Hans KAUTSKY, et al.
SILOXENE
2D siloxene sheets: A novel electrochemical sensor for selective dopamine detection Alkylamino- und Alkoxy-Siloxene Anwendung von Siloxen als Chemiluminescenz-Indicator in cerimetrischen und chromatometrisehen Titrationen Anwendung von Siloxen als Chemiluminescenz-Indicator in der Permanganometrie
Auswertung der von Kautsky, Gaubatz und Greiff gemessenen Adsorptionsisothermen von Gasen an Siloxen und Bromsiloxenen. I
Carbothermal conversion of siloxene sheets into silicon-oxy-carbide lamellae for high-performance supercapacitors
Chemiluminescence of Anodized and Etched Silicon: Evidence for a Luminescent Siloxene-Like Layer on Porous Silicon Chemische Umsetzungen des Siloxens mit Halogenverbindungen Controlling siloxene oxidization to tailor SiOx anodes for high performance lithium ion batteries Di- und Tetrasubstituierte Siloxene
Die Titration von Blei mit Chromat unter Verwendung von Siloxen als Chemiluminescenz-Indicator
Effects of pressure on the optical absorption and photoluminescence of Wöhler siloxene
Electronic-structure investigations of siloxenic clusters and films
Electronic transport in crystalline siloxene
Farbe und Fluoreszenz ringförmiger Si-Verbindungen, I. Darstellung eines Siloxens für optische Untersuchungen
Farbe und Fluoreszenz ringförmiger Si-Verbindungen, II. Fluoreszenz und Farbe des Siloxens und seiner Derivate
Farbe und Fluoreszenz ringförmiger Si-Verbindungen, III. Über das Bindungssystem des Siloxens
Farbe und Fluoreszenz ringförmiger Si-Verbindungen, IV. Bestimmung der Substituentenorientierung am Siloxen durch Brückenbildung
Fatigue Effect and Temperature Dependence in Luminescence of Disordered Silicide Layer Compound: Siloxene (Si 6 H 3 (OH) 3 )
First-principles study of siloxene and germoxene: stable conformations, electronic properties, and defects
Free radical mechanism in olefin isomerization. Isomerization of (Z)-but-2-ene and (Z)-[1,2-2H2]ethylene over siloxene
From CaSi2 to siloxene: epitaxial silicide and sheet polymer films on silicon Geschwindigkeit und Geschwindigkeitskonstanten der Zersetzung des Siloxens durch alkalische Pufferlösungen Highly efficient 2D siloxene coated Ni foam catalyst for methane dry reforming and an effective approach to recycle spent catalyst towards energy storage application Highly Stable Lithium-Sulfur Batteries Promised by Siloxene: An Effective Cathode Material to Regulate the Adsorption and Conversion of Polysulfides
Illustrating Chemiluminescence with Siloxene Indicator Kinetics of the Topotactic Formation of Siloxene
Light-emission phenomena from porous silicon: Siloxene compounds and quantum size effect
Light from Silicon—Renaissance of Siloxene and Polysilane? Local and Electronic Structure of Siloxene
Luminescence and optical properties of siloxene
Notizen: Metallkatalyse des Elektronenübergangs vom Siloxen auf reduzierbare Stoffe Notizen: Die Reduktion von Aldehyden und Ketonen durch Siloxen Notizen: Oxydationsprodukte des Siloxens und ihre Charakterisierung durch Fluoreszenzindikatoren
Notizen: Die Bedeutung elektronenmikroskopischer Untersuchungen für die Konstitutions- und Strukturaufklärung des Siloxens
Notizen: Umsetzungen des Siloxens in alkalischem Medium, Reaktionen der Si-Si-, Si-Η- und Si-O-Si-Bindung
Observation of silicon nanocrystals in siloxene On the relationship of porous silicon and siloxene
One-step controllable synthesis of amino-modification siloxene for enhanced solar water-splitting
Optical Properties of Siloxene Films Prepared by High-Temperature Heat Treatment from Thin Films of Polysilane Containing Anthryl Groups Optical properties of disordered silicide layer compound: Siloxene (Si6(OH)3H3) — Time resolved luminescence Organosilicon Chemistry III -- New Results in Cyclosilane Chemistry: Siloxene-Like Polymers Photo- and Chemiluminescence from Wöhler Siloxenes Photocatalytic NO removal over calcium-bridged siloxenes under ultraviolet and visible light irradiation Photoluminescence excitation spectroscopy of porous silicon and siloxene
Photoluminescence and laser-irradiation effect of siloxene compound
Photoluminescence and Photo-induced conductivity in 2D Siloxene Nanosheet for optoelectronic applications Photoluminescent Siloxenes in Nanoporous Aluminum Oxide Porous silicon and siloxene: Vibrational and structural properties
Preparation of siloxene nanosheet-supported palladium as sustainable catalyst for Mizoroki-Heck reaction
Preparation and structure of novel siloxene nanosheets
Silicene Quantum Dots Confined in Few-Layer Siloxene Nanosheets for Blue Light-Emitting Diodes
Silicon Chemistry -- Kautsky-Siloxene Analogous Monomers and Oligomers
Siloxene: A potential layered silicon intercalation anode for Na, Li and K ion batteries Siloxene as Chemiluminescent Indicator in Chromate Titration for Determination of Lead Siloxene, Germanane, and Methylgermanane: Functionalized 2D Materials of Group 14 for Electrochemical Applications Siloxene nanosheet: A metal-free semiconductor for water splitting Siloxene-Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Hydrogel for Supercapacitors Siloxene: Chemical quantum confinement due to oxygen in a silicon matrix Siloxene as Chemiluminescent Indicator in Titration Siloxene as a unique catalyst for structural isomerization of butene Siloxene-Supported Catalysts for Ethylene Polymerization Siloxen als Adsorbens SILOXENE AS A UNIQUE CATALYST FOR STRUCTURAL ISOMERIZATION OF N-BUTENE Siloxen und schichtförmig gebaute Siliciumsubverbindungen Similarities and differences of phonon modes in silicon materials depending on dimension: Raman spectroscopy of polysilanes and siloxene Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering from Light Emitting Porous Silicon and Siloxene
Spontaneous deposition of Ir nanoparticles on 2D siloxene as high-performance HER electrocatalyst with ultra-low Ir loading
Stabilized lithium-ion battery anode performance by calcium-bridging of two dimensional siloxene layers
Structural change from crystalline to amorphous states in siloxene by thermal annealing
Structural Stability and Electronic Properties of (SiH) 2 O-formed Siloxene Sheet: A Computational Study Structure and optical properties of the planar silicon compounds polysilane and Wöhler siloxene
Study of the Structure and Chemical Nature of Porous Si and Siloxene by STM, AFM, XPS, and LIMA Synthesis of a calcium-bridged siloxene by a solid state reaction for optical and electrochemical properties Synthesis of graphene-siloxene nanosheet based layered composite materials by tuning its interface chemistry...
Synthesis of Siloxene Derivatives with Organic Groups
THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON SILOXENE
Topochemical Reaction of CaSi2 to a Two-Dimensional Subsiliceous Acid Si6H3(OH)3 ( = Kautskys’ Siloxene)
Transient photoluminescence decay in porous silicon and siloxene
Transport properties and electroluminescence of siloxene Transport Properties of Siloxene Triplet excitons in porous silicon and siloxene
Triplet states in siloxene and porous silicon
Tubular Structures of Siloxenes Two-Dimensional Excitons in Siloxene
Two-dimensional siloxene nanosheets: Novel high-performance supercapacitor electrode materials
Two-dimensional silicon suboxides nanostructures with Si nanodomains confined in amorphous SiO 2 derived from siloxene...
Über das Siloxen und seine Derivate
Über die Konstitution des Siloxens
Umsetzungen des Siloxens mit Halogenverbindungen und ihre Auslösung durch Licht und chemische Reaktionen
Understanding the thermal treatment effect of two dimensional siloxene sheets...
Unimportance of Siloxene in Luminescent Porous Silicon as Determined by Nexafs & Exafs
Vibrational Anti-Crossing in Siloxene
Vibrational properties of siloxene: isotope substitution studies Visible-light-sensitive siloxene-based composite material with enhanced photocatalytic activity
Visible luminescence from porous silicon and siloxene Visible Luminescence from Porous Silicon and Siloxene: Recent Results Visible Luminescence from Silicon: Quantum Confinement or Siloxene?
Volumetric Determination of Sulfate by Titration of Excess Lead Nitrate with Potassium Chromate Using Siloxene Indicator
X-ray diffraction and x-ray absorption studies of porous silicon, siloxene, heat-treated siloxene, and layered polysilane
X-RAY PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY OF SILOXENE...
Zero field-ODMR and emission/microwave double resonance on optically excited siloxene
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/ee/c8ee00160j
Two-dimensional siloxene nanosheets: novel high-performance supercapacitor electrode materials†
Karthikeyan Krishnamoorthy
Silicon-based materials have attracted considerable interest for the development of energy storage devices because of their ease of integration with the existing silicon semiconductor technology. Herein, we have prepared siloxene sheets—a two-dimensional (2D) silicon material—and investigated their energy storage properties via fabrication of a symmetric supercapacitor (SSC) device containing 0.5 M tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate as the electrolyte. The formation of 2D siloxene sheets functionalized with oxygen, hydrogen, and hydroxyl groups was confirmed through X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and laser Raman mapping analyses. Cyclic voltammetric studies of the siloxene SSC device revealed the presence of pseudocapacitance in the siloxene sheets that arose from an intercalation/deintercalation phenomenon. The galvanostatic charge–discharge profiles of the device displayed sloped symmetric triangular curves with a maximum specific capacitance of 2.18 mF cm−2, high energy density of 9.82 mJ cm−2, good rate capability, and excellent cycling stability of 98% capacitance retention after 10 000 cycles. The siloxene SSC device delivered a maximum power density of 272.5 mW cm−2, which is higher than those of other silicon- and carbon-based SSCs, highlighting their potential for application in energy storage.
https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/73498
Novel Two-Dimensional Siloxene Material for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Sensor Applications
Rajendran Ramachandran, Zong-Xiang Xu and Fei Wang
Abstract
After discovering graphene, the two-dimensional materials have gained considerable interest in the electrochemical applications, especially in energy conversion, storage, and bio-sensors. Siloxene, a novel two-dimensional low-buckled structure of Si networks with unique properties, has received the researcher’s attention for a wide range of applications. Though the electronic and optical properties of siloxene have been explored in detail previously, there is a lack of electrochemistry studies of siloxene as the result of material degradation, and the investigation is still open-ended to enhance the electrochemical application. Recently, siloxene has been used for supercapacitor, lithium-ion batteries, and dopamine bio-marker detections. This chapter highlights the recent development of siloxene synthesis and its electrochemical properties in energy and sensor applications. The plannar Si structure with Si6 rings interconnected with different oxygen, hydroxyl functional groups, and large interlayer spacing of siloxene sheets can promote the active sites for enhanced electrochemical performance. This chapter provides the current state-of-the-art in the field and a perspective for future development in the electrochemistry field of siloxene.


https://www.greencarcongress.com/2019/02/20190217-siloxene.html
Siloxene as promising silicon intercalation anode for Li-, Na- and K-ion batteries
Researchers in France have shown the versatility of siloxene, a 2D silicon structure (Si6O3H6), as an anode material for Li-, Na- and K-ion batteries.
In a paper in the Journal of Power Sources, the researchers report that lamellar siloxene obtained from the topotactic deintercalation of Ca from CaSi2 delivered reversible capacities of 2300, 311 and 203 mAh/g for Li, Na and K, respectively, with good capacity retention and coulombic efficiency for Li and Na.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.3c00355
Two-Dimensional Siloxene Nanosheets: Impact of Morphology and Purity on Electrochemistry
Jessica Luo, et al
Two-dimensional (2D) siloxene (Si6O3H6) has shown promise as a negative electrode material for Li-ion batteries due to its high gravimetric capacity and superior mechanical properties under (de)lithiation compared to bulk Si. In this work, we prepare purified siloxene nanosheets through the removal of bulk Si contaminants, use ultrasonication to control the lateral size and thickness of the nanosheets, and probe the effects of the resulting morphology and purity on the electrochemistry. The thin siloxene nanosheets formed after 4 h of ultrasonication deliver an average capacity of 810 mA h/g under a 1000 mA/g rate over 200 cycles with a capacity retention of 76%. Interestingly, the purified siloxene shows lower initial capacity but superior capacity retention over extended cycling. The 2D morphology benefit is illustrated where the parent siloxene nanosheet morphology and structure were largely maintained based on operando optoelectrochemistry, in situ Raman, ex situ scanning electron microscopy, and ex situ transmission electron microscopy. Furthermore, the purified siloxene-based electrode free from crystalline Si impurity experiences the least expansion upon (de)lithiation as visualized by cross-section electron microscopy of samples recovered post-cycling.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/ee/c8ee00160j
Two-dimensional siloxene nanosheets: novel high-performance supercapacitor electrode materials†
Karthikeyan Krishnamoorthy
Silicon-based materials have attracted considerable interest for the development of energy storage devices because of their ease of integration with the existing silicon semiconductor technology. Herein, we have prepared siloxene sheets—a two-dimensional (2D) silicon material—and investigated their energy storage properties via fabrication of a symmetric supercapacitor (SSC) device containing 0.5 M tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate as the electrolyte. The formation of 2D siloxene sheets functionalized with oxygen, hydrogen, and hydroxyl groups was confirmed through X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and laser Raman mapping analyses. Cyclic voltammetric studies of the siloxene SSC device revealed the presence of pseudocapacitance in the siloxene sheets that arose from an intercalation/deintercalation phenomenon. The galvanostatic charge–discharge profiles of the device displayed sloped symmetric triangular curves with a maximum specific capacitance of 2.18 mF cm−2, high energy density of 9.82 mJ cm−2, good rate capability, and excellent cycling stability of 98% capacitance retention after 10 000 cycles. The siloxene SSC device delivered a maximum power density of 272.5 mW cm−2, which is higher than those of other silicon- and carbon-based SSCs, highlighting their potential for application in energy storage.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b04180
Silicene, Siloxene, or Silicane? Revealing the Structure and Optical Properties of Silicon Nanosheets Derived from Calcium Disilicide
Bradley J. Ryan
Si-nanosheets (Si-NSs) have recently attracted considerable attention due to their potential as next-generation materials for electronic, optoelectronic, spintronic, and catalytic applications. Even though monolayer Si-NSs were first synthesized over 150 years ago via topotactic deintercalation of CaSi2, there is a lack of consensus within the literature regarding the structure and optical properties of this material. Herein, we provide conclusive evidence of the structural and chemical properties of Si-NSs produced by the deintercalation of CaSi2 with cold (∼−30 °C) aqueous HCl and characterize their optical properties. We use a wide range of techniques, including XRD, FTIR, Raman, solid-state NMR, SEM, TEM, EDS, XPS, diffuse reflectance absorbance, steady-state photoluminescence, time-resolved photoluminescence, and thermal decomposition; when they are combined together, these techniques enable unique insight into the structural and optical properties of the Si-NSs. Additionally, we support the experimental findings with density functional theory (DFT) calculations to simulate FTIR, Raman, solid-state NMR, interband electronic transitions, and band structures. We determined that the Si-NSs consist of buckled Si monolayers that are primarily monohydride terminated. We characterize the nanosheet optical properties, finding they have a band gap of ∼2.5 eV with direct-like behavior and an estimated quantum yield of ∼9%. Given the technological importance of Si, these results are encouraging for a variety of optoelectronic technologies, such as phosphors, light-emitting diodes, and CMOS-compatible photonics. Our results provide critical structural and optical properties to help guide the research community in integrating Si-NSs into optoelectronic and quantum devices.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2352507X21000305
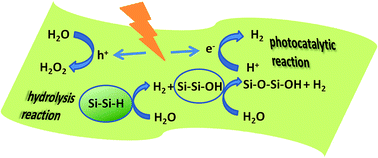
Siloxene: A novel 2D photocatalyst for degradation of dye molecules
Nav Deepak
Abstract
Silicon based materials on 2D landscape are gaining significant interest due to their exotic properties along with well-developed processing technologies. We report use of 2D siloxene nanosheets as a potential photocatalyst for remediation of water polluted from cationic dyes. Degradation of methylene blue (MB) is used as a representative case study. Systematic studies were performed by varying reaction time, pH, material mass concentration, and dye concentration. Results suggest that adsorption mechanism is prominent over the basic pH range. Adsorption isotherms reveal that the process can be described by Langmuir model, suggesting monolayer adsorption of MB on siloxene nanosheets and pseudo second order kinetics is obeyed. Samples exhibited adsorption capacity of 8.93 mg/g of MB within equilibrium time of
10 min. These are also found to be effective in removal of other cationic dyes such as Azure A, Azure B and Malachite Green. Siloxene nanosheets are expected to open a new avenue for efficient remediation for treatment of textile effluents by adsorption under diffuse light.
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/28/5/214
Siloxene Nanosheets and Their Hybrid Gel Glasses for Broad-Band Optical Limiting
Xugui Lv, et al
Abstract
With the development of laser technology, the research of novel laser protection materials is of great significance. In this work, dispersible siloxene nanosheets (SiNSs) with a thickness of about 1.5 nm are prepared by the top-down topological reaction method. Based on the Z-scan and optical limiting testing under the visible-near IR ranges nanosecond laser, the broad-band nonlinear optical properties of the SiNSs and their hybrid gel glasses are investigated. The results show that the SiNSs have outstanding nonlinear optical properties. Meanwhile, the SiNSs hybrid gel glasses also exhibit high transmittance and excellent optical limiting capabilities. It demonstrates that SiNSs are promising materials for broad-band nonlinear optical limiting and even have potential applications in optoelectronics.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/ta/c6ta07545b
Siloxene nanosheets: a metal-free semiconductor for water splitting†
Shuang Li, et al
Exploring efficient semiconductors for water splitting to produce hydrogen is considered as one of the most promising approaches to solve the world energy crisis. Herein, for the first time, we highlight that metal-free siloxene nanosheets can serve as a photocatalyst for efficient water splitting without the addition of any cocatalyst or sacrificial agent.
Siloxene Patents
TWO-DIMENSIONAL POROUS SILICON, AND PREPARATION METHOD AND USE THEREOF IN LITHIUM ION BATTERIES
US2025019247
[ PDF ]
Also published as: CN116835594
A two-dimensional porous silicon, and a preparation method and use thereof in lithium ion batteries. A silicocalcium powder is soaked in a hydrochloric acid solution, filtered under suction after reaction, and dried to obtain a siloxene powder. The siloxene powder is thermally treated in a vacuum environment, in which siloxene is oxidized into SiOx during the heating process, and SiOx is disproportionated in further high-temperature treatment to produce uniformly distributed two-dimensional Si/SiO2. The two-dimensional Si/SiO2 is soaked in a hydrofluoric acid solution, in which hydrofluoric acid reacts with SiO2. After complete reaction, a two-dimensional silicon material having a porous structure is obtained after repeatedly centrifugation and washing, and drying under vacuum. The two-dimensional porous silicon has a crystal structure and an ultra-thin lamellar structure, effectively alleviate the volume change of the negative electrode material, and accelerate the diffusion of lithium ions when used in a lithium ion battery.
SULFONIC ACID GROUP FUNCTIONALIZED SILOXENE FOR ZINC-BASED FLOW BATTERY, AND PREPARATION METHOD THEREFOR
WO2023173559
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
The present invention relates to the technical field of battery electrode material preparation. Disclosed are sulfonic acid group functionalized siloxene for a zinc-based flow battery, and a preparation method therefor. In the present invention, a silicide raw material (calcium silicide) is efficiently stripped in a topochemical solvent and an oxidizing agent of a monohydric or polybasic acid by means of a topochemical method, so as to obtain a siloxene nanosheet, and further, sulfonic acid group functionalized modification is performed on the siloxene nanosheet by using a sulfonic acid grafting agent, so as to obtain a high-quality sulfonated siloxene nanosheet. By using a zinc-based flow battery negative electrode coated with sulfonated siloxene, the problems of zinc dendrite growth, accumulation and the like can be effectively solved, stable and uniform low-overpotential zinc deposition/stripping are realized, and the development of further commercial application of the zinc-based flow battery is promoted.
Graphene-based two-dimensional heterostructure supercapacitor and manufacturing method thereof
WO2023282638
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
The present invention relates to: a siloxene-rGO heterocomposite comprising a two-dimensional electrically conductive siloxene sheet and a reduced graphene oxide sheet; a supercapacitor including the siloxene-rGO heterocomposite; and methods for producing same. The present invention provides a supercapacitor formed as a heterostructure by hybridizing two-dimensional materials including a graphene or reduced graphene oxide (rGO) sheet having extra double-layer capacitance (EDLC) properties and a siloxene sheet having pseudocapacitance properties, wherein the supercapacitor can be used as an advanced electrical energy storage system (EES) for collecting regenerative braking energy from an electric vehicle due to having excellent capacitance, a high energy-power ratio, operating performance over a wide temperature range, etc.
SILICENE QUANTUM DOTS-CONTAINING SILOXENE AND PREPARATION METHOD THEREFOR
US12221351
[ PDF ]
Also published as: CN114761355 // CN114761355 // WO2021035706
Provided are a silicene quantum dots-containing siloxene thin film and a preparation method therefor, which belong to the field of fluorescent functional nanomaterials. A siloxene thin film embedded with silicene quantum dots is prepared by uniformly mixing CaSi2 with a decalcification organic solvent and a transition metal chloride catalyst in a proportion, performing acid washing, and then performing ultrasonic dispersion. The thickness of such siloxene thin film is less than 1 to 2.5 nm, the size of the silicene quantum dots is 2 to 5 nm. In addition, the siloxene thin film has strong fluorescence emission performance in a blue light region, has a pseudodirect band gap, and shows a good application prospect in the fields of photoelectricity and the like.]
Probing method for monitoring the charge-storage in self-charging supercapacitor comprising a piezoelectric fiber and a method for manufacturing the same
WO2021261775
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
Disclosed are a validation method for monitoring charge-storage in self-charging supercapacitor comprising piezoelectric fiber and manufacturing method of supercapacitor. The present invention comprises: a step of manufacturing siloxene sheet; and a step of manufacturing siloxene-PVDF piezoelectric fiber.
SUPERCAPACITOR COMPRISING SILICON OXY CARBIDE LAMELLAS AND PREPARATION METHOD OF THE SAME
WO2021261774 // KR20220000212
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
Disclosed are a supercapacitor with improved energy density and power density, and a preparing method thereof. The present invention provides a preparing method of a supercapacitor, which comprises: a reaction step of reacting siloxene and alginate to obtain silicon oxycarbide; a slurry preparation step of preparing electrode material slurry by mixing the silicon oxycarbide, a conductive carbon material, and a binder; and a thin film layer preparing step of coating the electrode material slurry on a substrate and drying the same, to prepare a silicon oxycarbide thin film layer.
Two-Dimensional Silicon Nanostructures for storage of sodium ion and electrode comprising the same
KR20210128516
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
Provided is a two-dimensional silicon nanostructure for storing sodium ions including a siloxene compound including at least one siloxene. The present invention can ensure safety.
Two-dimensional silicon dioxide as well as preparation method and application thereof
CN113488376
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
The invention belongs to the technical field of materials, and particularly relates to two-dimensional silicon dioxide as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of acidizing a calcium silicide alloy to obtain siloxene, and carrying out heat treatment on the siloxene in an air atmosphere to prepare the two-dimensional silicon dioxide. According to the method, the two-dimensional silicon dioxide is obtained through acid treatment and heat treatment in the air atmosphere by adopting a commercial precursor, an expensive template agent is not needed in the whole preparation process, the precursor is also a commercially available material, the whole preparation process is few in step and simple in process, and large-scale and low-cost preparation of the two-dimensional silicon dioxide can be realized. The two-dimensional silicon dioxide prepared by the invention not only can be used as a negative electrode material in a lithium battery, shows excellent cycling stability, but also can be used for preparing a diaphragm with high thermal stability.
Cathode for lithium-sulfur battery comprising siloxene compound
KR102326642
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
The present invention relates to a cathode for a lithium-sulfur secondary battery comprising a siloxane compound including one or more siloxanes and a cathode active material. Specifically, the present invention relates to a cathode for a lithium-sulfur secondary battery, to which a siloxane compound and a cathode active material are added, which are effective in fixing polysulfide, an intermediate product of a lithium-sulfur secondary battery.
SUPERCAPACITOR COMPRISING TWO DIMENSIONAL SILOXENE SHEETS AND PREPARATION METHOD OF THE SAME
KR102053782
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a supercapacitor including a siloxane electrode. The method comprises a step of immersing a precursor containing calcium silicide in an acid to dissolve calcium and obtain siloxane; a slurry manufacturing step of mixing the siloxane, a conductive carbon material, and a binder and manufacturing electrode material slurry; and a sheet drying step of coating and drying the electrode material slurry on a substrate and manufacturing a siloxane sheet. The manufacturing method may provide a supercapacitor electrode material having an excellent capacitance using siloxane having a Kautsky-type Si plane and a hydroxyl group on the surface thereof. The capacity and periodic stability of the supercapacitor can be improved.
Siloxene material, preparation method of silicon-based oxide and cathode material
CN106058232
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
The invention provides a siloxene material. A chemical formula I of the siloxene material is shown as Si6OxHy(OH)6-y, wherein each of x and y is greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 6. The siloxene material has Si-O-Si bond, Si-H bond and Si-OH bond. The siloxene material is simple in preparation process and easy in large-scale preparation. A cathode material prepared by using the siloxene material has high circulating stability, high initial Coulomb efficiency and high rate performance. Experiment results show that under a condition of 150mA/g, initial lithium-removing capacity is 845-1329mAh/g, initial Coulomb efficiency is 65.2-84.1%, and capacity retention ratio after circulating for 200 circles is 75.0-85.3%; under a condition of 1.5A/g, capacity retention ratio is 71.1-86.0%. The invention further provides a preparation method of silicon-based oxide and the cathode material.
SILOXENE COMPOSITE MATERIAL, SILOXENE DERIVATIVE, AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING THESE
JP2012001604
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
To provide a method for producing a siloxene composite material, which can optionally select a functional group incorporated in siloxene.SOLUTION: The method for producing a siloxene composite material represented by the composition formula (1): SiH(O-E-CONRR)(wherein Rand Rare the same as those in the following formula (3); and E and a are the same as those in the following formula (2)) comprises reacting a siloxene derivative represented by formula (2): SiH(O-E-COOR)(wherein Ris a 1-10C hydrocarbon group; E is a 1-30C hydrocarbon group; and 1≤a≤5) with a nitrogen-containing compound represented by formula (3): HNRR(wherein Rand Rdenote a hydrogen atom, a hydrocarbon group or a hetero group, and may be bonded to each other in the NRRto form a nitrogen-containing hetero ring), in an organic solvent.
SILICA NANOSHEET, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE SAME AND DISPERSION OF SILICA NANOSHEET IN ORGANIC SOLVENT
JP2009184839
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
To provide a method for producing a silica nanosheet by which a silica nanosheet dispersible in an organic solvent can be obtained. ;SOLUTION: The method for producing a silica nanosheet includes a step of mixing monocalcium disilicide and concentrated hydrochloric acid to form layered siloxene, and a step of mixing and stirring the layered siloxene and an organic solvent to form a silica nanosheet in the organic solvent.
Device comprising a luminescent material
US5578379 // DE4139852 // EP0545388 // EP0545388 // JPH06145660
[ PDF ]
Siloxene and siloxene derivatives are compatible with silicon and may be generated as epitaxial layer on a silicon monocrystal. This permits the production of novel and advantageous electroluminescent devices, such as displays, image converters, optoelectric integrated circuits. Siloxene and siloxene derivatives may also be advantageously employed in lasers as laser-active material and in fluorescent lamps or tubes as luminescent material.
Silicon Nanosheet , Nanosheet Solution and Process for Producing the Same, Nanosheet -Containing Composite, and Nanosheet Aggregate
US2008050573 // JPWO2006009073 // WO2006009073
[ PDF ]
A silicon nanosheet comprising a silicon atom layer formed by bonding two-dimensionally and periodically arranged silicon atoms to each other through an Si-Si bond. A nanosheet solution prepared by dispersing or suspending the silicon nanosheets in a solvent. A nanosheet-containing composite having the silicon nanosheets on the surface and/or in the interior of a substrate. A nanosheet aggregate formed by aggregating the silicon nanosheets. A process for producing a nanosheet solution comprising: an acid treatment step of bringing a layered silicon compound into contact with an aqueous acid solution to derive a siloxene compound; and an exfoliation step of adding the siloxene compound into a solvent containing a surfactant, shaking the mixture, and peeling off the siloxene compound.
MANUFACTURE OF SILOXENE COMPOUND THIN FILM
JPH0964417
[ PDF ] [ Translation PDF ]
To form a siloxene compound thin film that the composition distribution in a film thickness direction is uniform with the silicide of calcium used as a main material on a silicon substrate by using a depositing method using calcium disilicide and silicon as evaporation sources, a quick heating method, and a chemically treating method of hydrochloric acid. SOLUTION: One of calcium disilicide (CaSi2 ), calcium silicide (CaSi) or dicalcium silicide (Ca2 Si) as the silicide of calcium and Si are used as evaporation sources, two or more layers of CaSix (0<x<2) thin film and an Si thin film are alternately laminated in vacuum on a silicon (Si) substrate 111 by a depositing method. The CaSix /Si multilayer thin film deposited Si substrate is heated in vacuum or in inert atmosphere to form a CaSi2 single crystal thin film on the substrate 111. Then, the CaSi2 single crystal thin film laminated layer Si substrate is treated with hydrochloric acid to form a siloxene compound thin film on the substrate 111.
Improvements in the preparation of mono-silane
US2912308 // GB831289
[ PDF ]
Siloxene Si6 O3 H6 is prepared as a grey powder by reacting a metal disilicide with an aqueous-alcoholic solution of mineral acid. Silicides specified are calcium, barium, and strontium silicide. Acids specified are hydrochloric, sulphuric, and acetic acid. Alcohols specified are methyl, ethyl, n- or iso-propyl, or n-, iso- or tert-butyl alcohol. 90-97% of alcohol may be present in the reaction mixture. Acidic hydrogen to metal ratios of 2-18 to 1 are specified. The temperature of reaction may be 0-95 DEG C. but is usually room temperature. The reaction mixture may be allowed to stand for 17 hours. The siloxene may be separated by filtration, washed with ethanol, and vacuum dried at 60 DEG C. Monosilane is produced by reacting siloxene, preferably prepared as described above, with liquid or gaseous ammonia, in a non-oxidizing atmosphere and at a temperature of at least -33 DEG C. Argon or helium may be employed as a carrier for gaseous ammonia which may be at a temperature of 350 DEG C. The system may be evacuated, or an inert gas atmosphere employed, when using liquid ammonia. In order to use liquid ammonia, increased pressure may be employed and/or up to 30% of ammonium chloride, bromide, or iodide may be added to the reaction mixture. The monosilane which is evolved together with ammonia and hydrogen may be condensed together with the ammonia in a liquid nitrogen trap, and thereafter selectively vaporized by replacing the liquid nitrogen by trichloromonofluoromethane at its freezing point.