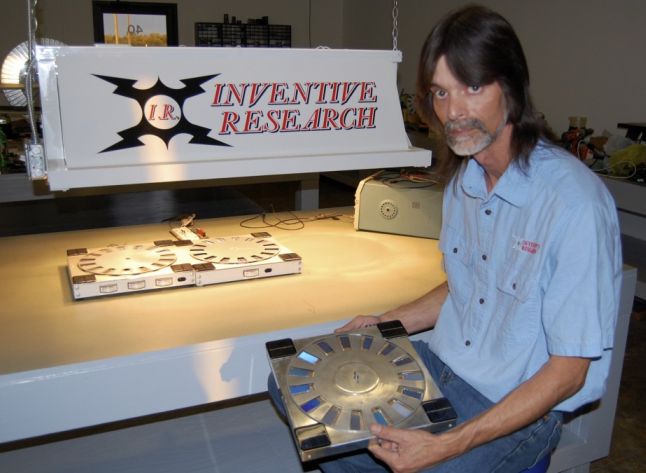
Contact : Stan Widows
Inventive Research
Div. S.R. Widows Co. Inc.
800-357-6290
Jason Oliver
& AC Solar Generator
Inventive Research, a
Division of S. R. Widows Company, Inc., of Indiana, has patented a
way to generate AC power directly from a solar panel. Why is this
so important? It makes it possible to simply hook the solar panels
directly into the power grid without the need for expensive DC to
AC power conversion equipment. This invention, when
commercialized, will make the cost of solar power more practical
and affordable.
We’ve heard about the promise of cheap solar energy now for
decades. You’d think by now that at least in the world’s sunniest
areas all the cities would be supplementing their power with clean
renewable solar power. Sadly this is not the case.
Here’s the problem. Solar panels today produce DC power which has
to be converted to AC to be used by by most homes and businesses.
The price of solar panels combined with the price of inverters,
phase synchronizers, installation and maintenance has made the
price of solar prohibitive. Add to that the loss of power from the
different components used in the DC to AC conversion process and
it becomes even more unattractive. But what if there was a better
way?
Nearly a century ago a battle between two of America’s most
influential inventors decided the power we use today. Thomas
Edison’s inventions generated and utilized DC power and Nikola
Tesla’s inventions used his newly discovered AC power. Tesla’s AC
eventually won out because it could be transfered over long
distances more efficiently.
Jason Oliver, lead
inventor for Inventive Research is not the typical researcher;
he’s an automotive master mechanic from Indiana who more than a
decade ago developed a passion for the inventions of Tesla. He
looked for clues from how power is generated today to come up with
their newest invention, the AC generating solar panel.
Today AC power is produced for the power grid by AC generators.
The generators are powered by mechanical energy provided by water
turbines (hydro-electric) or steam turbines powered from coal,
natural gas or nuclear fuel. The mechanical energy rotates the
coils of the generator in a magnetic field to produce voltage.
Because the conductor coil of the generator flips direction during
rotation in the magnetic field the resulting voltage produced is
sinusoidal or AC.
Inventive Research replicated this sinusoidal voltage by
mechanically manipulating alternate banks of solar cells to turn
off and on. They spent many years years developing this
technology. They call it the AC Solar Generator. It’s so simple
and practical you won’t believe it hasn’t been done before, but it
hasn’t. Inventive Research and their attorneys did an exhaustive
patent search to make sure of that.
The process Inventive Research used to do this is simple but pure
genius in its application. Jason arranged modified standard solar
cells into a circular pattern mounted on a base.
Half of the cells are wired in one circuit and half in another
circuit
Mounted above the solar cells is a spinning disk powered by a DC
electric motor. The DC motor gets its power from four small DC
solar cells mounted in the corners of the base. The disk has
portals cut into it allowing light to pass through to every other
solar cell below it. As the disk spins each of the banks of solar
cells is alternately exposed to light and alternately produce
power. When the portal is half way between the two cells the
voltage cancels and drops to zero. The resulting voltage is
sinusoidal or AC. It can even be configured to produce three phase
AC power...
Combining the phase matching with the alternating current
generation is what allows the AC solar generator to create AC
power without the losses and cost associated with the AC to DC
power conversion process.
Other benfits include:
• Generates free energy from the sun
• Non-polluting energy reduces emissions: Has no direct impact on
the environment
• It’s easily scalable
• Grid-Tie systems allow you to sell excess electricity back to
the utility
• Can be installed and operated anywhere including areas of
difficult access and remote locations
• Helps get us off dependence on foreign oil
• PV cells make no noise and give off no exhaust
This is truly a transforming technology. The AC solar generator
has the potential to reduce the use of fossil fuels tremendously
if you just imagine them installed photovoltaic solar power
centers around the country generating supplemental power for the
grid.
Inventive Research is expecting to receive the final patents later
this year. If you are interested in licensing or purchasing the
patents for this technology you can contact Stan Widows at
Inventive Research a division of S.R. Widows Co. Inc. at
800-357-6290
Inventor: OLIVER JASON ALLEN
EC: IPC: H01L25/00;
H01L25/00
Abstract -- A device,
system and method for generating alternating current (a/c)
electricity directly from photovoltaic cells utilize an array of
photovoltaic cell pairs that are each connected in anti-parallel
to form an a/c junction. The system, device and method
mechanically gradually exposes and shades photovoltaic cell pairs
to sunlight to generate alternating current electricity at an a/c
junction of the solar cell pairs. Gradually and alternately
exposing and shading the two anti-parallel connected solar cells
of each solar cell pair causes the amplitude and polarity of the
electricity at the a/c junction to gradually rise and fall to
produce alternating current electricity. The gradual, alternating
exposure and shading of the two anti-parallel solar cells is
accomplished by mechanically covering and exposing the solar cell
pairs. This is efficiently accomplished by a rotating segmented
disc positioned over an array of solar cell pairs.
Description
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to photovoltaics (i.e. technology
and research related to the application of photovoltaic cells in
producing electricity for practical use) and, more particularly,
to devices, systems and methods for generating alternating current
electricity from photovoltaic cells.
Background Information
The demand and need for clean and renewable energy is becoming
more urgent as earth undergoes global climate changes. Generation
of electricity from coal produces over 50% of the carbon dioxide
released into the atmosphere each year. Coal and other fossil
fuels will also eventually run out. The hydroelectric power
generation of electricity is limited to places where there is an
adequate water source. Nuclear energy for the creation of
electricity has the drawback of creating nuclear waste. However,
one type of clean renewable energy is solar energy or sunlight.
Solar energy is a constant source of clean energy that can shine
on all areas of the surface of the planet. Solar energy or
sunlight can be converted into electricity by a photovoltaic cell.
A photovoltaic cell known as a solar cell captures and converts
sunlight into electricity. A solar cell is made from a
semiconducting material (a semiconductor) such as silicon that
absorbs the sunlight which generates a flow of electricity through
the solar cell. Because of the properties of semiconductors,
positive and negative terminals of the solar cell are static and
electron flow from a solar cell is uni-directional (i.e. the
electricity can only flow in one direction). Thus, as with all
photovoltaic cells, the solar cell produces only direct current
(d/c) electricity. The problem with direct current electricity is
that direct current electricity is difficult to transmit any
appreciable distance, which limits its use. Thus, alternating
current electricity is more usable than direct current
electricity. Moreover, most electrical devices utilize alternating
current (a/c) electricity.
Various prior art devices have attempted to provide suitable
alternating current electricity from photovoltaic or solar cells.
For instance, U.S. Patent No. 4,075,034 issued to Butler on
February 21 , 1978 (hereinafter, "Butler") provides a solar
converter for producing variable amplitude alternating current
waveforms directly from solar energy by using a photo-voltaic cell
bank array formed of a plurality of weighted photo-voltaic
segments. A multi-sided high speed, rotating and light
concentrating concave mirror system provides light on and past the
weighted segments of the photo-voltaic bank to produce
instantaneous output which are proportional to the number of cells
scanned in each segment. A simulated alternating current (a/c)
waveform is produced by suitable arrangement of the photo-voltaic
segments. The simulated a/c waveform of Butler and its fragile
manner (glass mirrors) of producing the simulated a/c waveform by
the high speed rotating mirror is not efficient. Moreover, Butler
is not easily scalable to produce larger voltages/amperes nor is
it relatively maintenance free. In U.S. Patent Publication No.
2005/0034750 by Rabinowitz published February 17, 2005
(hereinafter, "Rabinowitz"), a solar cell alternating current
generator is provided that uses a dynamic spinning ensemble of
mini-mirrors to both concentrate and modulate rays from the sun
onto a photovoltaic collector array. The focusing and superimposed
spinning action produces single phase and multiphase alternating
current electricity. The problem with Rabinowitz is again, the use
of glass mirrors, the need for focusing the mini-mirrors and
maintain their high speed spinning is not efficient.
In U.S. Patent No. 6,774,299 issued to Ford on August 10, 2004
(hereinafter, "Ford"), a solar alternating current electricity
generator is provided that utilizes a rotating, partitioned array
of photovoltaic cells. Contact brushes and wiring are provided to
transfer the electric current to an applied load. The drawback to
Ford is the need for contact brushes and wiring to generate the
alternating current electricity. Moreover, the rotating
photovoltaic cell vanes of Ford are not efficient.
In U.S. Patent No. 4,728,878 issued to Anthony on March 1 , 1988
(hereinafter, "Anthony"), a solar energy electric generating
system is provided for space vehicles which directly generates
alternating current from ambient light without power conversion.
Light incident to photocell arrays is mechanically or electrically
gated to produce fluctuating direct current (d/c) electricity. A
number of transforming devices are provided to convert the
fluctuating d/c current to alternating current (a/c). Through
variation of the frequency and duty cycle of the pulsing output
voltage, frequency and phase relative to a reference may be
controlled. However, with the Anthony solar energy electric
generating system, the mechanical gating provides a square wave
that is then conditioned to provide an alternating current
waveform.
Last, in U.S. Patent No. 4,577,052 issued to Schutten et al. on
Mach 18, 1986 (hereinafter, "Schutten"), an alternating current
solar cell is provided by connecting solar cells (P/N junctions)
in anti-parallel between a pair of main terminals. Light is
provided alternately on the P/N junctions through a mirror system
that splits the beam and causes the split beam to impinge on the
P/N junctions.
It is clear from the above that the prior art devices for
generating alternating current electricity directly from
photovoltaic or solar cells are complicated, difficult to align
and maintain, and cannot provide adequate scaling for small and
large a/c current production.
In view of the above, it is desirable to have a solar powered
alternating current (a/c) electricity generator, system and method
that produces single or multi-phase a/c electricity that is
simple, efficient and easily scalable in voltage and/or amperage.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is a system, device and method for directly
generating alternating current electricity from photovoltaic
cells. The system, device and method mechanically gradually
exposes and shades photovoltaic cell pairs connected in
anti-parallel to sunlight to generate alternating current
electricity at an a/c junction of the solar cell pairs. Gradually
and alternately exposing and shading the two anti-parallel
connected solar cells of each solar cell pair causes the amplitude
and polarity of the electricity at the a/c junction to gradually
rise and fall to produce alternating current electricity. The
gradual, alternating exposure and shading of the two anti-parallel
solar cells is accomplished by mechanically covering and exposing
the solar cell pairs.
In particular, while one solar cell of an anti-parallel connected
solar cell pair undergoes gradual exposure to sunlight from 0%
exposure (100% shaded) of the solar cell electricity generating
area to 100% exposure (0% shaded) of the solar cell electricity
generating area, the other solar cell of the solar cell pair
undergoes gradual shading from sunlight from 0% shaded (100%
exposure) to 100% shaded (0% exposure). Such gradual, alternating
exposure and covering of each solar cell of each anti-parallel
connected solar cell pair is periodic. The rate of exposure and
shading determines frequency.
In one form, a rotating disc situated over the solar cell pairs
has spaced apart openings forming coverings between each opening
to alternately expose and shade the solar cell pairs during
rotation. A direct current motor is utilized to rotate the
segmented disc. The motor is preferably powered by separate solar
cells.
The present invention also provides a phase synchronizer for
maintaining a desired alternating current frequency. The phase
synchronizer controls the motor to control rotation of the
segmented disc.
The present invention makes solar energy a viable, cost effective,
environmentally friendly option for residential and/or commercial
use. The present invention is capable of being used on a minute,
small or large scale through appropriate scaling the solar cell
a/c electricity generator and/or the use of a plurality thereof.
Solar cell a/c electricity generator arrays can easily produce the
power equivalent to an average power plant today, while being
environmentally friendly enough to be located proximate a
playground, school or in any urban environment. Large scale solar
cell a/c electricity generator arrays can be easily set up even in
the most remote places in the world. The present invention reduces
the need of other forms of power. Moreover, the present solar cell
a/c electricity generator can be set up and used anywhere.
It is thus an object of the present invention to produce
alternating current electricity of specific frequencies, single or
three phase, from solar cells in a cost efficient and simple
manner.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The above mentioned and other features, advantages and objects of
this invention, and the manner of attaining them, will become
apparent and the invention itself will be better understood by
reference to the following description of an embodiment of the
invention taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings,
wherein:
Fig. 1 is a perspective
view of a photovoltaic alternating current (a/c) electricity
generator fashioned in accordance with the principles of the
present invention;
Fig. 2 is a lower
perspective view of the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of
Fig. 1 taken from another side of the generator;
Fig. 3 is a perspective
view of the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1 with
the rotating disk thereof removed;
Fig. 4 is a perspective view of the rotating disk of the
photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1 ;
Fig. 5 is a schematic view
of the underside connections of the photovoltaic a/c electricity
generator of Fig. 1 ;
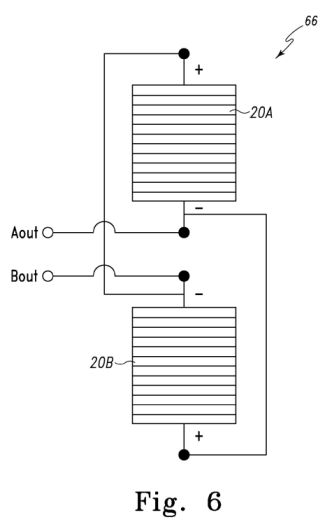
Fig. 6 is a diagram illustrating the anti-parallel
connection of a photovoltaic cell pair as used in the photovoltaic
a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1 ;
Fig. 7 is a diagram illustrating the parallel connection
of an exemplary photovoltaic cell pair array as may be used in the
photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1 ;
Fig. 8A is a first diagram in a sequence of
representative diagrams illustrating the manner of generating a/c
electricity from a photovoltaic cell pair of a photovoltaic cell
pair array of the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1
;
Fig. 8B is a second diagram in the sequence of
representative diagrams illustrating the manner of generating a/c
electricity from a photovoltaic cell pair of a photovoltaic cell
pair array of the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1
; Fig. 8C is a third diagram in the sequence of representative
diagrams illustrating the manner of generating a/c electricity
from a photovoltaic cell pair of a photovoltaic cell pair array of
the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1 ;
Fig. 8D is a fourth diagram in the sequence of
representative diagrams illustrating the manner of generating a/c
electricity from a photovoltaic cell pair of a photovoltaic cell
pair array of the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1
;
Fig. 8E is a fifth diagram in the sequence of
representative diagrams illustrating the manner of generating a/c
electricity from a photovoltaic cell pair of a photovoltaic cell
pair array of the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1
;
Fig. 9 is a schematic diagram of an exemplary phase
synchronizer as used in the photovoltaic a/c electricity generator
of Fig. 1 ; and
Fig. 10 is a flow chart illustrating a logic diagram of
an exemplary embodiment of the phase synchronizer of the
photovoltaic a/c electricity generator of Fig. 1.
Like reference numerals indicate the same or similar parts
throughout the several figures.
A description of the features, functions and/or configuration of
the components depicted in the various figures will now be
presented. It should be appreciated that not all of the features
of the components of the figures are necessarily described. Some
of these non discussed features as well as discussed features are
inherent from the figures. Other non discussed features may be
inherent in component geometry and/or configuration.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF AN
EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION
Referring to Figs. 1-5, there is depicted various views of an
exemplary embodiment of a photovoltaic alternating current (a/c)
electricity generator, generally designated 10, fashioned in
accordance with the present principles. The photovoltaic a/c
generator 10 is embodied as a solar cell a/c electricity generator
10, but it should be appreciated that a photovoltaic a/c
electricity generator fashioned in accordance with the present
principles may use photovoltaic cells other than solar cells.
The solar cell a/c electricity generator 10 has a base, frame or
other mounting structure 12 ("base 12") that supports the various
components thereof. The base 12 may be formed of wood, plastic or
other suitable material which is preferably, but not necessarily,
a non conducting material. It should be understood that while the
base 12 is shown as a box or a box-like structure, the base may be
a substrate, board or other suitable mounting or supporting
structure. The base 12 includes an alternating current (a/c)
electricity production portion 14 formed by a disk 15 and a
plurality of photovoltaic or solar cells 20 (hereinafter, "solar
cells 20"). As best seen in Fig. 3, the plurality of solar cells
20 is arranged in a generally circular array 21 on an upper
surface 13 of the base 12. It should be appreciated that arrays
other than circular may be used within the present principles. It
should also be appreciated that while the solar cells 20 are shown
as rectangles, the size and shape of the solar cells 20 may be
otherwise, such as truncated conical, triangular, polygonal or
square.
As best seen in Fig. 4, the disc 15 has a generally flat body made
of a sunlight blocking material that is generally the
circumference of the solar cell array 21 in order to extend over
the solar cell array 21 when in use (see, e.g., Figs. 1 and 2).
The disc 15 is also preferably made of a lightweight material that
resists warping or is not susceptible to warping. The disc 15 is
preferably reflective either inherently or via a coating, film,
overlay or the like. It should be appreciated that the disc 15 may
be partially reflective or non-reflective if desired. The disc 15
has a plurality of cutouts, openings, windows or the like 16
("cutouts 16") formed thereabout. The size and shape of the
cutouts 16 generally correspond to the size and shape of the solar
cells 20 and particularly is sized and shaped to allow total
exposure of a solar cell 20 to sunlight when the cutout 16 is
positioned over the solar cell 20. The cutouts 16 are situated and
spaced on the disc 15 so as to define a plurality of covers,
coverings, blocks or the like 18 ("coverings 18"). The coverings
18 are sized and shaped to completely cover or block a solar cell
20 when the covering is over the solar cell 20.
The cutouts 16 and coverings 18 are alternately radially situated
about the disc 15. The number of cutouts 16 corresponds by 1 /2 to
the number of solar cells 20 so that the number of coverings 18
corresponds by 1/2 to the number of solar cells 20. Therefore,
when the disc 15 is situated on frame 12 and over the solar cell
array 21 , the cutouts 16 and coverings 18 expose 1/2 of the total
solar cell array area and cover 1/2 of the total solar cell array
area. As the disc 15 rotates over the array 21 of solar cells 20,
the cutouts 16 and coverings 18 continuously gradually expose and
cover the array of solar cells.
The disc 15 is rotated over the solar cell array 21 by a direct
current motor 26 (see, e.g., Fig. 3) that is supported by the base
12. Rotation may be either clockwise or counterclockwise. A
counterclockwise rotation of the disc 15 is represented in the
figures by the curved arrow(s). The motor 26 is coupled to a phase
synchronizer 40 via a motor connection 44 (see Fig. 5). The phase
synchronizer 40 provides control/control signals to the motor 26
for varying the rotational speed of the disc 15. Rotational speed
of the disc 15 determines the frequency of resultant alternating
current(s) from the solar cell a/c electricity generator 10.
Additionally, the phase synchronizer 40 determines phase of the
resultant a/c electricity relative to a predetermined phase or
phase value (e.g. 60Hz) and causes the motor 26 to speed up or
slow down if necessary. The motor 26 is powered by photovoltaic
(solar) cells 22 that are situated on the base 12 so as to be
continuously exposed to any sunlight. As best depicted in Fig. 5,
the solar cells 22 are connected via connectors 23 to provide the
proper voltage and amperage to the motor 26 and motor controller
of the phase synchronizer 40) for properly operating the motor 26
for rotation of the disc 15. If desired, rechargeable batteries 28
may be connected to the phase synchronizer 40 that charge with
energy from the solar cells 22 and provide startup energy for the
motor 26.
The solar cell a/c electricity generator 10 may include a power
on/off switch 11 for making the solar cell a/c electricity
generator 10 operable or not operable. Alternately, or in
addition, the solar cell a/c electricity generator 10 may include
a light sensor 42 (shown in Fig. 5) that senses when sunlight is
present to then turn on the solar cell a/c electricity generator
10. Other configurations may be used.
As can be discerned from Figs. 1 and 2, rotation of the disc 15
causes the cutouts 16 and coverings 18 to alternately expose and
cover adjacent solar cells 20. The faster that the solar cells 20
are exposed and covered (rotation speed of the disc 15), the
higher the frequency of a/c electricity produced. The slower that
the solar cells 20 are exposed and covered (rotation speed of the
disc 15), the lower the frequency of the a/c electricity produced.
Since the solar cells are wired in anti-parallel, an alternating
current is generated between the a/c junction of the solar cell
pairs as the solar cell pairs are alternately, gradually exposed
and covered. Alternately stated, the total solar cell area of a
solar cell pair comprises 100% where one solar cell of the solar
cell pair defines 50% of the total area and the other solar cell
of the solar cell pair defines the other 50% of the total area.
The one solar cell of an anti-parallel connected solar cell pair
undergoes gradual exposure to sunlight from 0% exposure (100%
shaded) of the solar cell electricity generating area to 100%
exposure (0% shaded) of the solar cell electricity generating
area, the other solar cell of the solar cell pair undergoes
gradual shading from sunlight from 0% shaded (100% exposure) to
100% shaded (0% exposure). Such gradual, alternating exposure and
covering of each solar cell of each anti-parallel connected solar
cell pair is periodic.
This periodic sequence is illustrated in Figs. 8A through 8E.
Figs. 8A through 8E are a representation of the manner in which
two solar cells of a solar cell pair are alternately, gradually
exposed and covered to produce an a/c waveform. The principles of
the present invention are applicable to any connection
configuration of solar cell pairs, whether opposite one another as
in Figs. 8A through 8E, or adjacent one another as in Fig. 3.
Fig. 8A is an arbitrary beginning to the sequence wherein there is
represented a negative current at the output terminals Aout and
Bout of the solar cell pair, at its peak negative amplitude. In
Fig. 8A, solar cell 2OB of a solar cell pair is 100% exposed (0%
covered) while solar cell 2OA is 0% exposed (100% covered).
Particularly, a cutout 16 is fully over the solar cell 2OB thus
fully exposing solar cell 2OB, while at the same time, a covering
18 is fully over the solar cell 2OA thus fully shading (covering
or blocking) the solar cell 2OA. A peak negative current is thus
provided at output terminals Aout and Bout which is shown on the
graph of Fig. 8A as current point isA- In Fig. 8B of the sequence,
the rotating disc 15 has moved slightly counterclockwise such that
the opening 16 that was totally exposing the solar cell 2OB is now
exposing only 1/2 (and/or covering 1/2) of the area of the solar
cell 2OB, while the covering 18 that was totally shading the solar
cell 2OA is now covering only 1/2 (and/or exposing 1/2) of the
area of the solar cell 2OA. This results in a zero (0) current at
the output terminals Aout and Bout as shown on the graph of Fig.
8B as current point isB- It should be appreciated that the
rotational movement of the disc 15 from point shown in Fig. 8A to
that shown in Fig. 8B gradually exposes and covers the solar
cells, as described above, to create the gradual and not stepped
a/c waveform as depicted in the graph of Fig. 8B.
In Fig. 8C of the sequence, the rotating disc 15 has moved further
slightly counterclockwise. In Fig. 8C, solar cell 2OA of a solar
cell pair is now 100% exposed (0% covered) while solar cell 2OB is
now 0% exposed (100% covered). A cutout 16 is fully over the solar
cell 2OA thus fully exposing solar cell 2OA, while at the same
time, a covering 18 is fully over the solar cell 2OB thus fully
shading (covering or blocking) the solar cell 2OB. A peak positive
current is thus provided at output terminals Aout and B0Ut which
is shown on the graph of Fig. 8A as current point i8C. Again, it
should be appreciated that the rotational movement of the disc 15
from point shown in Fig. 8B to that shown in Fig. 8C gradually
exposes and covers the solar cells, as described above, to create
the gradual and not stepped a/c waveform as depicted in the graph
of Fig. 8C.
In Fig. 8D of the sequence, the rotating disc 15 has moved further
slightly counterclockwise such that the opening 16 that was
totally exposing the solar cell 2OA is now exposing only 1/2
(and/or covering 1/2) of the area of the solar cell 2OA, while the
covering 18 that was totally shading the solar cell 2OB is now
covering only 1/2 (and/or exposing 1/2) of the area of the solar
cell 2OB. While opposite to that of Fig. 8B, this results in a
zero (0) current at the output terminals Aout and Bout as shown on
the graph of Fig. 8D as current point i8D. Again, it should be
appreciated that the rotational movement of the disc 15 from point
shown in Fig. 8C to that shown in Fig. 8D gradually exposes and
covers the solar cells, as described above, to create the gradual
and not stepped a/c waveform as depicted in the graph of Fig. 8D.
Lastly, in Fig. 8E of the sequence, the disk has moved further
counterclockwise such that a cutout 16 has moved fully over solar
cell 2OB such that solar cell 2OB is again 100% exposed (0%
covered) while a covering 18 has again moved fully over the solar
cell 2OA such that the solar cell 2OA is 0% exposed (100%
covered). Particularly, the cutout 16 is fully over the solar cell
2OB thus fully exposing solar cell 2OB, while at the same time, a
covering 18 is fully over the solar cell 2OA thus fully shading
(covering or blocking) the solar cell 2OA. A peak negative current
is thus again provided at output terminals Aout and Bout which is
shown on the graph of Fig. 8E as current point i8E- Again, it
should be appreciated that the rotational movement of the disc 15
from point shown in Fig. 8D to that shown in Fig. 8E gradually
exposes and covers the solar cells, as described above, to create
the gradual and not stepped a/c waveform as depicted in the graph
of Fig. 8E. Fig. 8E completes a full cycle of the a/c waveform.
Referring back to Fig. 3, the total number of solar cells 20 must
be an even number since two solar cells 20 are utilized to provide
a solar cell pair having a single a/c junction. Multiple solar
cell pairs are connected together to increase the voltage or
amperage depending on the connection. Connection of all of the
solar cell pairs of the array 21 produces a single phase a/c
waveform. The solar cell pairs may use three connected banks of
solar cells pairs to achieve a three-phase a/c waveform. In Fig.
3, since the total number of solar cell pairs is fifteen (15) they
all can be connected to form a single phase a/c waveform, or they
can be divided into three (3) banks of five (5) solar cell pairs
each to achieve a three-phase a/c/ waveform.
Referring additionally to Fig. 6, a solar cell pair 66 of solar
cells 2OA and 2OB is shown. As can be seen, the solar cell pair 66
is connected in anti-parallel to provide an a/c junction (i.e. two
a/c output terminals Aout and Bout)- Particularly, the positive
terminal of the solar cell 2OB is connected to the negative
terminal of the solar cell 2OA, while the positive terminal of the
solar cell 2OA is connected to the negative terminal of the solar
cell 2OB. It should be appreciated that Fig. 6 is illustrative of
the manner in which solar cell pairs 66 are connected and form an
a/c junction. Other configurations are contemplated. In Fig. 3 for
example, two adjacent solar cells 20 are connected in
anti-parallel to provide a solar cell pair such that junctions 60
and 61 (as seen in Figs. 3 and 5) correspond to the two a/c output
terminals Aout and Bout-
A single solar cell pair 66 may be used to create a/c electricity
utilizing an appropriately fashioned rotating disc. A single solar
cell pair would thus produce a single phase a/c waveform. Three,
single solar cell pairs can produce a three-phase a/c waveform.
Multiple, single solar cell pairs can produce a multi-phase a/c
waveform. However, to generate a 60 Hz a/c waveform, the disc
(having only a single cutout) would have to spin at a rate of
sixty revolutions per second. Therefore, multiple solar cell pairs
may be connected together to provide a single a/c junction. This
allows voltage and amperage to be increased as desired since the
number of such series or parallel connected solar cells is
unlimited, as well as slow down the rate of revolution of the disc
15.
Referring to Fig. 7, the array 21 is shown connected for a single
phase a/c waveform wherein any number of solar cells represented
by solar cells 20Ai, 20A2, 20A3, 20A4, 20A5 through 20An are
coupled to form the single a/c junction terminal Aout, while any
number of solar cells represented by solar cells 20B1, 20B2, 20B3,
20B4, 20B5 through 20Bn are coupled to form the single a/c
junction terminal Bout> thereby forming a "solar cell pair".
The solar cells 20 are shown connected in parallel to increase the
amperage and maintain the voltage. Connecting the solar cells 20
in series would increase the voltage and maintain the amperage. In
Fig. 3, the solar cell array 21 is wired to produce single phase
a/c electricity. Each solar cell pair of the array 21 has the
first and second a/c junctions 60, 61 which can be seen in Fig. 5
to be connected to provide a single a/c junction 56, 58. As such
one of the output terminals 46, 48 would provide the single phase
a/c electricity.
The connections 24 to and from the phase synchronizer 40, as best
discerned in Fig. 5, provide a/c output from the phase
synchronizer and signal input to the phase synchronizer. Terminals
46 and 48 provide a/c electricity output. Terminal 51 provides a
shared signal input, while terminal 52 provide a commercial signal
input. These can be used by the phase synchronizer to regulate the
present a/c generator.
Fig. 9 is a schematic of an exemplary embodiment of the motor
control portion of the phase synchronizer 40. Motor speed is
controlled in order to adjust the rotation rate of the disc 15 to
provide a correct phase. As discerned in Figs. 2 and 3, the
present solar cell a/c electricity generator 10 includes three (3)
photo or opto transistors 30, 32, and 34 that are situated
proximate one solar cell 20. Particularly, a first phototransistor
30 is positioned ahead of the solar cell 2Op (see Fig. 3) as per
counterclockwise rotation of the disc 15. A second phototransistor
32 is positioned at the middle of the solar cell 2Op, while a
third phototransistor 34 is positioned at the end of the solar
cell 2Op. The first, second and third phototransistors 30, 32, 34
work to provide a signal to control the motor which controls the
rate of rotation of the disc 15 which controls the frequency of
the generated a/c electricity. Although 60 Hz is shown as an input
(a predetermined operating frequency) to the phase synchronizer,
other frequencies can be generated and synchronized by the present
solar cell a/c electricity generator 10. The inputted signal
provides power for the phototransistors 30, 32, 34 through
transistor Ti . The phototransistors detect phase of the waveform
through rotation of the disc 15 and, particularly the cutouts 16
and/or the coverings 18 relative to the phototransistors 30, 32,
34. The phototransistor 30 provides a slow phase signal, the
phototransistor 32 provides an in-phase signal, while the
phototransistor 34 provides a fast phase signal. The
phototransistors provide their signals to the signal conditioning
network TN which, in turn, provides a signal to the motor 26.
Phototransistor 30 connects through transistor T2, while
phototransistor 34 connects through transistor T3. An in-phase LED
68 is provided for indicated when the waveform is in phase. As
well, a bank of LEDs 770 may be provided to provide visual
indication of phase. It should also be appreciated that the
resistor Ri and R2 may be variable resistors if desired to provide
adjustment to the signal conditioning network TN.
Fig. 10 is a flow chart 100 of an exemplary manner of operation of
the present solar cell a/c electricity generator 10. Through use
of the photocell 42, the light intensity is checked via the light
sensor 102. If there is low light or no light, the generator 10
goes into a timed standby 104. At the end of the standby period,
light intensity is checked again 102. If there is sufficient
light, the phase choice is started 106. It should be appreciated
that the check light intensity portion may be excluded when there
is a switched on and off. After the start of phase choice 106, it
is determined whether a commercial signal is detected 108. If no,
then it is determined whether it is a shared signal 110. If yes
then on to motor control 114. If no, then it is determined whether
the signal is an internal signal 112. Motor control 114 is then
started if it is. If a commercial signal is detected at 108, then
motor control 114 is started.
Once motor control is started, it is determined whether phase
match is reached 116. If yes, then the generator 10 will connect
to a load 118. If no, then phasing is adjusted 120. Thereafter, it
is determined when phase match is reached in order to connect to
load 118. Also, there may be a periodic check or ongoing check to
determine phase match with a possible disconnect of the load if
phase match is not occurring.
It should also be appreciated that the present solar cell a/c
electricity generator 10 may be one of a plurality of solar cell
a/c electricity generators that can form a power station or any
wattage assembly. A plurality of solar cell a/c electricity
generators may be connected as desired to provide various power
configurations.
While the invention has been illustrated and described in detail
in the drawings and foregoing description, the same is to be
considered as illustrative and not restrictive in character, it
being understood that only a preferred embodiment has been shown
and described and that all changes and modifications that come
within the spirit of the invention are desired to be protected.