding to the Chinese meridian points.
[Extracted from The Field: The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe, by Lynne McTaggart]
Light in human consciousness
I mention this latest work for those who may wish to explore the boundaries of photon research and theory. In a ground-breaking paper with the lengthy title of "Orchestrated Objective Reduction of Quantum Coherence in Brain Microtubules: The 'Orch OR' Model for Consciousness" by Stuart Hameroff and Roger Penrose, the brain is described as a quantum computer whose main architecture are the cytoskeletal microtubules and other structures within each of the brain's neurons.
If you examine a neuron, you will see that there are many hollow tubes surrounding the axon. These microtubules have been thought of as a kind of scaffold to support the nerve fiber. But they are now getting a second look as the possible architecture of our consciousness.
The particular characteristics of microtubules that make them suitable for quantum effects include their crystal-like lattice structure, hollow inner core, organization of cell function and capacity for information processing. According to the researchers, their size appears perfectly designed to transmit photons in the UV range.
[Above:] Schematic of central region of neuron (distal axon and dendrites not shown), showing parallel arrayed microtubules interconnected by MAPs. Microtubules in axons are lengthy and continuous, whereas in dendrites they are interrupted and of mixed polarity. Linking proteins connect microtubules to membrane proteins including receptors on dendritic spines.
"Traditionally viewed as the cell's 'bone-like' scaffolding, microtubules and other cytoskeletal structures now appear to fill communicative and information processing roles. Theoretical models suggest how conformational states of tubulins within microtubule lattices can interact with neighboring tubulins to represent, propagate and process information as in molecular-level 'cellular automata' computing systems." -- Hameroff and Watt, 1982; Rasmussen et al, 1990; Hameroff et al, 1992
In their paper, Hameroff and Penrose present a model linking microtubules to consciousness using quantum theory. In their model, quantum coherence emerges, and is isolated in brain microtubules until a threshold related to quantum gravity is reached. The resultant self-collapse creates an instantaneous "now" event. Sequences of such events create a flow of time, and consciousness.
Don't worry if you can't understand this. It's heavy reading but it does show that the existence of internal photons -- inner light -- is very real and is the basis of virtually all human cellular and systemic function.
Could the Russian scientists really have changed a salamander embryo into a frog with lasers? I prefer to wait until the actual details of the experiment are published and reviewed -- but I am much less apt to dismiss this as fiction now that I know about our inner lights.
http://books.google.com/books?id=VtNaz_vSnIIC&pg=PA54&lpg=PA54&dq=Popp+mistletoe&source=bl&ots=yeswwqdMFm&sig=shfjLuUwPf9A5m3rMLhcQaAHnEI&hl=en&ei=8cXXTq-iCsmKsQKnvYH0DQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=3&sqi=2&ved=0CDYQ6AEwAg#v=onepage&q=Popp%20mistletoe&f=false
The Field: The Quest for the
Secret Force of the Universe
By Lynne McTaggart
By Lynne McTaggart
http://naturalnews.com
http://www.naturalpedia.com/mistletoe.html
MISTLETOE -- VISCUM, JUNIPER mistletoe
(PHOR-ADENDRON JUNIPERINUM)
This particular mistletoe may or may not be poisonous, but too little is known about it for any wise person to use it for anything but holding up at Christmas time and kissing beneath. MISTLETOE, VISCUM, EUROPEAN mistletoe (VISCUM ALBUM) This branch of mistletoe definitely contains toxic amines and is considered poisonous. MORNING GLORY (IPOMOEA PURPUREA) The seeds of this particular morning glory do contain amides of lysergic acid, but with a potency much less than that of LSD." - Earl Mindell, Earl Mindell's Vitamin Bible for the 21st Century
"The single success story was mistletoe, which seemed to help the body to 'resocialize' the photon emission of tumor cells back to normal. In one of numerous cases, Popp came across a woman in her thirties with breast and vaginal cancer. Popp tried mistletoe and other plant extracts on samples of her cancerous tissue and found that one particular mistletoe remedy created coherence in the tissue similar to that of the body. With the agreement of her doctor, the woman began forgoing any treatment other than this mistletoe extract." - Lynne Mctaggart, The Field - The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe
"Popp tried mistletoe and other plant extracts on samples of her cancerous tissue and found that one particular mistletoe remedy created coherence in the tissue similar to that of the body. With the agreement of her doctor, the woman began forgoing any treatment other than this mistletoe extract. After a year, all her laboratory tests were virtually back to normal. A woman who was given up as a terminal cancer case had her proper light restored, just by taking a herb.2? To Fritz-Albert Popp, homeopathy was another example of photon sucking. He had begun to think of it as a 'resonance absorber'." --- Lynne Mctaggart, The Field - The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe
"Iscador P contains mistletoe extract from V. pini (mistletoe from pine trees). • Iscador Qu contains mistletoe extract from V. quercus (mistletoe from oak trees). The three types are also available formulated with low concentrations (10~8 g per 100 mg fresh plant extract) of certain metal salts, such as those of copper and mercury. A lectin-standardized extract, also prepared according to the anthroposophic approach, is available, although this formulation does not include metal salts." --- Dr. Michael Heinrich, Joanne Barnes, Simon Gibbons and Elizabeth M. Williamson, Fundamentals of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy
"A recent study shows that mistletoe can induce a condition known as eosinophilic (an increase in the number of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell) in healthy adults. [Journal Society Integrative Oncology 4: 3-7, 2006] mistletoe extract has been shown to reduce adverse effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy on the microcirculation and the immune system of cancer patients. [Anticancer Research 25:601-10, 2005] Iscador is popular in Germany where it was recently shown to improve survival (slightly) among malignant melanoma patients. --- Bill Sardi, You Don't Have to be Afraid of Cancer Anymore
"Disch Med Wochenschr 125: 1222-26, 2000] A study of patients who had undergone bladder cancer surgery did not find that mistletoe extract significantly delayed recurrence of cancer. [Journal Urology 168: 72-75, 2002] In 2002, a German medical journal reported that mistletoe therapy has not gained an established placed in the treatment of cancer and no overall improvement in survival had been reported."
"Alternative Therapy Health Medicine 7: 57-66, 68-72, 2001 ] For comparison, some widely promoted anticancer drugs like Erbitux only extend life by an average of four months and cost $48,000. A survey of German physicians found that the probability to achieve complete or partial remissions with mistletoe extract was estimated to be 6% and 15% respectively. [Disch Med Wochenschr 125: 1222-26, 2000] A study of patients who had undergone bladder cancer surgery did not find that mistletoe extract significantly delayed recurrence of cancer." --- Bill Sardi, You Don't Have to be Afraid of Cancer Anymore
"With the agreement of her doctor, the woman began forgoing any treatment other than this mistletoe extract. After a year, all her laboratory tests were virtually back to normal. A woman who was given up as a terminal cancer case had her proper light restored, just by taking a herb.2? To Fritz-Albert Popp, homeopathy was another example of photon sucking. He had begun to think of it as a 'resonance absorber'. Homeopathy rests upon the notion that like is treated with like. A plant extract that at full strength can cause hives in the body is used in an extremely dilute form to cure them." --- Lynne Mctaggart, The Field - The Quest for the Secret Force of the Universe
"The host trees are usually at least twenty years old before mistletoe encroaches, and they are not usually killed by the mistletoe. The plant forms pendant bushes where it grows. Its leaves are thick, oval to round, and 1 to 2 inches long. Its small, inconspicuous, sticky, white flowers are about V4 inch long. It is dioecious, meaning that male and female flowers are borne on different plants." --- Brigitte Mars, A.H.G., The Desktop Guide to Herbal Medicine: The Ultimate Multidisciplinary Reference to the Amazing Realm of Healing Plants, in a Quick-study, One-stop Guide
"Indeed, Frazer concludes that the Golden Bough itself was probably a sprig of berries still used ceremonially today: mistletoe..." - Adam Leith Gollne, The Fruit Hunters: A Story of Nature, Adventure, Commerce and Obsession
"Lectin-standardized mistletoe extracts, which are distinct from anthroposophical mistletoe preparations, are also available, particularly in Germany. mistletoe products prepared from different host trees are prescribed for patients with different types of cancer. Treatment is usually given by subcutaneous injection, although the intravenous injection route is sometimes used, and oral formulations are also available. In the preparation of anthroposophical medicines, particular attention is paid to the source and methods of farming used in growing plant raw materials." --- Dr. Michael Heinrich, Joanne Barnes, Simon Gibbons and Elizabeth M. Williamson, Fundamentals of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy
"In folk medicine, mistletoe is also used for attacks of dizziness, amenorrhea, and joint diseases. Side effects: Refer to the German Commission E monograph excerpt; with long-term administration, allergic reactions may occur. Making the tea: Pour cold water over 2.5 g finely cut dried herb. Allow to stand at room temperature for 10— 12 hours and then strain. Drink 1— 2 cups daily (see also: Indications). 1 teaspoon = about 2.5 g. Tea preparations: mistletoe herb is offered as a single herb tea in loose pack and in filter tea bags and is a component of cardiac/circulation herbal tea formulas." --- Josef A. Brinckmann and Michael P. Lindenmaier, Herbal Drugs and Phytopharmaceuticals: A Handbook for Practice on a Scientific Basis
"MISTLETOE • Viscum album (European mistletoe); Phoradendron flavescens (American mistletoe). A parasitical plant with a root firmly attached to the wood of the tree on which it grows, it was sacred to the Druids and reputedly used by them to cure sterility and epilepsy; and as an antidote for poisons. Hippocrates and Galen used it as an external remedy and internally to treat sleep disorders. It is also used in "organic" cosmetics. See also Juniper Berry. MITRACARPUS SCABER • A South American vine. MIXED CRESOLS • A preservative. See Cresols. MIXED IONONES • Fragrance ingredients." --- Ruth Winter, M.S., A Consumer's Dictionary of Cosmetic Ingredients
"Medicinal species containing lectins include Phytolacca decandra, Viscum album, Urtica dioica and Juglans nigra (Lewis and Elvin-Lewis 1977). mistletoe (Viscum album) contains lectins, viscotoxins (low-molecular-weight polypeptides), amines, polysaccharides, alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpenes, sterols, fatty acids and phenyl-propanoids. mistletoe lectins have been found to bind to erythrocytes, lymphocytes, leucocytes, macrophages, glycoproteins and plasma proteins." --- Andrew Pengelly, The Constituents of Medicinal Plants: An Introduction to the Chemistry and Therapeutics of Herbal Medicine
"Rudolph Steiner, PhD popularized the use of mistletoe in the early 20th century. A certain lectin in mistletoe has been found to inhibit the growth of proliferating cells. By the 1980s, about 40,000 patients worldwide were receiving Iscador, a fermented form of mistletoe that is injected. Iscador and its variations are licensed in Germany as drugs. -Stanislaw R. Burzynski, MD, PhD theorized that certain anti-neoplastons, or naturally occurring peptides, could inhibit the growth of tumor cells without interrupting normal cell growth." --- Patrick Quillin, PhD,RD,CNS, Beating Cancer with Nutrition
"Mistletoe In a Phase I/II study, the effect of mistletoe (Eurixor) treatment was evaluated in 16 patients with pancreatic cancer. mistletoe was administered twice a week by subcutaneous injection. Apart from one anaphylactic reaction, which necessitated suspension of treatment for a few days, no severe side effects were observed. Eight patients (50%) showed a CT-verified status of "no change" (according to the World Health Organization criteria) for at least 8 weeks. Median survival time in all patients was 5.6 months (range = 1.5-26.5 months). --- The Life Extension Editorial Staff, Disease Prevention and Treatment
"All except two patients claimed that mistletoe had a positive effect on their quality of life, with an obvious decline only during the last weeks of life. These results indicate that mistletoe can stabilize quality of life and therefore may help patients to maintain adequate life quality in their few remaining months (Friess et al. 1996). Another, more recent paper described a patient with inoperable cancer of the pancreas who developed marked eosinophilia during treatment (on day 22) with injections of Viscum album (mistletoe)." --- The Life Extension Editorial Staff, Disease Prevention and Treatment
"Mistletoe In a Phase I/II study, the effect of mistletoe (Eurixor) treatment was evaluated in 16 patients with pancreatic cancer. mistletoe was administered twice a week by subcutaneous injection. Apart from one anaphylactic reaction, which necessitated suspension of treatment for a few days, no severe side effects were observed. Eight patients (50%) showed a CT-verified status of "no change" (according to the World Health Organization criteria) for at least 8 weeks. Median survival time in all patients was 5.6 months (range = 1.5-26.5 months)." --- The Life Extension Editorial Staff, Disease Prevention and Treatment
"Scientists found that cultures of human cells produced more antitumor hormones when they were treated with a mistletoe protein. Since then, some clinics have adopted Iscador for treatment of cancer. A few warnings are in order for the herbal enthusiast eager to experiment. Steiner's extract is made from European mistletoe plants. mistletoe berries are poisonous, so never eat them. The stems and leaves must be processed before they are used as medicine, and the finished product raises one's blood pressure and pulse. Those with heart problems should not use it." --- William L. Fischer, How to Fight Cancer & Win
"The mistletoe most widely sold in America is Phoradendron flavescens, but it is the true mistletoe of Europe that holds the best medicinal properties and should be used. Dead Men DO Tell Tales "What I'm about to share with you is worthy of an investigation by the great Sherlock Holmes himself. mistletoe has been used since the time of Christ for alleviating the symptoms of hypertension. But the evidence doesn't come from ancient Celtic inscriptions painted on a broken pottery shard or stiff piece of leather; instead it comes from the stomach of a very waterlogged and mummified ancient Briton." --- John Heinerman, Heinerman's Encyclopedia of Healing Herbs and Spices
"History & Folklore In Norse mythology, a mistletoe bough was used to slay Balder, the god of peace. The plant was subsequently entrusted to the goddess of love, and kissing under it became obligatory. Medicinal Actions & Uses European mistletoe is chiefly used to lower blood pressure and heart rate, ease anxiety, and promote sleep. In low doses it also relieves panic attacks, headaches, and improves concentration. European mistletoe is also prescribed for tinnitus and epilepsy. In anthroposophical medicine, extracts of the berries are injected to treat cancer." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"Mistletoe [Viscum album) Popular throughout Europe, mistletoe is one of the most widely used plants for hypertension and in the treatment of cancer. It is the main therapy used to treat cancer by anthroposophical physicians. Iscador, a fermented extract of Viscum album, reduces the leukocytopenia produced by radiation and chemotherapy. mistletoe is tumor-inhibiting and cytotoxic to a number of different tumor types. It also increases natural killer-cells. Viscum's cytotoxic components include viscumin and viscotoxins. Viscumin is a lectin component that causes agglutination of tumor cells." --- Donald R. Yance, j r.,C.N., M.H., A.H.G., with Arlene Valentine, Herbal Medicine, Healing and Cancer: A Comprehensive Program for Prevention and Treatment
"European herbalists have a couple of different ways of using mistletoe as a heart sedative and antihypertensive. One way is to take equal parts (about two tablespoons each) of mistletoe and hawthorn berries and lemon balm leaves and steep them in two pints of boiling water for 25 minutes. One-half cup of the warm tea is taken morning and evening. The other way is to soak 4 teaspoons of chopped mistletoe in 1-1/4 pints of cold water overnight, and take one cup of the cool beverage first thing the next morning." --- John Heinerman, Heinerman's Encyclopedia of Healing Herbs and Spices
"Recent studies on the anticancer activities of mistletoe (Viscum album) and its alkaloids. Oncology; 43(suppl l):42-50. 1986 Konopa J, Woynarowski JM, Lewandowska-Gumieniak M. Isolation of viscotoxins. Cytotoxic basic polypeptides from Viscum album L. Hoppe-Seylers Z Physiol Chem; 361(10): 1525-1533. 1980 Kovacs E, Hajto T & Hostanska K. Improvement of DNA repair in lymphocytes of breast cancer patients treated with Viscum album extract (Iscador): Eur J Cancer; 27(1):1672-1676. 1991 Metzner G, Franz H, Kindt A, et al." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"Effects of a standardized mistletoe preparation on metastatic B16 melanoma colonization in murine lungs. Drug Res; 48:497-502. 1998 Woynarowski J & Konopa J. Interaction between DNA and viscotoxins. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem; 361(10): 1535-1545. 1980 Zarkovic N, Kalisnik T, Loncaric I et al: Comparison of the effects of Viscum album lectin ML-1 and fresh plant extract (Isorel) on cell growth in vitro and tumorigenicity of melanoma B16F10. Cancer Biother Radiopharmacol; 13:121 -131." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"Action of viscumin, a toxic lectin from mistletoe, on cells in culture. J Biol Chem. Nov 25;257(22): 13271-7. 1982 Timoshenko AV et al. Influence of the galactoside-specific lectin from Viscum album and its subunits on cell aggregation and selected intracellular parameters of rat thymocytes. In: PM; 61(2):130-133. 1995 Timoshenko AV & Gabius HJ. Efficient induction of superoxide release from human neutrophils by the galactoside-specific lectin from Viscum album. Biol Chem; 374:237-243. 1993 Wagner H. Die Mistel in der Tumortherapie. In: DAZ; 132(20):1087/1088." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"It served as a urinary aid and was used in the treatment of epilepsy, in combination with mistletoe and peony. At the end of the 19th century, the drug was applied as an ointment for rheumatism. The infusion is used as a remedy for worm infestation, to treat stomach disorders and cramps and to promote menstruation. In Greece, it is used as a tonic and stimulant. precautions and adverse reactions BURNING BUSH ROOT AND HERB Health risks or side effects following the proper administration of designated therapeutic dosages are not recorded." --- Thomson Healthcare, Inc., PDR for Herbal Medicines, Fourth Edition
"MISTLETOE • Viscum album (European mistletoe); Phoradendron flavescens (American mistletoe). A parasitical plant with a root firmly attached to the wood of the tree on which it grows, it was sacred to the Druids and reputedly used by them to cure sterility and epilepsy; and as an antidote for poisons. Hippocrates and Galen used it as an external remedy and internally to treat sleep disorders. It is also used in "organic" cosmetics. See also Juniper Berry.
"Tieghem (Loranthaceae)—mistletoe This Australian plant, which is similar to the true mistletoe (Viscum album L.; Loranthaceae), is a parasite on several plants, including Duboisia myoporoides (see Duboisia spp.). The leaves contain scopolamine and are smoked in Australia as an inebriant (Bock 1994, 85*). It is possible that the scopolamine is extracted from the host tree Duboisia myoporoides as a result of the mistletoe's parasitic activity and is then incorporated into the plant's own tissue. Bernoullia flammea Oliver in Hook." --- Christian Ratsch, The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications
"In vitro effects of mistletoe extracts and mistletoe lectins. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1993; 43:1221-27. 95. Bussing A Suzart K et al. Induction of apoptosis in human lymphocytes treated with Viscum album L. is mediated by the mistletoe lectins. Cancer Letters 1996; 99:59-72. 96. Mochizuki, et al. Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside-Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3, of red ginseng. Biological if Pharmaceutical Bulletin 1995 Sept; 18(9)4197-202. 97. Block G, Patterson B, Subar A." --- David Hoffman, FNIMH, AHG, Medical Herbalism: The Science Principles and Practices Of Herbal Medicine
"Mistletoe (Viscum album) contains lectins, viscotoxins (low-molecular-weight polypeptides), amines, polysaccharides, alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpenes, sterols, fatty acids and phenyl-propanoids. mistletoe lectins have been found to bind to erythrocytes, lymphocytes, leucocytes, macrophages, glycoproteins and plasma proteins. Cytotoxic activity has been demonstrated for the glycoprotein fraction, alkaloid fraction and Iscador™ (plant juice preparation)—positive in vitro and in vivo. Human studies with Iscador™ have shown slight improvement over controls, with best results for colon cancer." --- Andrew Pengelly, The Constituents of Medicinal Plants: An Introduction to the Chemistry and Therapeutics of Herbal Medicine
"Injectable mistletoe should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Turmeric (page 753) may be another useful herb with immune effects in people infected with HIV. One preliminary trial found that curcumin, the main active compound in turmeric, helped improve CD4+ cell counts.92 The amount used in this study was 1 gram three times per day by mouth. These results differed from those found in a second preliminary trial using 4.8 or 2.7 grams of curcumin daily. In that study, there was no apparent effect of curcumin on HIV replication rates." --- Alan R. Gaby, M.D., Jonathan V. Wright, M.D., Forrest Batz, Pharm.D. Rick Chester, RPh., N.D., DipLAc. George Constantine, R.Ph., Ph.D. Linnea D. Thompson, Pharm.D., N.D., The Natural Pharmacy: Complete A-Z Reference to Natural Treatments for Common Health Conditions
"European mistletoe was the "golden" bough that saved the legendary Aeneas from the underworld. Habitat & Cultivation Native to Europe and northern Asia, European mistletoe grows on host trees, especially apple trees. It is harvested in autumn. parts Used Leaves, branches, berries. Constituents European mistletoe contains glycoproteins, polypeptides (viscotoxins), flavonoids, caffeic and other acids, lignans, acetylcholine, and, in the berries, polysaccharides. Viscotoxins inhibit tumors and stimulate immune resistance." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"European mistletoe was the "golden" bough that saved the legendary Aeneas from the underworld. Habitat & Cultivation Native to Europe and northern Asia, European mistletoe grows on host trees, especially apple trees. It is harvested in autumn. parts Used Leaves, branches, berries. Constituents European mistletoe contains glycoproteins, polypeptides (viscotoxins), flavonoids, caffeic and other acids, lignans, acetylcholine, and, in the berries, polysaccharides. Viscotoxins inhibit tumors and stimulate immune resistance." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"Kleijnen J, Knopschild P, (1994) mistletoe treatment for cancer. Review of controlled trials in humans. Phytomedicine 1:255-260. Kwaja TA et al, (1980) Experientia 36:599. Loew, B, In: Loew D, Rietbrock N: Phytopharmaka II: Forschung und klinische Anwendung, Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt, 1996. Luther P et al., (1980) Int J Biochem 11:429. Miiller J, (1962) Ger Offen DE 1:130:112. Olsnes S et al„ (1982) J Biol Chem 257:1371. Rentea R et al., (1981) Lab Invest. 44(1):43." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"The stem of mistletoe is used for its calming effect; in the treatment of mental and physical exhaustion; as a tranquilizer against nervous conditions such as agitation, anxiety and increased excitability. visci albi herba ¦ Rheumatism ¦ Tumor therapy adjuvant For treating degenerative inflammation of the joints by stimulating cuti-visceral reflexes following local inflammation brought about by intradermal injections. Also used as a palliative therapy for malignant tumors through non-specific stimulation." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"Schwarz T et al, Stimulation by a stable, standardised mistletoe preparation of cytokine production in an in vitro human skin bioassay. In: PM 62, Abstracts of the 44th Ann Congress of GA, 1996. Stirpe F et al, (1982) J Biol Chem 257(22): 13271. Timoshenko AV et al, Influence of the galactoside-specific lectin from Viscum album and its subunits on cell aggregation and selected intracellular parameters of rat thymocytes. In: PM 61(2):130-133. 1995. Uhlenbrock S, Weihnachten, Miraculix und die Anthroposophie. In: PZ 140(51/52):4602-4603. 1995. Wagner H et al, (1986) Planta Med (2): 102." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"I was impressed to leam that the Maoris were aware of the mistletoe's medical properties. mistletoe ?Viscum album ?was widely used by the Maoris for the prevention of illness and disease and nowadays it once again holds an important place in herbal medicine. Since the rediscovery of this plant it has been used as an excellent remedy for balancing blood pressure, to treat migraines and epilepsy, and is also used by cancer patients." --- Jan De Vries, Life Without Arthritis: The Maori Way
"Three subspecies of parasitic mistletoe ?one parasitic on broad-leaved trees and two on coniferous trees ?are native to Europe. Common mistletoe is the one that interests us most. The leafy tips of young twigs without the thick basal stems and without the berries are the parts used medicinally. These are collected only in the wild and therefore include, albeit in small quantities, also mistletoe subspecies parasitic on coniferous trees ?subsp. abietis and subsp. austriacum." --- Frantisek Stary, The Natural Guide to Medicinal Plants and Herbs
"Local reactions can occur with parenteral administration of mistletoe extracts (wheal formation, possibly also necroses), chills, fever, headache, anginal complaints, orthostatic circulatory disorders and allergic reactions. The wheal formation and the elevation of body temperature are considered signs of immune system stimulation and therefore as positive therapeutic effects. DOSAGE visci albi herba Mode of Administration: Fresh plant, cut and powdered herb for the preparation of solutions for injections. Preparation: A medicinal tea is prepared using 2." --- Joerg Gruenwald, Ph.D., PDR for Herbal Medicines
"Mistletoe. mistletoe is a cardiac tonic that stimulates circulation. Fifteen drops taken three times a day, or three cups of tea daily, help lower blood pressure and alleviate heart strain. mistletoe should not be overused, nor should the berries be eaten. Motherwort. Helps stabilize the electrical rhythm of the heart. The amount taken should be monitored by a doctor. Wild yam. Stimulates production of DHEA. Low levels of this hormone have been related to higher incidences of heart disease. Wild yam can provide added protection and is completely safe." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"Reinsubstanz Gegen Standardisierten Extrakt" [Comparative Studies on the Immunoactive Action of Galactoside-Specific mistletoe Lectin: Pure Substance Compared to the Standardized Extract], Arzneimittelforschung 43, no. 2 (February 1993): 166-69. Iscador, a mistletoe (Viscum album) extract, was shown to have an anti-breast-cancer effect. T. Hajto, "Immunomodulatory Effects of Iscador: A Viscum Album Preparation," Oncology, 43, suppl. (1986): 51-65. Breast cancer patients in a study were administered a single infusion of iscador, an extract of mistletoe (Viscum album) intravenously." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"Loranthaceae) A relative of mistletoe (Viscum album L.), Phrygilanthus eugenioides is used in the voodoo cult as a magical plant. It is said to have psychoactive or hallucinogenic powers (Schultes and Farnsworth 1982, 187*; Schultes and Hofmann 1980, 367*). Curiously, the ancient texts suggest that mistletoe may also produce psychoactive effects (cf. Benthamia alyxifolia). Podophyllum peltatum L." --- Christian Ratsch, The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications
"MISTLETOE Of two notable studies of mistletoe, the plant hung up at Christmas, one indicated that iscador, an extract from European mistletoe, when combined with lactobacillus, doubles the ability of natural killer cells to destroy malignant cells; while a second examination, reported at a 1992 AIDS conference, indicated one extract from the herb "had anti-HIV, immunomodulating and anti-cancer activities in 12 symptomatic HIV disease patients followed for 6 years." --- Gary Null, James Feast, AIDS: A Second Opinion
"Rudolph Steiner, PhD popularized the use of mistletoe in the early 20th century. A certain lectin in mistletoe has been found to inhibit the growth of proliferating cells. By the 1980s, about 40,000 patients worldwide were receiving Iscador, a fermented form of mistietoe that is injected. Iscador and its variations are licensed in Germany as dmgs. -Stanislaw R. Burzynski, MD, PhD theorized that certain anti-neoplastons, or naturally occurring peptides, could inhibit the growth of tumor cells without intermpting normal cell growth." --- Patrick Quillin, Beating Cancer with Nutrition
"PHARMACOLOGY: Despite the popular knowledge that the two types of mistletoe have opposite pharmacologic effects (ie, American mistletoe: Stimulates smooth muscle, raises blood pressure, increases uterine and intestinal motility; European mistletoe: Reduces blood pressure, antispasmodic, calming agent), investigations have shown that the stems and leaves of these plants contain the proteinaceous phoratoxins and viscotoxins and thus exert similar pharmacologic effects." --- Ara Dermarderosian, Guide to Popular Natural Products
"BOTANY: American mistletoe comprises the Phoradendron species and European misdetoes V. album, V. abi-etis and V. austriacum. Mistletoes are semiparasitic woody perennials commonly found on oaks and other deciduous trees. These evergreen plants produce small white berries and are used as Christmas ornaments. These plants should not be confused with the New Zealand mistletoe (Ileostylus micran-thus), which contains cytotoxic compounds that may be derived from the host tree {Podocarpus totara)." --- Ara Dermarderosian, Guide to Popular Natural Products
"PHARMACOLOGY: Despite the popular knowledge that the two types of mistletoe have opposite pharmacologic effects (ie, American mistletoe: Stimulates smooth muscle, raises blood pressure, increases uterine and intestinal motility; European mistletoe: Reduces blood pressure, antispasmodic, calming agent), investigations have shown that the stems and leaves of these plants contain the proteinaceous phoratoxins and viscotoxins and thus exert similar pharmacologic effects." --- Ara Dermarderosian, Guide to Popular Natural Products
"Mistletoe. mistletoe is a cardiac tonic that stimulates circulation. Fifteen drops taken three times a day, or three cups of tea daily, help lower blood pressure and alleviate heart strain. mistletoe should not be overused, nor should the berries be eaten. Motherwort. Helps stabilize the electrical rhythm of the heart. The amount taken should be monitored by a doctor. Wild yam. Stimulates production of DHEA. Low levels of this hormone have been related to higher incidences of heart disease. Wild yam can provide added protection and is completely safe." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"A study examining the effects of a mistletoe extract on breast cancer patients found an immune-enhancing effect. J. Beuth et al., "Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Immu-naktiven Wirkung von Galaktosid-Spezifischem Mistellektin. Reinsubstanz Gegen Standardisierten Extrakt" [Comparative Studies on the Immunoactive Action of Galactoside-Specific mistletoe Lectin: Pure Substance Compared to the Standardized Extract], Arzneimittelforschung 43, no. 2 (February 1993): 166-69. Iscador, a mistletoe (Viscum album) extract, was shown to have an anti-breast-cancer effect. T." --- Dr. Gary Null, The Woman's Encyclopedia of Natural Healing
"Journal Society Integrative Oncology 4: 3-7, 2006] mistletoe extract has been shown to reduce adverse effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy on the microcirculation and the immune system of cancer patients. [Anticancer Research 25:601-10, 2005] Iscador is popular in Germany where it was recently shown to improve survival (slightly) among malignant melanoma patients. [Arzneimiftelforschung 55:38-49, 2005] Iscador has also been shown to prolong survival among breast cancer patients." --- Bill Sardi, You Don't Have to be Afraid of Cancer Anymore
"Iscador (Mistletoe) Iscador is the trade name for a mistletoe preparation that has been used by European physicians since 1920. Iscador consists of fermented extracts of European mistletoe (Viscum album), some forms of which are combined with small amounts of metals to produce anticancer effects.227 Originally conceived by Rudolf Steiner (1864-1925), Austrian scientist and founder of anthroposophic medicine, the therapeutic success of Iscador has been reported in nearly 5,000 case studies." --- Larry Trivieri, Jr., Alternative Medicine the Definitive Guide, Second Edition
"History & Folklore In Norse mythology, a mistletoe bough was used to slay Balder, the god of peace. The plant was subsequently entrusted to the goddess of love, and kissing under it became obligatory. Medicinal Actions & Uses European mistletoe is chiefly used to lower blood pressure and heart rate, ease anxiety, and promote sleep. In low doses it also relieves panic attacks, headaches, and improves concentration. European mistletoe is also prescribed for tinnitus and epilepsy. In anthroposophical medicine, extracts of the berries are injected to treat cancer." --- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants
"In this review article, the author notes that studies from their lab have demonstrated that mistletoe extact exhibits significant anticancer activity against a variety of experimental tumor systems, in vitro and in vivo, particularly those modeling for lung, breast and colon carcinomas. —T.A. Khwaga, "Biopharmacological Studies of Different Components of Viscum Album (Mistletoe)," Anticancer Research, 10(5B), 1990, p. 1374-1375. This study examined the antiproliferative effects of Viscum album C, Viscum album Qu and Viscum album M on melanoma cell lines." --- Gary Null, Ph.D., The Clinician's Handbook of Natural Healing
"This study examined the cellular aspects of the immunomodulating activity of propriety mistletoe extract (Eurixor) standardized for mistletoe lectin-1 (ML-1) in 20 mammary cancer patients. Results showed that subcutaneous injections of the different dosages (0.5 and 1.0 ng ML-1/kg body weight, twice a week, for 5 weeks) led to statistically significant increases of defined peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets (helper T cells, natural killer cells) which are gerneally beleived to be involved in antitumor activity." --- Gary Null, Ph.D., The Clinician's Handbook of Natural Healing
"This study isolated a tumor reducing component from mistletoe extract (Iscador) and identified to be a peptide of approximate molecular weight 5000. The isolated peptide reduced the solid tumour induced by Dalton's lymphoma ascites tumour cells in mice and was highly cytotoxic to the DLA cells but was not cytotoxic to normal lymphocytes, indicating a cell dependent specificity. —G. Kuttan, et al., "Isolation and Identification of a Tumour Reducing Component from mistletoe Extract (Iscador)," Cancer Letters, 41(3), August 30, 1988, p. 307-314." --- Gary Null, Ph.D., The Clinician's Handbook of Natural Healing
"Petricic J and Kalogjera Z: Isolation of glucosides from mistletoe leaves (Viscum album L.). Acta Pharm Jugosl 30,163,1980. 10. Wagner H, et al.: Phenylpropanes and lignanes of Viscum album. Planta Medica 2,102, 1986. 11. Petkov V: Plants with hypotensive, antiatheromatous and coronary dilatating action. Am J Chin Med 7,197-236,1979. 12. Hajto T: Immunomodulating effects of Iscador: A Viscum album preparation. Oncology 43(Suppl. 1), 51-65,1986. 13. Jordan E and Wagner H: Detection and quantitative determination of lectins and viscotoxins in mistletoe preparations." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"Since pharmacologically active compounds appear to be concentrated within the mistletoe, different host trees providing different chemical constituents could be used for different therapeutic action. In addition, the proteins/lectins are present only in aqueous (water) extracts, indicating therapeutic activity may differ from aqueous and alcoholic/aqueous (tincture) extracts. The alcoholic/aqueous extracts would also demonstrate considerably less toxicity. History and folk use Mistletoe was held in great reverence by the druids. Dressed in white robes, they would search for the sacred plant." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"The historic use of mistletoe for cancer is now being tested by research. It is interesting to note that mistletoe grows on trees similar to a cancerous growth in the body. Contraindications: It is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the emmenagogue and abortifacient effects in animals which are associated with tyramine. It is also contraindicated in protein hypersensitivity and chronic, progressive infections like tuberculosis and AIDS. This is a potentially dangerous herb and should only be used by skilled practitioners." --- Sharol Tilgner, N.D., Herbal Medicine From the Heart of the Earth
"The blood pressure-lowering activity may depend on the form in which the mistletoe is administered and the host tree from which it was collected. Studies indicate aqueous extracts are more effective and the highest hypotensive activity was demonstrated by a macerate of leaves of mistletoe growing on willow, gathered in January.11 If nonprotein viscum components (e.g., flavonoids, phenol carboxylic acids, phenylpropanes, and lignans) were shown to possess blood pressure-lowering action, then alcoholic solutions (tinctures and fluid extracts) may be useful solutions." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"Even the mistletoe growing on the mulberry tree has positive therapeutic properties not unlike European mistletoe (Viscum album). Both are used for hypertension and are classified as being antispasmodic and antirheumatic. Both have analgesic and anticarcinogenic properties. They are used for hypertension and to relieve rheumatic pains and spasms especially of the upper part of the body. Dose, 9-15 grams." --- Michael Tierra, The Way of Herbs
"In one study of women with breast cancer who were undergoing chemotherapy, half the patients were given a preparation of mistletoe, while half were given a placebo. After the fourth round of chemo, those getting mistletoe had three times as many white blood cells as the control group (3,000 count vs. 1,000 count). The Journal of the National Cancer Institute reported that polyphenals from green tea induced cell death in carcinoma cells in vitro. An extract of green algae showed a "pronounced antitumor effect" in mice." --- The Disinformation Company, Everything You Know Is Wrong: The Disinformation Guide to Secrets and Lies
"Skeptics make fun of the manner in which mistletoe is gathered. A quack-baiting Website sneers at claims that "the time of picking the plants [is] important because they react to the influences of the sun, moon, and planets." However, there is a core of rationality to many traditional practices. Certain chemicals in mistletoe can combine with metals to form organometaflic compounds, which have different biological or medicinal properties than the ones naturally found in the plant." --- Ralph W. Moss PhD, Herbs Against Cancer: History and Controversy
"Those with late-stage cancers say mistletoe makes a dramatic improvement in general health. See Materia Medica for dose. (Mistletoe resources, page 167.) • Vaccine-like preparations of killed bacteria stimulate dramatic activity in the immune system, including an increase in tumor necrosis factor which causes tumors to hemorrhage and liquefy. These preparations are currendy being tested on women with breast (and ovarian) cancers. • Chemotherapy is being urged on more and more women in earlier and earlier stages of breast cancer." --- Susun S. Weed, Breast Cancer? Breast Health! The Wise Woman Way
"Results & Notes: mistletoe has been used clinically in Europe for the treatment of breast (and other) cancers since 1926. It is most effective when injected under the skin near the tumor, but the tincture is also used orally as a systemic treatment. mistletoe is said to work by causing an inflammatory reaction which walls off the tumor, checking its growth and spread. References: 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, 18, 21, 23. Illustrated on page 158." --- Susun S. Weed, Breast Cancer? Breast Health! The Wise Woman Way
"Other Names: European mistletoe (Do not use American mistletoe) Type: Stimulating/Sedating Found in: Semiparasitic on deciduous trees in Europe, northern Asia. Part Used: Leaves and young twigs collected just before berries form; best after fermentation in water. Actions & Uses: Inhibits tumors; cytotoxic; cytostatic; enhances immune system (increases macrophages, natural killer cells, and T-cells); increases weight of thymus; tonifies heart and nerves. Important Constituents: Flavonoids, lectins, polypeptides, polysaccharides, saponins, tannins, tri-terpenes, viscotoxin." --- Susun S. Weed, Breast Cancer? Breast Health! The Wise Woman Way
"Heiny BM: Adjuvant treatment with standardized mistletoe extract reduces leukopenia and improves the quality of life of patients with advanced carcinoma of the breast getting palliative chemotherapy (VEC regimen). Krebsmedizin 12, 3-14,1991. 29. British Herbal Medicine Association, Scientific Committee: British Herbal Pharmacopoeia. British Herbal Medicine Association, Cowling, England, 1983, pp. 235-236. 30. Khwaja TA, et al.: Isolation of biologically active alkaloids from Korean mistletoe Viscum album, coloratum. Experientia 36, 599-600,1980. 31." --- Michael T. Murray, N.D., The Healing Power of Herbs: The Enlightened Person's Guide to the Wonders of Medicinal Plants
"Pharmacological activity of phenyl-propanoids of the mistletoe, Viscum album L. Host Pyrus caucasica Fed.', Phytomedicine 5: 11-17. Panossian, A., Wikman, G. and Wagner, H. 1999, 'Plant adaptogens III. Earlier and more recent aspects and concepts on their mode of action', Phytomedicine 6: 287-300. Pieretti, S., Di Giannuario, A., Capasso, A. and Nicoletti, M. 1992, 'Pharmacological effects of phenylpropanoid glycosides from Orobanche bederae', Phytotherapy Research 6: 83-93. Pintao, A., Pais, M., Coley, H. and Judson, I." --- Andrew Pengelly, The Constituents of Medicinal Plants: An Introduction to the Chemistry and Therapeutics of Herbal Medicine
"A Swiss study of fourteen breast cancer patients showed that a standardized extract of mistletoe, iscador, increased the rate at which breast cells were able to repair their DNA. Repairing DNA prevents mutations that can result in the formation of cancerous cells. At the beginning of the study, the rate at which cancer patients' cells repaired DNA damage was only 16 percent of that in healthy individuals. After just nine days of treatment, the rate increased to nearly 50 percent. In animal studies, mistletoe extracts prevent the spread of melanoma to lung tissue by approximately 80 percent." --- Phyllis A. Balch, CNC, Prescription for Herbal Healing: An Easy-to-Use A-Z Reference to Hundreds of Common Disorders and Their Herbal Remedies
"Tumors that are ordinarily immune to natural killer (NK) cells are conditioned by treatment with mistletoe to allow NK cells to "lock onto" and destroy cancer cells. mistletoe extracts increase the activity of NK cells by as much as five- to tenfold. The extracts also stimulate movement of immune cells called T cells that "patrol" the body seeking cancer and infection. In addition, these extracts also increase the production of beneficial free radicals that fight a wide range of cancers." --- Phyllis A. Balch, CNC, Prescription for Herbal Healing: An Easy-to-Use A-Z Reference to Hundreds of Common Disorders and Their Herbal Remedies
Fritz-Albert POPP Patents
Example
In any case, a DC voltage of 80 volts is applied for a period of 5 seconds. At the same time, the intensities of photon emission (in number of photons / 100 ms) are measured over the period of 5 s. The measurement is repeated three times. The mean values and scatterings of the three measurements are formed. Table I contains the results. Table I
The result shows that this method can significantly detect 10 bacteria / ml.
ZA9208094 -- Method and means of determining the health conditions of a living creature.
The invention relates to a method and device for determining the state of health of a living being. The invention provides for a selected, physiological parameter of the living being, e.g. the conductivity of the skin, to be recorded on a statistically significant multiplicity of measuring points distributed over a defined part of the body of the living being, for the frequency distribution of the recorded measurements to be determined and compared with a reference frequency distribution of the selected, physiological parameter. The reference frequency distribution is a logarithmic distribution which can be determined directly from the measurements obtained from the particular test subject by statistical methods. The invention permits reliable statements to be made regarding the overall state of health of the test subject.
US7692788 -- Method for quickly determining qualities/qualitative changes in any system
The invention relates to a method for testing the slightest quality differences or quality features of any objects and agents interacting therewith based on measuring the percentage scatter of "ultraweak" photon emissions ("biophotons" in biological systems) and the delayed luminescence in a scatter chamber (darkroom). These scatter percentages can vary to such an extent as to enable the sufficiently sensitive registration of slightest quality differences (quality features).
US4458531 -- Method of and apparatus for examining biological effects in cell-lots
In a method of testing the biological effects of cell-lots, which release a characteristic or stimulatable ultra-weak photon radiation, the intensity and/or the photon statistic of the ultra-weak photon radiation is measured, as the test factor, for the purpose of the in vitro examination of substances for possible cell-damaging or regenerating effects, or for the purpose of carrying out quality control on biological substances, such as foodstuffs, edible plants or seed materials.
EP0430150 -- Method for testing quality and quality changes of biological systems and organochemical compositions interacting with these systems using measurements of ultraweak photon emission.
Known status parameters for the quality of biological systems, foodstuffs and organic chemical compounds interacting with the latter are with the methods of comparative statistical analysis with measured parameters of ultraweak photon emission. This makes it possible to reflect reproducibly the quality content and the vitality of a biological system in the sense of Erwin Schrödinger's quality term by means of measured parameters, to measure the quality of foodstuffs and to determine in advance expected changes in quality on storage, and to predict the biocompatibility of organic chemical compounds. Foodstuffs irradiated for preservation purposes can still be distinguished significantly from non-irradiated even one year after the irradiation by the intensity of the photon emission. Environmental effects on live systems can be characterised almost directly as environmental stress or damage by observing the ultraweak photon emission over a short time.
EP1776042 -- DEVICE FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FUNCTIONAL VALUES
The invention relates to a device for the determination of functional values of biological systems, whereby in particular, the conductivity of the skin is recorded as a functional value. The measured values for the conductivity are determined using an electrode matrix (1) in a measuring device (11), whereby a current circuit to a reference electrode (13) is formed and the measured values are subsequently stored and analysed.
EP1340066 -- METHOD FOR DETECTING BACTERIAL INFECTION
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacterial infection or contamination of or in products in order to be able to rapidly determine the product's quality or sterility. To this end, the intensity of photon emission of a nutrient medium is determined and measured with a sample of the object to be examined.
EP1188041 -- METHOD, SYSTEM AND USE OF MEASURING DEVICES FOR DETERMINING THE GERMINABILITY OF SEEDS
A process (I) and apparatus for determining the germination characteristics of seed corn by bio-photon and water moisture detection, are new. In a process (I) to determine the germination capacity of seed grain especially cereals, the seed grain is first exposed to light pulses for a defined period and the exposure then terminated. A measurement is made of at least one characteristic of the light then emitted by the seed without further light stimulation especially the residual luminescence or spontaneous light emission. The light emitted gives an indication of the germination capacity of the seed. In addition a further measurement is made especially of the seed grain water content, and is used as a correction factor to the germination characteristic based on the light value. An Independent claim is also included for apparatus for use in (I).
EP1126271 -- Method and device for determining the malignancy of tumor tissue and for choosing substances beneficial to the tissue
Method involves measurement of the bio-photon emission from tumor tissue using a very sensitive light detector. The tissue can first be excited using illumination with suitable wavelength light, using ultrasound, etc and then the value of emitted light measured. From the measurements a suitable medicine can be selected to treat the tumor. An Independent claim is made for a system for treating malignant cancers by determining the degree of malignancy from light measurements and then determining the optimum medicine.
DE102005058332 -- Method for optimal interpretation of data evaluating regulatory capacity of biological system...
One of the physiological parameters of a biological system in particular of a human being, which can be the galvanic skin response, is measured at a large number of subjects. The data are evaluated by using various appropriate statistical methods. The log-normal distribution and the Gaussian distribution are calculated. The resulting matrix is used as a base for a factor analysis already containing the data of a reference group. The position of the factors can be used as a criterion for the evaluation of the condition of an individual regarding the regulatory capacity of his/her system.
DE102004055200 -- Functional value e.g. regulating capability, determining method for e.g. human being...
The method involves evaluating a light signal after a deviation from a pure random distribution and a correlation to an ideally regulating distribution. A strewing portion of a photon is measured, where the photon is used for stimulation of a biological system. The light signal is utilized as a trigger pulse for treatment of a relevant skin area of the biological system.
DE10355348 -- Function data determination method e.g. for regulation capabilities of biological system...
The method involves collecting a multiplicity of measured values of the conductivity of the skin and determining the frequency distribution of the measured values. The frequency distribution of the measured values is compared with a normal distribution (1) and a logarithmic normal distribution (2). The conductivity of the skin is determined on a hand. Approximately 500 measured values in approximately 10 minutes are determined. An independent claim is included for a device for the determination of function values.
DE10147701 -- Testing for the smallest possible quality differences between biological tissue by measurement of bio-photon emission and application of photon count statistics
Method for testng for the smallest possible quality differences between biological tissue by measurement of bio-photon emission and delayed luminescence. Measurement of photon emission is with or without the effect of interacting agents. Differences in measurements are determined using photon count statistics.
DE10132549 -- Determining heat regulating capacity of biological systems involves irradiating with infrared light, detecting relaxation of photon intensity and compensating using hyperbolic function
The process involves determining the quality and/or quality changes of biological systems by measuring the ultra-weak photon emission of a system subjected to the light after ending the radiation. The biological system is irradiated with infrared light and the relaxation of the photon intensity is detected against time and then the relaxation function of the investigated system is compensated using a hyperbolic function.
DE4439451 -- Examining changes in the condition of biological tissue
In a method for examining changes in the condition of human, animal or plant tissue by measurement of ultra-weak photo emission, the new feature is that the measuring parameters of the emission are employed.
DE4401169 -- Faster procedure for detecting differences in fluid characteristics
A method for discriminating between the characteristics of similar fluids employs differences in the respective photon emissions of fluid samples after their identical excitation at a controlled temperature. Each sample (1) is successively enclosed in a transparent quartz vessel having a pair of titanium electrodes (2,3) supplied with a DC potential of typically 18 volts. An excitation system (4) activates the sample either by energising a tungsten light source of controlled spectrum or by EM/sound waves of constant intensity and wavelength. After a definite period of excitation the luminescence of the sample is measured by the detector(s).
DE4308520 -- Method for differentiating between homozygotes, heterozygotes and normal cells of an organism
A method is specified for differentiating between homozygotes, heterozygotes and normal cells of an organism. It is characterised in that the cells to be investigated are irradiated with UV light and/or treated with a substance which partly damages the cells and the intensity of the photon emission of these cells is subsequently measured. The method is preferably used before X-ray diagnosis in which the risk of inducing a disease triggered by the radiation is to be no greater than the probability of early diagnosis of a disease.
DE3040855 // DE3038255 -- Examining biological effects on foodstuffs of seeds - by measuring intensity of ultra-weak photon radiation in vitro
A measurement of the spontaneous or stimulated emission of ultra-weak photon radiation is used as an in vitro parameter of a cell lot. The parameter is used to detect possible cell-damaging or regenerating effects or to act as a quality control. The measured quantity is either the photon intensity or a photon statistic e.g. the distribution of numbers of photons emitted in a measuring interval. The ultra-weak radiation is typically in the infra red band and has an energy very much less than that of thermal radiation. Typically the radiation is 10 power (-10) less than thermal radiation. The radiation is detected by a photo multiplier with a gain of over 10 power 6. The method may be used to determine whether a cell lot is in a healthy state. Alternatively it can be used to determine the effect of an agent on the cells. The method is partic. suitable for quality control in foodstuffs.
http://biophotonservices.com/dr-fritz-albert-popp/biophotons-and-relationship-to-the-ultraviolet-spectrum/
Biophoton Services // 1151 Harbor Bay Parkway, Suite 100, Alameda, CA 94502
Biophotons
: How they Influence Healing by Increasing the
Communication of DNA.
Dr. Fritz Albert Popp showed with this experiment using onions that UV light causes onions to communicate with each other. He showed that cancer tumors reacted to high intensity levels of UV light in the range of 380 nanometers. By using a method called photo repair he illuminated cells with a weaker intensity of UV light, causing the DNA to undergo rapid healing.
It is only when UV light is at a lower intensity level that the healing of DNA occurs. With the help of a lab assistant, Dr. Popp built a machine called the “photomultiplier” which measures weak photon emissions that stimulate healing. While measuring these photons in humans, he discovered that the cells of the body have a biological rhythms of 7, 14, 32, 80 and 270 days respectively. These numbers all readily divided into 7. It also showed that people who had these disturbed biological rhythms were cancer patients. His research also showed that stress triggered an increase in biophotons, which short term can be beneficial to good health.
It is no surprise that foods highest in biophotons are also used as natural cancer cures, especially when you eat them within 3 hours after being picked from the ground. Dr. Gabriel Cousens states that people who have a junk food diet register 1,000 or less biophotons in their systems, whereas people eating a fresh raw food diet have 83,000 or more biophotons in their bodies.
Scientist Dr. Pjotr Garajajev used UV photons to transfer a frogs embryo into a salamanaders embryo, which in turn caused the salamander to give birth to a frog. Below is a video showing a machine where German researchers add biophotons to a dead leaf of a plant and how it “brings it back to life” again.
It is my theory that because mistletoe is highest in biophontons, which are connected to sunlight, and vitamin D promotes bone growth and stimulates the immune system, and many leukemia patients show a vitamin D deficiency, than foods highest in these “biophotons” would increase the flow of biophotons in the body.
Foods highest in biophotons: wild dandelion greens, nettles, grasses, mushrooms, nuts and berries
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18314258
Cancer Lett. 2008 Jun 18;264(2):218-28.
Molecular mechanisms of mistletoe plant extract-induced apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia in vivo and in vitro.
Seifert G1, Jesse P, Laengler A, Reindl T, Lüth M, Lobitz S, Henze G, Prokop A, Lode HN.
Abstract
Viscum album (Mistletoe) is one of the most widely used alternative cancer therapies. Aqueous mistletoe extracts (MT) contain the three mistletoe lectins I, II and III as one predominant group of biologically active agents. Although MT is widely used, there is a lack of scientifically sound preclinical and clinical data. In this paper, we describe for the first time the in vivo efficacy and mechanism of action of MT in lymphoblastic leukemia. For this purpose, we first investigated both the cytotoxic effect and the mechanism of action of two standardized aqueous MTs (MT obtained from fir trees (MT-A); MT obtained from pine trees (MT-P)) in a human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell line (NALM-6). MT-A, MT-P and ML-I inhibited cell proliferation as determined by Casy Count analysis at very low concentrations with MT-P being the most cytotoxic extract. DNA-fragmentation assays indicated that dose-dependent induction of apoptosis was the main mechanism of cell death. Finally, we evaluated the efficacy of MT-A and MT-P in an in vivo SCID-model of pre-B ALL (NALM-6). Both MTs significantly improved survival (up to 55.4 days) at all tested concentrations in contrast to controls (34.6 days) without side effects.
Partial Bibliography
Popp, E.A. : "Photon Storage in Biological Systems";Electromagnetic Bioinformation, Proceedings of the Symposium, Marburg, September 5, 1977 (Munchen-wien-Baltimore (1979)
Popp, F. A., Ruth, B., Bahr, W., Bohm, J.,Grass, P., Grolig, G, Rattemeyer, M. Schmidt,H.G., and Wullle, P.;“Emission of Visible and Ultraviolet Radiation by Active Biological Systems”, Collective Phenomena, Vol. 3, pp. 187-214 (1981)
Popp, E.A., ed., Electromagnetic Bioinformation, Urban & Schwartzenberg, Munchen-Wien- Baltimore (1989)
Popp, F.A., et al., Recent Advances in Biophoton Research and Its Applications, eds. F.A.Popp et al, World Scientific, Singapore (1992)
Popp, F.A., and Li, K.H., “Hyperbolic Relaxation as a Sufficient Condition of a Fully Coherent Ergodic Field,” Int. J. Theor. Phys., Vol. 32, pp. 1573-1583 (1993)
Popp, F.A., Chang, J.J., Gu, Q., and Ho, M.W., “Nonsubstantial biocommunication in terms of Dicke’s theory,” in Bioelectrodynamics and Biocommunication, ed. by Ho, M.W., Popp, F.A., and Warnke, U., World Scientific, Singapore (1994)
Popp, F.A.; Gu, Q.; and Li, K.H.; “Biophoton Emission: Experimental Background and Theoretical Approaches,” Mod. Phys. Lett. B, Vol. 8, Nos. 21 & 22, pp. 1269-1296 (1994a)
Popp, F.A., Chang, J.J., Herzog, A., Yan, Z., and Yan, Y., “Evidence of Non-Classical (Squeezed) Light in Biological Systems,” Physics Letters A, Vol. 293, Nos. 1-2, pp. 98-
102 (2002)
Popp, F.A., “Properties of Biophotons and Their Theoretical Implications,” Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, Vol. 41, May, pp.391-402 (2003)
Popp, F.A., “Biophysical Aspects of the Psychic Situation,” International Institute of Biophysics, http://www.lifescientists.de/ib0203e_1.htm
MISTLETOE PATENTS
KR20100102471 -- EFFECT OF KOREAN MISTLETOE
EXTRACT ON THE EXTENSIONS OF LIFE SPAN
Abstract -- PURPOSE: A
Viscum album extract with anti-aging activity is provided to
ensure life extension and to improve human health by being
applied to functional foods or pharmaceutical compositions.
CONSTITUTION: A Viscum album extract has an anti-aging
activity. The Viscum album extract is obtained by cold water
extraction or hot water extraction. The cold water extraction
is performed by adding 1L of water to 200g of Viscum album and
stirring for 2-4 hours. The hot water extraction is performed
by adding 1L of water to 200 of Viscum album cold water
extract and heating at 100[deg.]C for 30 minutes. A functional
food composition with anti-aging activity contains Viscum
album extract as an active ingredient. A pharmaceutical
composition for anti-aging activity contains Viscum album
extract as an active ingredient.CN101486772
-- Mistletoe polysaccharide, as well as preparation
and use thereof
Abstract -- A mistletoe
polysaccharide consists of glucose, arabinose, galactose,
glucuronic acid and galacturonic acid, with the molecular
weight of 1.1 multiplied by 10-3.4 multiplied by 10Da, the
terminal group carbon of Alpha-configuration, and the specific
rotation of [Alpha]D being equal to plus 134.6 degrees to plus
167.3 degrees; and the basic skeleton of the polysaccharide
consists of 1-5 glycosidic bond connected Arab sugar and 1-6
glycosidic bond connected galactose. The mistletoe
polysaccharide is obtained by water extraction and alcohol
precipitation, an ion exchange chromatography and a molecular
sieve chromatography by further purification. The mistletoe
polysaccharide has obvious inhibition action on Hela cells and
mouse transplanted tumors S-180, so the polysaccharide can be
used for preparing drugs for treating cancer.KR20090120348 -- EXTRACTS ISOLATED FROM
MISTLETOE FOR ENHANCING POWER OF EXERCISE PERFORMANCE AND
SUPPRESSING FATIGUE
Abstract -- PURPOSE: A
composition containing Viscum album extract is provided to
enhance exercise ability and suppress fatigue in muscle.
CONSTITUTION: A Viscum album extract which relieves fatigue is
obtained by cold water extraction or hot water extraction. The
cold water extract is obtained by adding 1L of water to 200g
of Viscum album then stirring at 4[deg.]C for two hours. The
hot water extract is obtained by adding 1L of water to 200g of
residual extract of cold water then heating at 100[deg.]C for
30 minutes. A functional food composition or pharmaceutical
composition for enhancing exercise activity or relieving
fatigue contains the Viscum album extract as an active
ingredient.KR100841453
--
THE METHOD OF
EXTRACTING USEFUL COMPONENT FROM MISTLETOE, AND THE
EXTRACT
Abstract -- A method for
extracting a useful anticancer component from mistletoe(Viscum
album L.) is provided to inhibit hypersensitivity causing
allergy and improve anticancer and immunity cell-activating
effects by fermentation, and reduce the extraction costs by
simplifying the extraction procedures. A method for extracting
a useful component from mistletoe comprises the steps of: (a)
dipping mistletoe in water of pH 5.5-5.7 for 2 hours; (a)
steaming the dipped mistletoe in a vessel to sterilize it; (c)
inoculating a mycelium of shiitake mushroom into the
sterilized mistletoe and fermenting it at 25-27 deg.; C for
2-3 weeks, and further comprises a step (d) of drying and
pulverizing the fermented mistletoe, extracting and filtering
the mistletoe powder with sodium chloride solution, and
regulating pH of the filtered solution by treatment of
acid/alkali, wherein the useful component is lectin having
anticancer activity. Further, 1 to 10% of yeast powder is
additionally added into the water in the step (a).DE19641518 -- Mistletoe chitin-binding lectin
Abstract -- Mistletoe
chitin-binding lectin in the form of a homo-dimeric protein
consisting of two identical subunits with a molecular weight
of 10.8 kDa, is new. Also claimed is a process for producing
the lectin by extraction from plant material followed by
chromatography.ill be explained in more detail:
Example 1
Isolation of a chitin mistletoe lectin
1 kg leaves and twigs of mistletoe (Viscum album L.) are homogenized in 10 l of 20 mM acetic acid with a Waring blender.
The homogenate was filtered and centrifuged (8,000 g for 10 minutes), the supernatant is decanted and filtered through glass wool (to remove the floating particles).
After addition of 1.5 g / l CaCl 2 with 1N NaOH, the extract is adjusted to a pH 9.0 and held for 3 hours at 2 ° C.
The precipitate is separated by centrifugation (3,000 g for 10 min) removed and the clear extract is adjusted with 1 N acetic acid to pH 3.0.
After standing overnight in a cold room, the extract was centrifuged again (3,000 g for 10 minutes) and the supernatant is filtered through filter paper (Whatman 3MM).
The filtrate is dissolved in an equivalent amount of distilled water and applied to a cation exchange column (10 cm x 5 cm, 200 ml volume) of S Fast Flow (Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden) equilibrated with 20 mM acetic acid.
After loading the proteins, the column with 2 liters of 20 mM sodium formate (pH 3.8) is washed and the bound proteins were eluted with 500 ml of 0.5 M NaCl in the same buffer.
To eliminate the type 2 RIP lectins ML I, ML II and ML III, the desorbed protein mixture is subjected to the S Fast Flow column following affinity chromatography on a galactose-Sepharose 4B and fetuin-Sepharose 4B.
Thus, the partially purified protein fraction with 1 N NaOH to pH 7.4 and is set to a column (10 cm x 2.6 cm, about 50 ml) with galactose-Sepharose 4B applied, which is eliminated in ML-I.
After passing through the protein fraction of the column with 200 ml of PBS (phosphate buffered saline).
The ML-I-free fraction and the washed solution to a fetuin-Sepharose 4B column (10 cm x 2.6 cm, about 50 ml) was added for removal of ML II and ML III.
The unbound proteins (which are free of ML II, ML II and ML III) are the first 200 ml of PBS wash solution and combined on a chitin column (20 cm x 2.6 cm, approximately 100 ml - Type C-7170, Sigma brought).
Unbound proteins are removed by washing the column with PBS until the A280 fell below 0.01.
At the end of the lectin was desorbed with 20 mM acetic acid and then either dialyzed against PBS and stored at -20 ° C until his use or dialyzed against water and lyophilized.
Example 7
Influence the immune system
VisalbCBA causes the release of cytokines TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-j from peripheral mononuclear cells from healthy blood donors at concentrations> 90 ng / ml